|
Nderit Pottery
Nderit pottery is a type of ceramic vessel found at archaeological sites in Africa, particularly Tanzania and Kenya. Nderit pottery, previously known as ceramic tradition "Gumban A ware," was initially documented by Louis Leakey in the 1930s at sites in the Central Rift Valley of Kenya.Stylistic characteristics of Nderit pottery discovered in the Central Rift Valley include an exterior decoration of basket-like and triangular markings into the clay’s surface. The vessels here also have intensely scored interiors that do not appear to follow a distinct pattern. Nderit Ware exemplifies the transition from Saharan wavy-line early Holocene pottery towards the basket-like designs of the middle Holocene. Lipid residue found on Nderit pottery can be used to analyze the food products stored in them by early pastoralist societies. Characteristics Composition Majority of Nderit vessels' paste type composition is gritty, well-sorted, and includes medium-to-coarse sized sand. At the Jar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrich Eggshell Beads
Ostrich eggshell beads, considered among the earliest ornaments created by ''Homo sapiens'', represent some of the most ancient fully manufactured beads. Archaeologists have traced their origins back to the Late Pleistocene, with evidence suggesting they were crafted as early as 75,000 years ago in Africa. Certain populations continue to produce and utilize these beads in contemporary times. Ostrich eggshell beads likely originated from eastern Africa. They appear in the archaeological record all throughout Africa in a variety of contexts, including those of foraging, herding, and farming societies. They are particularly well-represented in the archaeological record of the Holocene, and are well-studied in eastern and southern Africa. They can be useful to archaeologists as a way to study symbolic meanings, the creation and maintenance of social identities, exchange, and can even be used to radiocarbon date sites. They also appear in the archaeological record of Asia, with some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Pottery
African folk art consists of a variety of items: household objects, metal objects, toys, textiles, masks, and wood sculpture. Most traditional African art meets many definitions of folk art generally, or at least did so until relatively recent dates. Metal objects Much African folk art consists of metal objects due in part to the cultural status of forging as a "process that is likened to the creation of life itself." While in the past ceremonial pieces were exchanged as part of social rituals (i.e. marriage), today in Senegal, metal objects are recycled as utilitarian African folk art. Jewellery In West Africa, the Asante are popular for their crafts and trade in gold. For the people of Ghana, not only does the colour gold represent wealth and status but there is also belief that it is a protection to whoever wears it. Necklaces have been made of gold bells, disks, and cross-shaped beads for those to wear around the neck. In the Alkan culture, each of these elements are made b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology Of Kenya
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
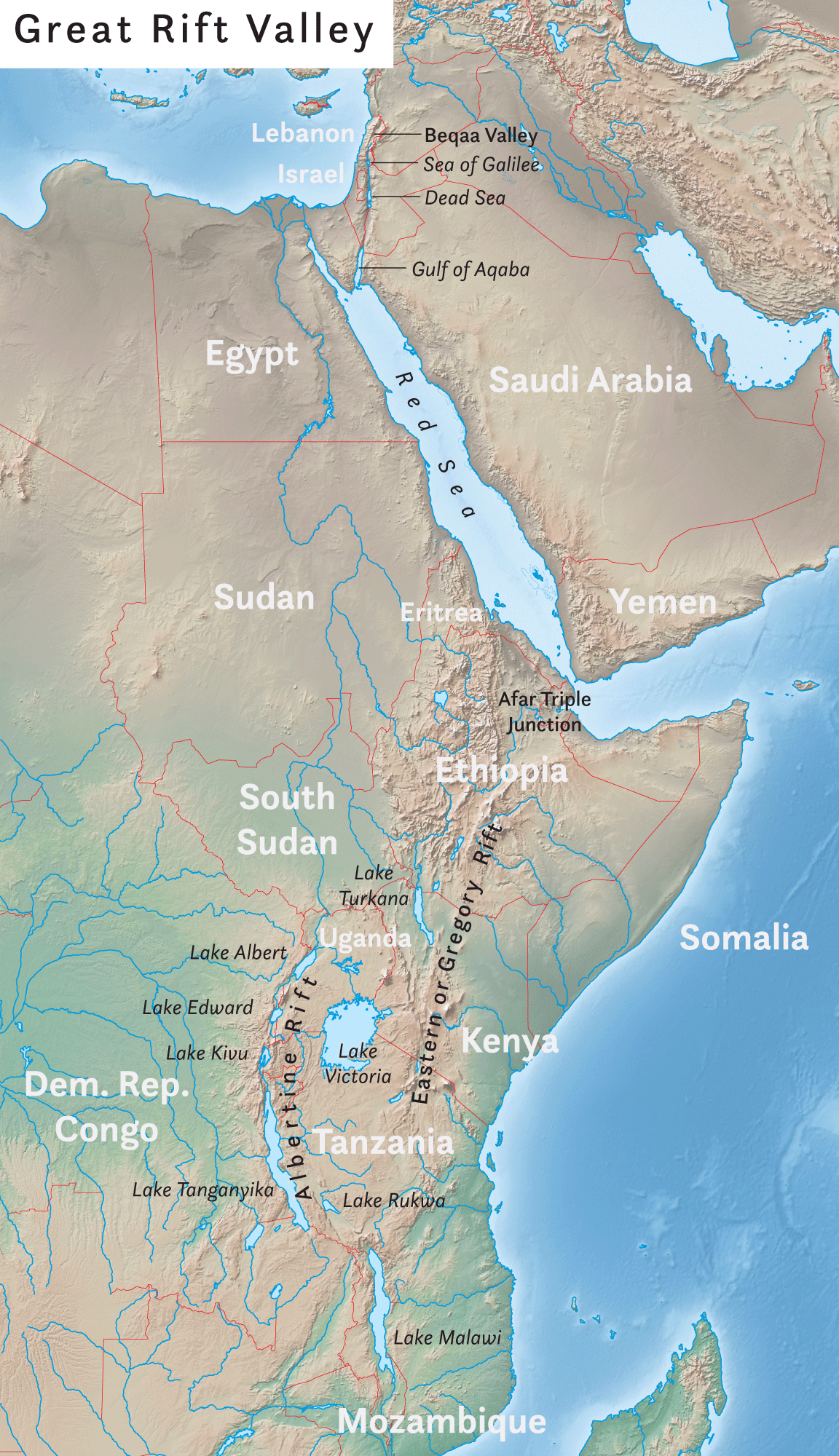
Great Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley is a series of contiguous geographic trenches, approximately in total length, that runs from Lebanon in Asia to Mozambique in Southeast Africa. While the name continues in some usages, it is rarely used in geology as it is considered an imprecise merging of separate though related rift and fault systems. This valley extends northward for 5,950 km through the eastern part of Africa, through the Red Sea, and into Western Asia. Several deep, elongated lakes, called ribbon lakes, exist on the floor of this rift valley: Lakes Malawi, Rudolf and Tanganyika are examples of such lakes. The region has a unique ecosystem and contains a number of Africa's wildlife parks. The term Great Rift Valley is most often used to refer to the valley of the East African Rift, the divergent plate boundary which extends from the Afar Triple Junction southward through eastern Africa, and is in the process of splitting the African Plate into two new and separate pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastoralists
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as "livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The animal species involved include cattle, camels, goats, yaks, llamas, reindeer, horses and sheep. Pastoralism occurs in many variations throughout the world, generally where environmental characteristics such as aridity, poor soils, cold or hot temperatures, and lack of water make crop-growing difficult or impossible. Operating in more extreme environments with more marginal lands means that pastoral communities are very vulnerable to the effects of global warming. Pastoralism remains a way of life in many geographic areas, including Africa, the Tibetan plateau, the Eurasian steppes, the Andes, Patagonia, the Pampas, Australia and many other places. , between 200 million and 500 million people globally practised pastoralism, and 75% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastoral Neolithic
The Pastoral Neolithic (5000 BP - 1200 BP) refers to a period in Africa's prehistory, specifically Tanzania and Kenya, marking the beginning of food production, livestock domestication, and pottery use in the region following the Later Stone Age. The exact dates of this time period remain inexact, but early Pastoral Neolithic sites support the beginning of herding by 5000 BP. In contrast to the Neolithic in other parts of the world, which saw the development of farming societies, the first form of African food production was nomadic pastoralism, or ways of life centered on the herding and management of livestock. The shift from hunting to food production relied on livestock that had been domesticated outside of East Africa, especially North Africa. This period marks the emergence of the forms of pastoralism that are still present. The reliance on livestock herding marks the deviation from hunting-gathering but precedes major agricultural development. The exact movement tendencies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope Analysis
Isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature, abundance of certain stable isotopes of chemical elements within organic and inorganic compounds. Isotopic analysis can be used to understand the flow of energy through a food web, to reconstruct past environmental and climatic conditions, to investigate human and animal diets, for food authentification, and a variety of other physical, geological, palaeontological and chemical processes. Stable isotope ratios are measured using mass spectrometry, which separates the different isotopes of an element on the basis of their mass-to-charge ratio. Tissues affected Isotopic oxygen is incorporated into the body primarily through ingestion at which point it is used in the formation of, for archaeological purposes, bones and teeth. The oxygen is incorporated into the hydroxylcarbonic apatite of bone and tooth enamel. Bone is continually remodelled throughout the lifetime of an individual. Although the rate of tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Before Present
Before Present (BP) years, or "years before present", is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use 1 January 1950 as the commencement date ( epoch) of the age scale. The abbreviation "BP" has been interpreted retrospectively as "Before Physics", which refers to the time before nuclear weapons testing artificially altered the proportion of the carbon isotopes in the atmosphere, which scientists must now account for. In a convention that is not always observed, many sources restrict the use of BP dates to those produced with radiocarbon dating; the alternative notation RCYBP stands for the explicit "radio carbon years before present". Usage The BP scale is sometimes used for dates established by means other than radiocarbon dating, such as stratigraphy. This usage differs from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrich Egg
The egg of the ostrich (genus ''Struthio'') is the largest of any living bird. The shell has a long history of use by humans as a container and for decorative artwork. The eggs are not commonly eaten. Biology The female common ostrich lays her fertilized eggs in a single communal nest, a simple pit, deep and wide, scraped in the ground by the male. The dominant female lays her eggs first, and when it is time to cover them for incubation she discards extra eggs from the weaker females, leaving about 20 in most cases. A female common ostrich can distinguish her own eggs from the others in a communal nest. Ostrich eggs are the largest of all eggs, though they are actually the smallest eggs relative to the size of the adult bird — on average they are long, wide, and weigh , over 20 times the weight of a chicken's egg and only 1 to 4% the size of the female. They are glossy cream-colored, with thick shells marked by small pits. The eggs are incubated by the females by day and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Leakey
Louis Seymour Bazett Leakey (7 August 1903 – 1 October 1972) was a Kenyan-British palaeoanthropologist and archaeologist whose work was important in demonstrating that humans evolved in Africa, particularly through discoveries made at Olduvai Gorge with his wife, fellow palaeoanthropologist Mary Leakey. Having established a programme of palaeoanthropological inquiry in eastern Africa, he also motivated many future generations to continue this scholarly work. Several members of the Leakey family became prominent scholars themselves. Another of Leakey's legacies stems from his role in fostering field research of primates in their natural habitats, which he saw as key to understanding human evolution. He personally focused on three female researchers, Jane Goodall, Dian Fossey, and Birutė Galdikas, calling them The Trimates. Each went on to become an important scholar in the field of primatology. Leakey also encouraged and supported many other PhD candidates, most notabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jarigole Pillar Site
The Jarigole pillar site is one of the megalithic communal cemetery sites in Lake Turkana Basin in Northern Kenya associated with the Pastoral Neolithic period. The site is located on the eastern shores of Lake Turkana in the southeastern edge of the Sibiloi National Park. Situated in a recessional beach which is above the 1973 lake level, the site includes oval platforms > with a circular mound ( of sediments), and 28 basalt pillars each weighing about and moved over a distance of from the site. The site is believed to have been constructed by the first wave of ancient herders who migrated to the region down from the Sahara around 5,000 years ago, a period marked by rapid climatic, economic and social change. Radiocarbon dates suggest that the site was used over a relatively short period of time from 4940 to 4630 BP. However, the accuracy of these dates are contestable owing to the fact the dateable materials, which includes Ostrich Egg Shell (OES) beads and charcoal does not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)