|
Natural Orifice Translumenal Endoscopic Surgery
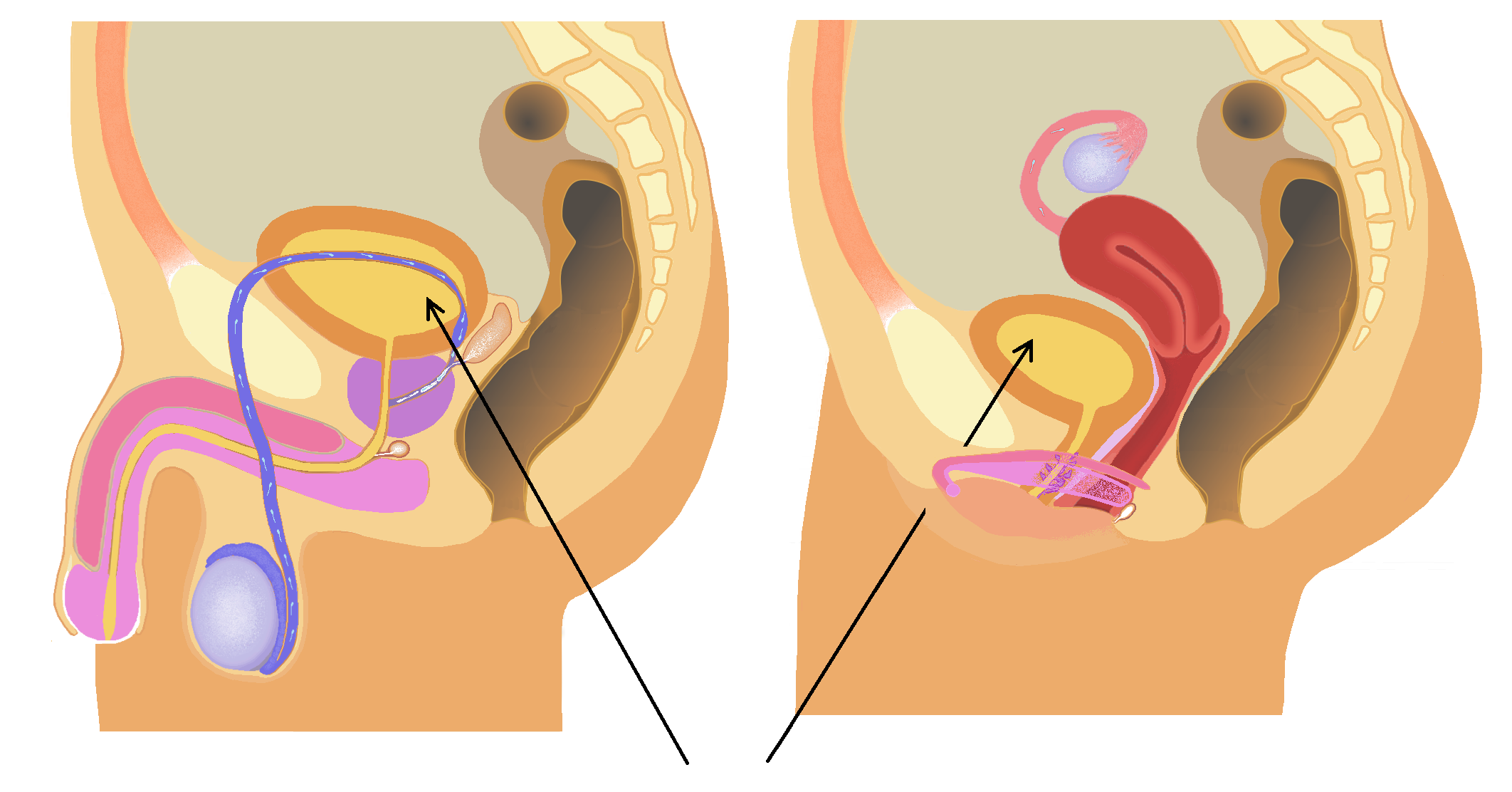
Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) is a surgical technique whereby "scarless" abdominal operations can be performed with an endoscope passed through a natural orifice (mouth, urethra, anus, vagina, etc.) then through an internal incision in the stomach, vagina, bladder or colon, thus avoiding any external incisions or scars. Memic's hominis robotic system is the first and only FDA-authorized surgical robotic platform for NOTES procedures. The system is currently at use for transvaginal hysterectomies through the rectouterine pouch - the removal of the uterus, along with one or both of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, in cases where there is no cancer present, as well as with the removal of ovarian cysts See also * Single port laparoscopy Single-port laparoscopy (SPL) is a recently developed technique in laparoscopic surgery. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which the surgeon operates almost exclusively through a single entry point, ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trocar
A trocar (or trochar) is a medical device, medical or veterinary medicine, veterinary device used in minimally invasive surgery. Trocars are typically made up of an Wiktionary:awl, awl (which may be metal or plastic with a pointed or tapered tip), a cannula (essentially a rigid hollow tube) and often a seal (mechanical), seal. Some trocars also include a valve mechanism to allow for insufflation (medicine), insufflation. Trocars are designed for placement through the chest and abdominal walls during thoracoscopy, thoracoscopic and laparoscopic surgery, and each trocar functions as a portal (architecture), portal for the subsequent insertion of other endoscopic instruments such as forceps, grasper, surgical scissors, scissors, surgical staple, stapler, electrocautery, suction (medicine), suction tip, etc. — hence the more commonly used colloquial jargon "port". Trocars also allow passive evacuation of excess gas or fluid from organs within the body. Etymology The word ''trocar' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Port Laparoscopy
Single-port laparoscopy (SPL) is a recently developed technique in laparoscopic surgery. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which the surgeon operates almost exclusively through a single entry point, typically the patient's navel. Unlike a traditional multi-port laparoscopic approach, SPL leaves only a single small scar. Technique, equipment and training SPL is accomplished through a single 20 mm incision in the navel (umbilicus or belly button), or through only an 11 mm incision in the navel, minimizing the scarring and incisional pain associated with the multiple points of entry used during traditional laparoscopic surgery. Specialized equipment for SPL surgery falls into two broad categories; access ports and hand instruments. There are a number of different access ports, including GelPOINT system from Applied Medical, the SILS device from Covidien, the TriPort+, TriPort15 and QuadPort+ a from Advanced Surgical Concepts and the Uni-X from Pnavel. Hand i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C). However, the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Cyst
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac within the ovary. They usually cause no symptoms, but occasionally they may produce bloating, lower abdominal pain, or lower back pain. The majority of cysts are harmless. If the cyst either #Cyst rupture, breaks open or causes ovarian torsion, twisting of the ovary, it may cause severe pain. This may result in vomiting or Lightheadedness, feeling faint, and even cause headaches. Most ovarian cysts are related to ovulation, being either follicular cyst of ovary, follicular cysts or corpus luteum cysts. Other types include Endometrioma, cysts due to endometriosis, dermoid cysts, and cystadenomas. Many small cysts occur in both ovaries in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Pelvic inflammatory disease may also result in cysts. Rarely, cysts may be a form of ovarian cancer. Diagnosis is undertaken by pelvic examination with a pelvic ultrasound or other testing used to gather further details. Often, cysts are simply observed over time. If they c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
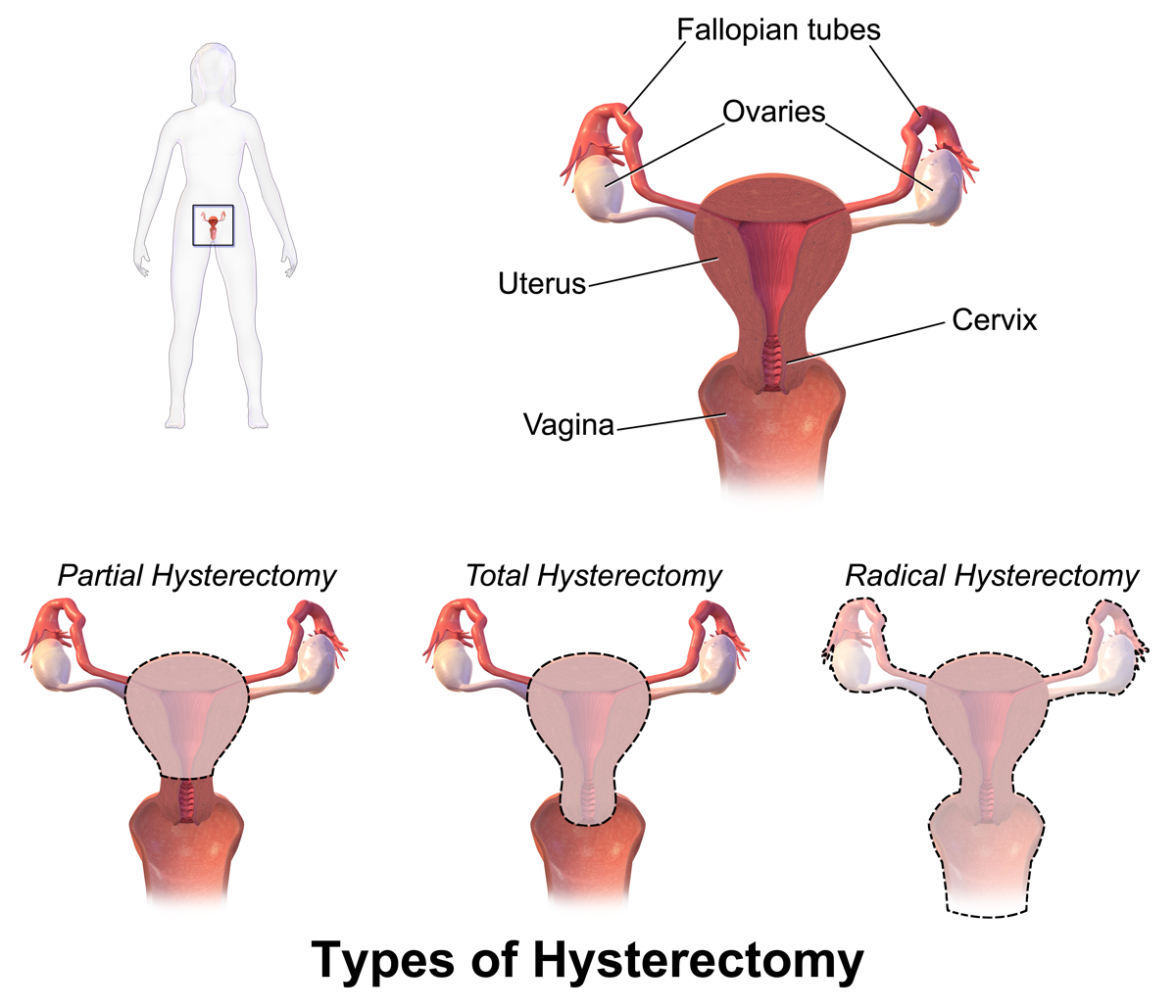
Ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocrine glands, secreting various hormones that play a role in the Menstruation (mammal), menstrual cycle and Fecundity, fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal development, prenatal period through menopause. Structure Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The ovaries are surrounded by a capsule, and have an outer cortex and an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fallopian Tubes
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (: salpinx), are paired tubular sex organs in the human female body that stretch from the ovaries to the uterus. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In other vertebrates, they are only called oviducts. Each tube is a muscular hollow organ that is on average between in length, with an external diameter of . It has four described parts: the intramural part, isthmus, ampulla, and infundibulum with associated fimbriae. Each tube has two openings: a proximal opening nearest to the uterus, and a distal opening nearest to the ovary. The fallopian tubes are held in place by the mesosalpinx, a part of the broad ligament mesentery that wraps around the tubes. Another part of the broad ligament, the mesovarium suspends the ovaries in place. An egg cell is transported from an ovary to a fallopian tube where it may be fertilized in the ampulla of the tube. The fallopian tubes are line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectouterine Pouch
The rectouterine pouch (rectovaginal pouch, pouch of Douglas or cul-de-sac) is the extension of the peritoneum into the space between the posterior wall of the uterus and the rectum in the human female. Structure In women, the rectouterine pouch is the deepest point of the peritoneal cavity. It is posterior to the uterus, and anterior to the rectum. Its anterior boundary is formed by the posterior fornix of the vagina. The pouch on the other side of the uterus near to the anterior fornix is the vesicouterine pouch. After passing over the fundus of the uterus, the peritoneum extends inferiorly along the entire posterior aspect of the uterus, reaching the posterior vaginal wall before reflecting superior-ward onto the anterior aspect of the rectal ampulla (i.e. the inferior portion of the rectum). In men, the region corresponding to the rectouterine pouch is the rectovesical pouch, which lies between the urinary bladder and rectum. Peritoneal fluid It is normal to have appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hysterectomies
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix. Supracervical hysterectomy refers to removal of the uterus while the cervix is spared. These procedures may also involve removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy), fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and other surrounding structures. The term “partial” or “total” hysterectomy are lay-terms that incorrectly describe the addition or omission of oophorectomy at the time of hysterectomy. These procedures are usually performed by a gynecologist. Removal of the uterus is a form of sterilization, rendering the patient unable to bear children (as does removal of ovaries and fallopian tubes) and has surgical risks as well as long-term effects, so the surgery is normally recommended only when other treatment options are not available or have failed. It is the second most commonly performed gynecological surgical procedure, after cesarean section, in the United States. Nearly 68 percent were performed for conditions such as endo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scars
SCARS or S.C.A.R.S. is an acronym that may refer to: * SCARS (military) (Special Combat Aggressive Reactionary System), an American combat fighting system * Severe cutaneous adverse reactions Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs) are a group of potentially lethal adverse drug reactions that involve the skin and mucous membranes of various body openings such as the eyes, ears, and inside the nose, mouth, and lips. In more sever ..., often abbreviated as SCARs, i.e. the last letter is lower case * ''S.C.A.R.S.'' (video game) (''Super Computer Animal Racing Simulator''), a video game featuring cars that are shaped like animals See also * Scar (other) * SCAR (other) * Scarred (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colon (anatomy)
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being removed by defecation. The colon (progressing from the ascending colon to the transverse, the descending and finally the sigmoid colon) is the longest portion of the large intestine, and the terms "large intestine" and "colon" are often used interchangeably, but most sources define the large intestine as the combination of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. Some other sources exclude the anal canal. In humans, the large intestine begins in the right iliac region of the pelvis, just at or below the waist, where it is joined to the end of the small intestine at the cecum, via the ileocecal valve. It then continues as the colon ascending the abdomen, across the width of the abdominal cavity as the transverse colon, and then desce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical terms related to the stomach. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase, gastric phase of digestion, following the cephalic phase in which the sight and smell of food and the act of chewing are stimuli. In the stomach a chemical breakdown of food takes place by means of secreted digestive enzymes and gastric acid. It also plays a role in regulating gut microbiota, influencing digestion and overall health. The stomach is located between the esophagus and the small intestine. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, the first and shortest part of the small intestine, where p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |