|
Nayak (title)
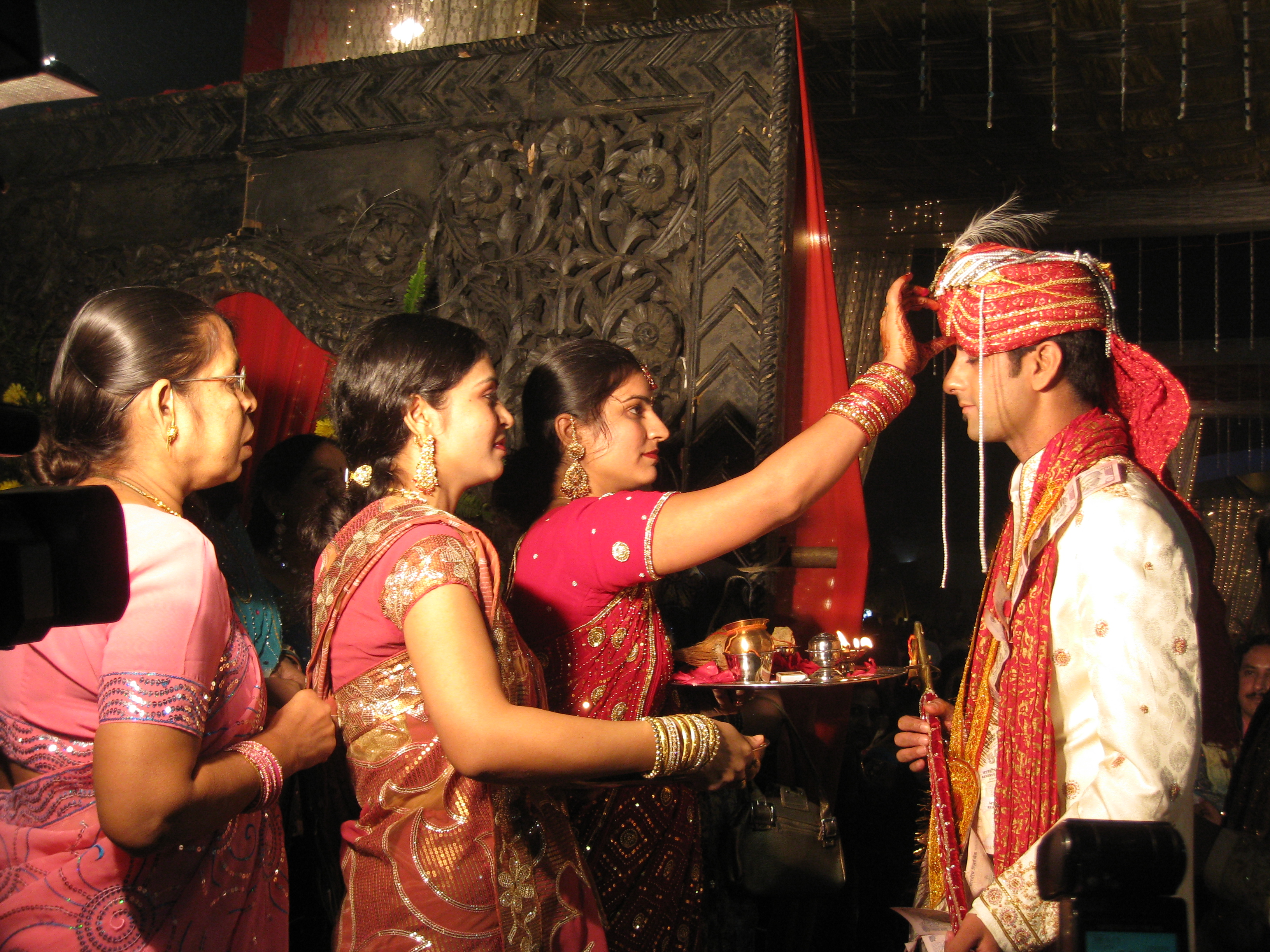
Nayak, Nayaka, Nayakar, or Naik was historically a Indian honorifics, honorific title conferred on a Kshatriya Captain (armed forces), captain upon achieving a successful military expedition in various Indian feudalism, feudal states of the Indian subcontinent, as a derivative of the ancient Sanskrit word Nāyaka. The Noble title, title often came with a Prize of war, prize in the form of a Polygar, palayam, jagir, zamindari, or similar grant of a fief carved out of the newly annexed territory. Today, they are also used as surnames by the descendants of the original recipients and as the modern military rank of Naik (military rank), Naik, while the film industry has co-opted the term with Katha Nayagan and Kathanayakudu. The title is closely related to the Telugu Nayakudu, Nayudu, or Naidu, the Malayali Nair, and the Tamil List of Nayakars, Nayakar, Nayakan, Naicken and Naicker. Nayaks are mostly Hindu with a few Sikh, Sikhs. As a title Today, the title is used by various Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nayak (caste)
The Nayak are a Hindu Caste system in India, caste; also some Nayak are Punjabi people, Punjabi found in India and Pakistan. Mainly Nayak follows Hindu. According to Vinay Krishin Gidwani, the Nayaks claim that they were, historically, Brahmins. Demographics and occupation The Nayaks reside in Haryana, Punjab, Odisha, Rajasthan and West Bengal. They also live in Khammam district and West Godavari district in Andhra Pradesh and in a number of villages near Ahmedabad in Gujarat. According to Kathryn Hansen, the main occupation of Gujarati Nayaks had been "singing, dancing and acting in plays". Present circumstances The Nayak caste is classified as a Scheduled Caste in Gujarat and Rajasthan states of India. See also * Nayak dynasty * Nayakas of Keladi References Indian castes Social groups of Andhra Pradesh Social groups of Gujarat Social groups of Haryana Scheduled Castes of Rajasthan {{India-ethno-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naidu
Naidu (also spelled as Nayudu, Naidoo) is a Telugu language, Telugu title commonly used by various Telugu people, Telugu castes. 'Nayudu/Naidu' is a contraction of the Telugu language, Telugu word 'Nayakudu' meaning leader, chief, headman. Telugu castes such as the Kapu (caste), Kapu/Balija Kamma (caste), Kamma, Gavara, Golla (caste), Golla, Turpu Kapu, Velama, Boya (caste), Boya among others use the title. In Rayalaseema and North Tamil Nadu, the term Naidu primarily refers to Kamma (caste), Kamma caste. In Coastal Andhra, the term Naidu primarily refers to Kapu (caste), Kapu caste. Notable people People bearing the title Naidu include: * Ama Naidoo, social activist from South Africa * Baddukonda Appala Naidu, politician, YSR Congress Party, YSRCP leader * B. Munuswamy Naidu, former Chief Minister of Madras Presidency * M. Buchi Babu Naidu, Buchi Babu Naidu, Indian cricket pioneer known as the 'father of South Indian cricket' * Chandra Nayudu, India's first female cricket commen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
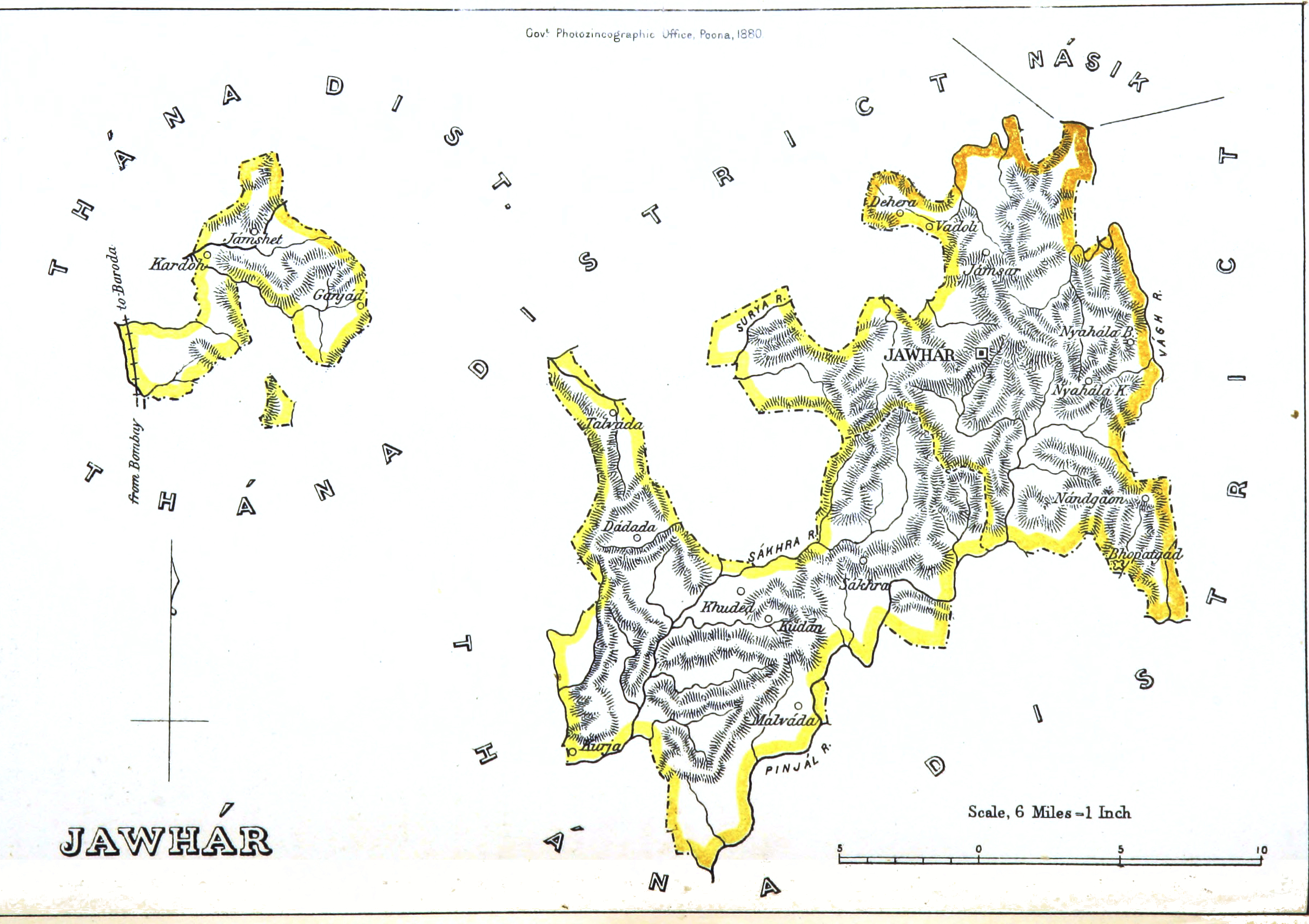
Jawhar State
The Jawhar State was a princely state in India. As a princely state, it became a part of Bombay Presidency during the British Raj. It was the only state belonging to the Thana Agency. The coat of arms consisted of a shield in three parts; dexter, tenne a dexter fist holding two crossed arrows (points dexter) and a bow, all argent; sinister, argent a round shield sable bordured or, in the chief argent, a sword or pointed sinister. The flag was a rectangular saffron swallow-tail with a star of eleven rays, yellow in the canton. History Up to the first Mohammedan, Muhammadan invasion of the Deccan Plateau, Deccan (1294) the greater part of the northern Konkan was held by Koli and Varli chiefs. Jawhar was held by a Varli chief and from him it passed to a Koli named Jayaba Mukne, Paupera. According to the Kolis' story, Paupera who was apparently called Jayaba, had a small mud fort at Mukane, Maharashtra, Mukne near the Tal pass. Once when visiting a shrine of Sadruddin Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to the southeast and Chhattisgarh to the east, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh to the north, and the Indian union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the northwest. Maharashtra is the second-most populous state in India, the third most populous country subdivision in South Asia and the fourth-most populous in the world. The state is divided into 6 divisions and 36 districts. Mumbai is the capital of Maharashtra due to its historical significance as a major trading port and its status as India's financial hub, housing key institutions and a diverse economy. Additionally, Mumbai's well-developed infrastructure and cultural diversity make it a suitable administrative center for the state, and the most populous urban are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
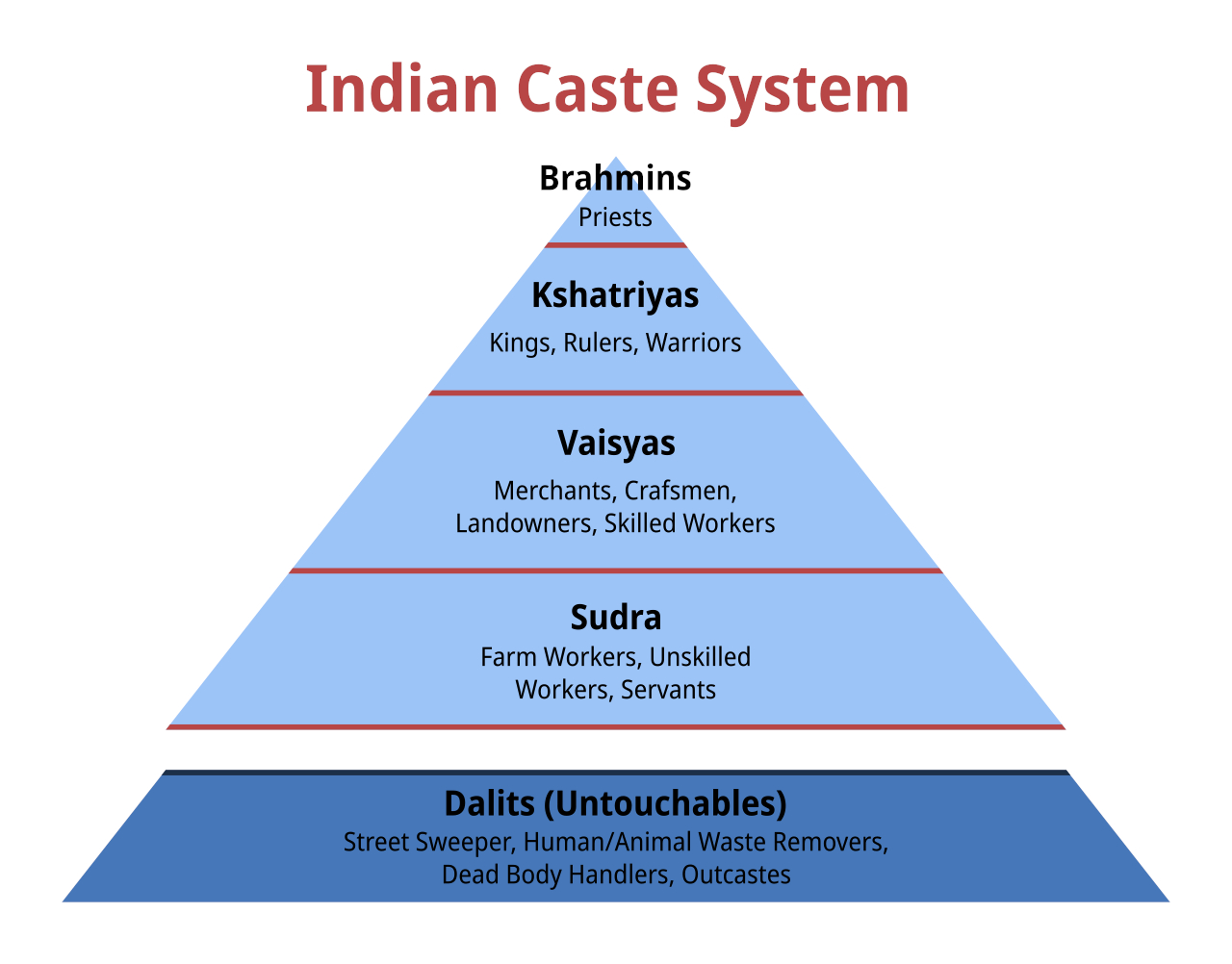
Caste System In India
The caste system in India is the paradigmatic ethnographic instance of social classification based on castes. It has its origins in ancient India, and was transformed by various ruling elites in medieval, early-modern, and modern India, especially in the aftermath of the collapse of the Mughal Empire and the establishment of the British Raj. Beginning in ancient India, the caste system was originally centered around '' varna'', with ''Brahmins'' (priests) and, to a lesser extent, ''Kshatriyas'' (rulers and warriors) serving as the elite classes, followed by '' Vaishyas'' (traders, merchants, and farmers) and finally '' Shudras'' (labourers). Outside of this system are the oppressed, marginalised, and persecuted '' Dalits'' (also known as " Untouchables") and '' Adivasis'' (tribals). Over time, the system became increasingly rigid, and the emergence of '' jati'' led to further entrenchment, introducing thousands of new castes and sub-castes. With the arrival of Islamic rule, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koli People
The Koli is an Indian caste that is predominantly found in India, but also in Pakistan and Nepal. Koli is an agriculturist caste of Gujarat but in coastal areas they also work as fishermen along with agriculture. In the beginning of 20th century, the Koli caste was recognised as a denotified tribe under Criminal Tribes Act by the British-Indian Government because of their anti-social activities during World War I. The Koli caste forms the largest caste- cluster in Gujarat and Himachal Pradesh, comprising 24% and 30% of the total population in those states respectively. History Early There has historically been some difficulty in identifying people as Koli or as Bhil people in what is now the state of Gujarat. The two communities co-existed in the hills of that area and even today there is confusion regarding their identity, not helped, in the opinion of sociologist Arvind Shah, by there being "hardly any modern, systematic, anthropological, sociological or historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nayak (surname)
Nayak is an Indian surname. List of people with the name A * Aarti Nayak, Indian classical music vocalist * Abhinav Sunder Nayak, Indian film director * Achutha Ramachandra Nayak (), ruler of the Nayaks of Gingee * Achuthappa Nayak (), ruler of the Nayaks of Tanjore * Akash Das Nayak (born 1981), Indian actor * Alagiri Nayak, king of the Madurai Nayak Dynasty * Amar Kumar Nayak (born 1973), Indian politician * Ambika Nayak, known professionally as Kayan, Indian musician * Amrit Keshav Nayak (1877–1907), Indian theatre actor and director * Ananta Nayak (born 1969), Indian politician * Archana Nayak (born 1966), Indian politician * Atanu Sabyasachi Nayak, Indian politician B * B. V. Nayak (born 1966), Indian politician * Baksi Nayak (1922–1993), Indian politician * Bapulal Nayak (1879–1947), Indian stage actor and director * Barsha Patnaik (née Nayak), Indian actress * Bibhuti Bhushan Nayak (born 1965), Indian journalist and martial artist * Bijay Kumar Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ethnic Groups
Ethnic groups in South Asia are ethnolinguistic groupings within the diverse populations of South Asia, including the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Afghanistan is variously considered to be a part of both Central Asia and South Asia, which means Afghans are not always included among South Asians, but when they are, South Asia has a total population of about 2.04 billion. The majority of the population fall within three large linguistic groups: Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, and Iranic. These groups are also further subdivided into numerous sub-groups, castes and tribes. Indo-Aryans form the predominant ethnolinguistic group in India (North India, East India, West India, and Central India), Bangladesh, Pakistan, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. Dravidians form the predominant ethnolinguistic group in southern India, the northern and eastern regions of Sri Lanka and a small pocket of Pakistan. The Iranic peoples also have a signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Castes
The caste system in India is the paradigmatic ethnographic instance of social classification based on castes. It has its origins in Outline of ancient India, ancient India, and was transformed by various ruling elites in medieval India, medieval, early-modern, and modern India, especially in the aftermath of the collapse of the Mughal Empire and the establishment of the British Raj. Beginning in ancient India, the caste system was originally centered around ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'', with ''Brahmin, Brahmins'' (priests) and, to a lesser extent, Kshatriya, ''Kshatriyas'' (rulers and warriors) serving as the elite classes, followed by ''Vaishya, Vaishyas'' (traders, merchants, and farmers) and finally ''Shudra, Shudras'' (labourers). Outside of this system are the oppressed, marginalised, and persecuted ''Dalit, Dalits'' (also known as "Untouchability, Untouchables") and ''Adivasi, Adivasis'' (tribals). Over time, the system became increasingly rigid, and the emergence of ''J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikh
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' has its origin in the Sanskrit word ', meaning 'seeker', or . According to Article I of Chapter 1 of the Sikh ''Rehat Maryada'' (), the definition of Sikh is: Any human being who faithfully believes in One Immortal Being Ten Gurus, from Guru Nanak Sahib to Guru Gobind Singh Sahib The Guru Granth Sahib The utterances and teachings of the ten Gurus and The initiation, known as the Amrit Sanchar, bequeathed by the tenth Guru and who does not owe allegiance to any other religion, is a Sikh. Male Sikhs generally have '' Singh'' () as their last name, though not all Singhs are necessarily Sikhs; likewise, female Sikhs have '' Kaur'' () as their last name. These unique last names were given by the Gurus to allow Sikhs to stand out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. It is assumed that the term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Avestan scripture Vendidad which refers to land of seven rivers as Hapta Hendu which itself is a cognate to Sanskrit term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ''. (The term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ'' is mentioned in Rig Veda and refers to a North western Indian region of seven rivers and to India as a whole.) The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). Likewise the Hebrew cognate ''hōd-dū'' refers to India mentioned in Hebrew BibleEsther 1:1. The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |