|
Nauen Transmitter Station
Nauen Transmitter Station (German: ''Grossfunkstelle Nauen'' or ''Sender Nauen'') in Nauen, Havelland (district), Havelland district, Brandenburg, Germany, is the oldest continuously operating radio transmitting installation in the world. Germany's first high power radio transmitter, it was founded on 1 April 1906 by Telefunken corporation and operated as a longwave radiotelegraphy station through World War II, and during World War I became Germany's main link with the outside world when its submarine communications cables were cut. Upgraded with shortwave transmitters in the 1920s it was Germany's most advanced long range radio station, continually upgraded with the latest equipment and serving as an experimental station for Telefunken to test new technology. At the end of World War II, invading Russian troops dismantled and removed the transmitting equipment. During the Cold War it served as the German Democratic Republic, GDR's (East Germany's) international shortwave station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
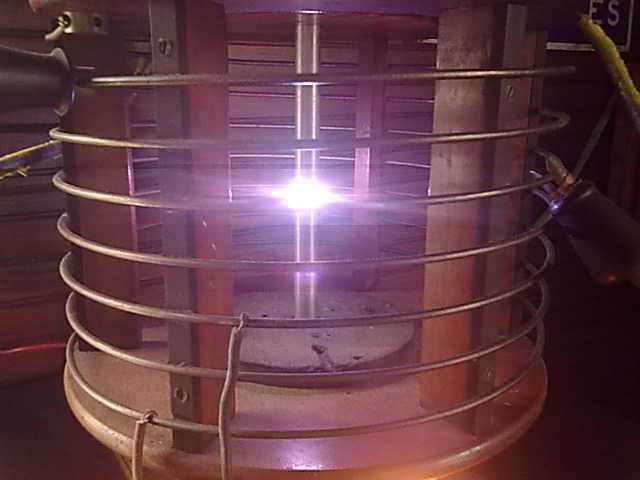
Spark-gap Transmitter
A spark-gap transmitter is an obsolete type of transmitter, radio transmitter which generates radio waves by means of an electric spark."Radio Transmitters, Early" in Spark-gap transmitters were the first type of radio transmitter, and were the main type used during the wireless telegraphy or "spark" era, the first three decades of radio, from 1887 to the end of World War I. German physicist Heinrich Hertz built the first experimental spark-gap transmitters in 1887, with which he proved the existence of radio waves and studied their properties. A fundamental limitation of spark-gap transmitters is that they generate a series of brief transient pulses of radio waves called Damped wave (radio transmission), damped waves; they are unable to produce the continuous waves used to carry audio signal, audio (sound) in modern AM broadcasting, AM or FM broadcasting, FM radio transmission. So spark-gap transmitters could not transmit audio, and instead transmitted information by radiotelegra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
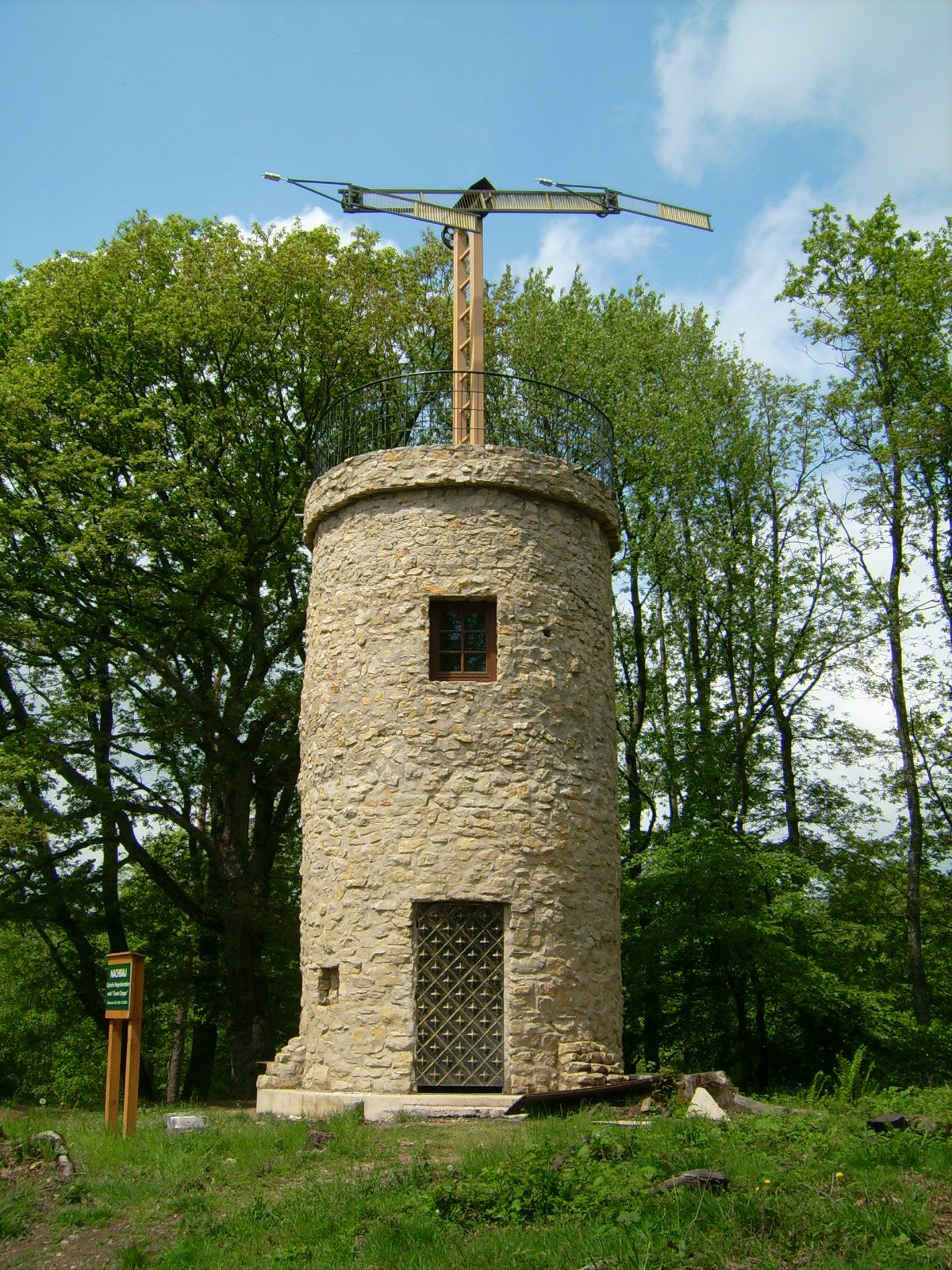
Umbrella Antenna
An umbrella antenna is a capacitively top-loaded wire monopole antenna, consisting in most cases of a mast fed at the ground end, to which a number of radial wires are connected at the top, sloping downwards. One side of the feedline supplying power from the transmitter is connected to the mast, and the other side to a ground (Earthing) system of radial wires buried in the earth under the antenna. They are used as transmitting antennas below 1 MHz, in the MF, LF and particularly the VLF bands, at frequencies sufficiently low that it is impractical or infeasible to build a full size quarter-wave monopole antenna. The outer end of each radial wire, sloping down from the top of the antenna, is connected by an insulator to a supporting rope or cable anchored to the ground; the radial wires can also support the mast as guy wires. The radial wires make the antenna look like the wire frame of a giant umbrella (without the cloth) hence the name. Design The antenna is supported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spark Gap Transmitter
A spark-gap transmitter is an obsolete type of radio transmitter which generates radio waves by means of an electric spark."Radio Transmitters, Early" in Spark-gap transmitters were the first type of radio transmitter, and were the main type used during the wireless telegraphy or "spark" era, the first three decades of radio, from 1887 to the end of World War I. German physicist Heinrich Hertz built the first experimental spark-gap transmitters in 1887, with which he proved the existence of radio waves and studied their properties. A fundamental limitation of spark-gap transmitters is that they generate a series of brief transient pulses of radio waves called damped waves; they are unable to produce the continuous waves used to carry audio (sound) in modern AM or FM radio transmission. So spark-gap transmitters could not transmit audio, and instead transmitted information by radiotelegraphy; the operator switched the transmitter on and off with a telegraph key, creating puls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marconi Wireless Telegraph Co
The Marconi Company was a British telecommunications and engineering company founded by Italian inventor Guglielmo Marconi in 1897 which was a pioneer of wireless long distance communication and mass media broadcasting, eventually becoming one of the UK's most successful manufacturing companies. Its roots were in the Wireless Telegraph & Signal Company, which underwent several changes in name after mergers and acquisitions. In 1999, its defence equipment manufacturing division, Marconi Electronic Systems, merged with British Aerospace (BAe) to form BAE Systems. In 2006, financial difficulties led to the collapse of the remaining company, with the bulk of the business acquired by the Swedish telecommunications company, Ericsson. History Naming history * 1897–1900: The Wireless Telegraph & Signal Company * 1900–1963: Marconi's Wireless Telegraph Company * 1963–1987: Marconi Company Ltd * 1987–1998: GEC-Marconi Ltd * 1998–1999: Marconi Electronic Systems Ltd * 1999� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Ferdinand Braun
Karl Ferdinand Braun (; ; 6 June 1850 – 20 April 1918) was a German physicist, electrical engineer, and inventor. Braun contributed significantly to the development of radio with his 2 circuit system, which made long range radio transmissions and modern telecommunications possible, and with his invention of the phased array antenna in 1905, which led to the development of radar, smart antennas, and MIMO. Before that, he built the first cathode-ray tube in 1897, which led to the development of television, and the first semiconductor device in 1874, which co-started the development of electronics and electronics engineering. Braun shared the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Guglielmo Marconi "for their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy". He was a founder of Telefunken, one of the pioneering communications and television companies, and has been called the "father of television" (shared with inventors like Paul Gottlieb Nipkow), the "great grandfather o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Von Arco
Georg Wilhelm Alexander Hans Graf von Arco (30 August 1869 in Gorzyce, Silesian Voivodeship, Großgorschütz – 5 May 1940 in Berlin) was a German physicist, radio pioneer, and one of the joint founders of the "''Society for Wireless Telegraphy''" which became the Telefunken company. He was an engineer and the technical director of Telefunken. He was crucial in the development of wireless technology in Europe. Arco served for a time as an assistant to Adolf Slaby, who was close to William II, German Emperor. Until 1930, Arco was one of the two managing directors of the company. He participated in the development of high performance vacuum tube, tube transmitters. Together with his teacher, Slaby, he was considerably involved in the study and development of high-frequency engineering in Germany. He was a Monist and a pacifist. Between 1921 and 1922, he was a chairman of the German Monist Federation. Early years Arco was born on the estate of his father, Count Alexander Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Slaby
Adolf Karl Heinrich Slaby (18 April 1849 – 6 April 1913) was a German electronics pioneer and the first Professor of electro-technology at ''Technische Hochschule Charlottenburg'' (today Technische Universität Berlin, 1886). Education Slaby was born in Berlin, the son of a bookbinder. He studied at ''Berliner Gewerbeakademie'', the predecessor of ''Technische Hochschule Charlottenburg'' to study mechanical engineering and mathematics under Franz Reuleaux. He was employed as a housekeeper with the machine manufacturer Louis Schwartzkopff, leading to an interest in mechanical engineering. Slaby continued his studies at the University of Jena, and received his doctorate in mathematics. Early research Slaby taught mathematics and mechanics at a vocational school at Potsdam, where he conducted experiments on steam engines and petrol engines. He wrote his book ''Theorie der Gasmaschinen'' (Theory of Gas Engines), which had an important part in the development of Internal combu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Telegraph Cable
A submarine communications cable is a cable laid on the seabed between land-based stations to carry telecommunication signals across stretches of ocean and sea. The first submarine communications cables were laid beginning in the 1850s and carried telegraphy traffic, establishing the first instant telecommunications links between continents, such as the first transatlantic telegraph cable which became operational on 16 August 1858. Submarine cables first connected all the world's continents (except Antarctica) when Java was connected to Darwin, Northern Territory, Australia, in 1871 in anticipation of the completion of the Australian Overland Telegraph Line in 1872 connecting to Adelaide, South Australia and thence to the rest of Australia. Subsequent generations of cables carried telephone traffic, then data communications traffic. These early cables used copper wires in their cores, but modern cables use optical fiber technology to carry digital data, which includes telep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punched Paper Tape
Punch commonly refers to: * Punch (combat), a strike made using the hand closed into a fist * Punch (drink), a wide assortment of drinks, non-alcoholic or alcoholic, generally containing fruit or fruit juice Punch may also refer to: Places * Punch, U.S. Virgin Islands * Poonch (other), often spelt as Punch, several places in India and Pakistan People * Punch (surname), a list of people with the name * Punch (nickname), a list of people with the nickname * Punch Masenamela (born 1986), South African footballer * Punch (rapper), 21st century American rapper Terrence Louis Henderson Jr. * Punch (singer), South Korean singer Bae Jin-young (born 1993) Arts, entertainment and media Fictional entities * Mr. Punch (also known as Pulcinella or Pulcinello), the principal puppet character in the traditional ''Punch and Judy'' puppet show * Mr. Punch, the masthead image and nominal editor of '' Punch'', largely borrowed from the puppet show * Mr. Punch, a fictional charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morse Code
Morse code is a telecommunications method which Character encoding, encodes Written language, text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one of the early developers of the system adopted for electrical telegraphy. International Morse code encodes the 26 ISO basic Latin alphabet, basic Latin letters to , one Diacritic, accented Latin letter (), the Arabic numerals, and a small set of punctuation and procedural signals (Prosigns for Morse code, prosigns). There is no distinction between upper and lower case letters. Each Morse code symbol is formed by a sequence of ''dits'' and ''dahs''. The ''dit'' duration can vary for signal clarity and operator skill, but for any one message, once the rhythm is established, a beat (music), half-beat is the basic unit of time measurement in Morse code. The duration of a ''dah'' is three times the duration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telegram
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pigeon post is not. Ancient signalling systems, although sometimes quite extensive and sophisticated as in China, were generally not capable of transmitting arbitrary text messages. Possible messages were fixed and predetermined, so such systems are thus not true telegraphs. The earliest true telegraph put into widespread use was the Chappe telegraph, an optical telegraph invented by Claude Chappe in the late 18th century. The system was used extensively in France, and European nations occupied by France, during the Napoleonic era. The electric telegraph started to replace the optical telegraph in the mid-19th century. It was first taken up in Britain in the form of the Cooke and Wheatstone telegraph, initially used mostly as an aid to railw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |