|
National Railway Museum
The National Railway Museum (NRM) is a museum in York, England, forming part of the Science Museum Group. The museum tells the story of rail transport in Britain and its impact on society. It is the home of the national collection of historically significant railway vehicles such as LNER Class A4 4468 Mallard, Mallard, GNR Stirling 4-2-2, Stirling Single, LMS Princess Coronation Class 6229 Duchess of Hamilton, Duchess of Hamilton and a Japanese Shinkansen, bullet train. In addition, the National Railway Museum holds a diverse collection of other objects, from a household recipe book used in George Stephenson's house to film showing a "People mover, never-stop railway" developed for the British Empire Exhibition. It has won many awards, including the European Museum of the Year Award in 2001. Starting in 2019, a major site development was underway. As part of the York Central redevelopment which will divert Leeman Road, the National Railway Museum will be building a new entrance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
York
York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a York Minster, minster, York Castle, castle and York city walls, city walls, all of which are Listed building, Grade I listed. It is the largest settlement and the administrative centre of the wider City of York district. It is located north-east of Leeds, south of Newcastle upon Tyne and north of London. York's built-up area had a recorded population of 141,685 at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census. The city was founded under the name of Eboracum in AD 71. It then became the capital of Britannia Inferior, a province of the Roman Empire, and was later the capital of the kingdoms of Deira, Northumbria and Jórvík, Scandinavian York. In the England in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages it became the Province of York, northern England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. British Railways was formed on 1 January 1948 as a result of the Transport Act 1947, which nationalised the Big Four British railway companies along with some other (but not all) smaller railways. Profitability of the railways became a pressing concern during the 1950s, leading to multiple efforts to bolster performance, including some line closures. The 1955 Modernisation Plan formally directed a process of dieselisation and electrification to take place; accordingly, steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction (except for the narrow-gauge Vale of Rheidol Railway tourist lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mallard (locomotive)
LNER Class A4 4468 ''Mallard'' is a 4-6-2 ("Pacific") steam locomotive built in 1938 for operation on the London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) at Doncaster Works to a design of Nigel Gresley. Its streamlined, wind tunnel tested design allowed it to haul long-distance express passenger services at high speeds. On 3 July 1938, ''Mallard'' broke the world speed record for steam locomotives at , which still stands today. While in British Railways days regular steam-hauled rail services in the UK were officially limited to a 'line speed', before the war, the A4s had to run significantly above just to keep schedule on trains such as the ''Silver Jubilee'' and '' The Coronation'', with the engines reaching 100 mph on many occasions. ''Mallard'' covered almost one and a half million miles (2.4 million km) before it was retired in 1963. The locomotive is long and weighs 165 long tons (168 tonnes, 369,600 lbs), including the tender. It is painted in LNER garter blue with r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
0 Series Shinkansen
The trains were the first generation Shinkansen trainsets built to run on Japan's Tokaido Shinkansen, Tōkaidō Shinkansen High-speed rail, high-speed line which opened in 1964. The last remaining trainsets were withdrawn in 2008 after 44 years of service. History The 0 series trains (which were not originally classified, as there was no need to distinguish classes of trainset until later) entered service with the start of Tokaido Shinkansen, Tōkaidō Shinkansen operations in October 1964. These units were white with a blue stripe along the windows and another at the bottom of the car body, including the front pilot (locomotive attachment), pilot. Unlike previous Japanese trains on the national network, the Tōkaidō Shinkansen and all subsequent Shinkansen lines are between the rails. The trains were powered by 25 kV AC electricity at 60 Hz with all axles of all cars powered by traction motors, giving a operation top speed. The original trains were introduced as 12-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
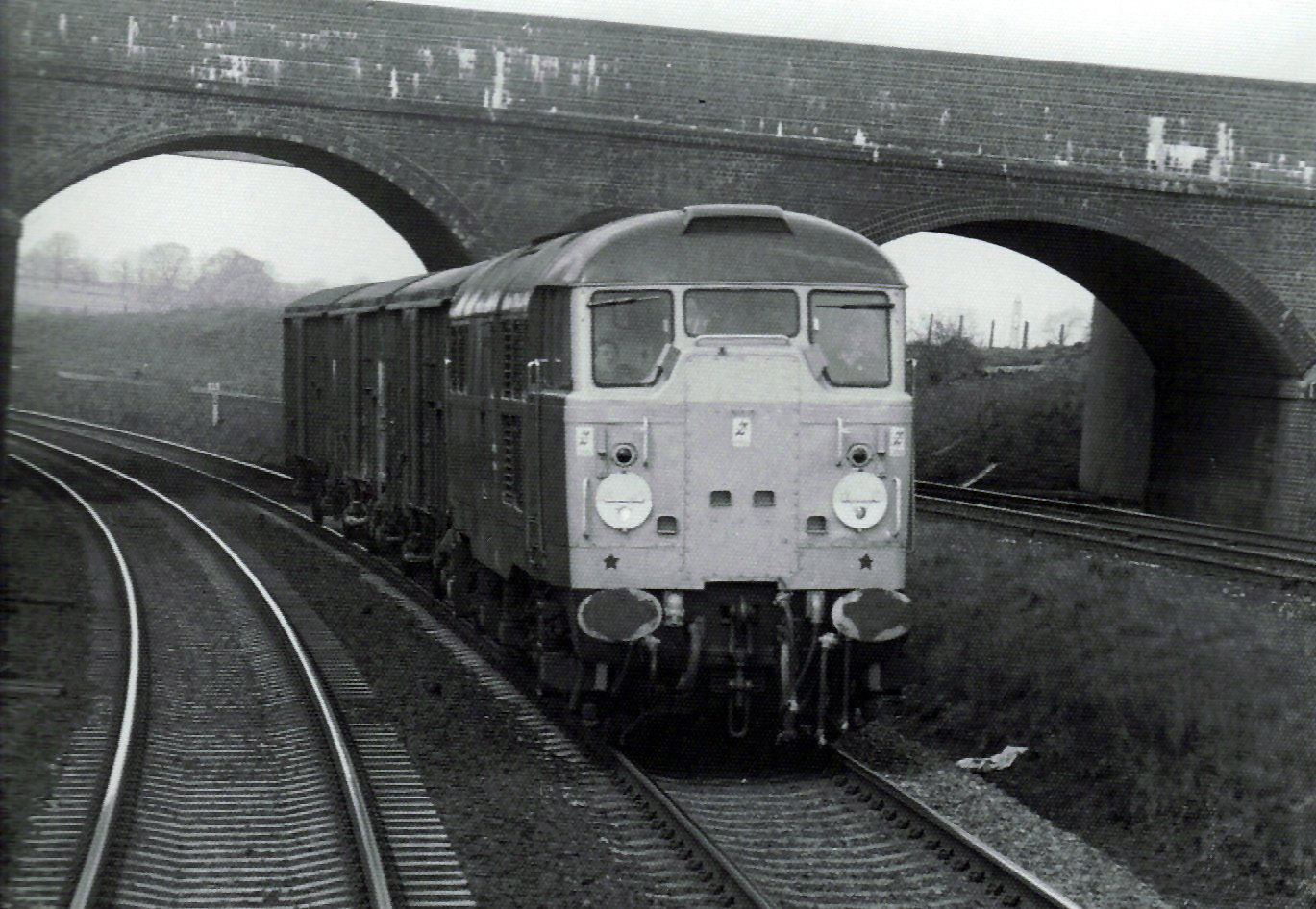
British Rail Class 31
The British Rail Class 31 diesel locomotives, also known as the Brush Type 2 and previously as Class 30, were built by Brush Traction from 1957 to 1962. They were numbered in two series, D5500-D5699 and D5800-D5862. Construction of the first locomotive was completed in the final week of September 1957, and the handing-over took place on 31 October. The first Class 31 entered service in November 1957, after the launch of the British Rail Class 20, Class 20 locomotive and was one of the Pilot Scheme locomotives ordered by British Railways to replace steam traction. Engines They were originally built with Mirrlees Blackstone, Mirrlees JVS12T (D5500–D5519) and engines and Brush electrical equipment, but the engines were not successful and in 1964 D5677 was fitted with an English Electric 12SVT engine (similar to the 12CSVT used in the British Rail Class 37, Class 37 but without an intercooler) rated at . The trial proved successful, and between 1965 and 1969 the entire class was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
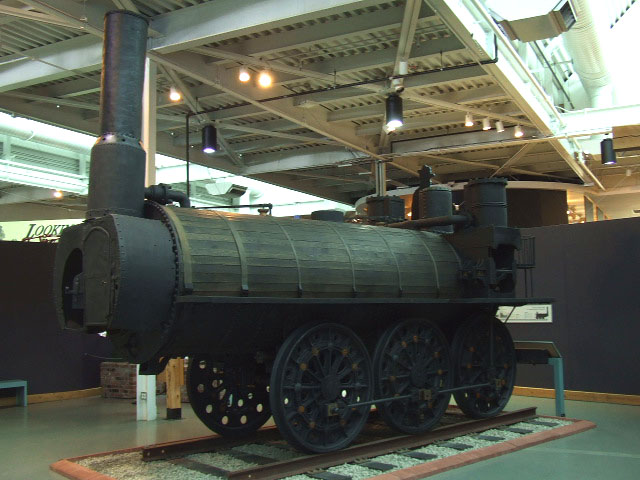
Timothy Hackworth
Timothy Hackworth (22 December 1786 – 7 July 1850) was an English steam locomotive engineer who lived in Shildon, County Durham, England and was the first locomotive superintendent of the Stockton and Darlington Railway. Youth and early work Timothy Hackworth was born in Wylam in 1786, five years after his fellow railway pioneer George Stephenson had been born in the same village. Hackworth was the eldest son of John Hackworth who occupied the position of foreman blacksmith at Wylam Colliery until his death in 1804; the father had already acquired a considerable reputation as a mechanical worker and boiler maker. At the end of his apprenticeship in 1810 Timothy took over his father's position. Since 1804, the mine owner, Christopher Blackett had been investigating the possibilities of working the mine's short colliery tramroad by steam traction. Blackett set up a four-man working group including himself, William Hedley, the viewer; Timothy Hackworth, the new foreman smith a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The Railway Magazine
''The Railway Magazine'' is a monthly United Kingdom, British railway magazine, aimed at the Railfan, railway enthusiast market, that has been published in London since July 1897. it was, for three years running, the railway magazine with the largest circulation in the United Kingdom, having a monthly average sale during 2009 of 34,715 (the figure for 2007 being 34,661). It was published by IPC Media until October 2010, and in 2007 won IPC's 'Magazine of the Year' award. Since November 2010, ''The Railway Magazine'' has been published by Mortons of Horncastle. History ''The Railway Magazine'' was launched by Joseph Lawrence (British politician), Joseph Lawrence and ex-railwayman Frank E. Cornwall of Railway Publishing Ltd, who thought there would be an amateur enthusiast market for some of the material they were then publishing in a railway staff magazine, the ''Railway Herald''. They appointed as its first editor a former auctioneer, George Augustus Nokes (1867–1948), who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Durham County Council
Durham County Council is the Local government in England, local authority for the non-metropolitan county of County Durham (district), County Durham in North East England. The council is a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority, being a non-metropolitan county council which also performs the functions of a non-metropolitan district council. It has its headquarters at County Hall, Durham, County Hall in Durham, England, Durham. Until 1 May 2025 the council had been under no overall control since the 2021 Durham County Council election, 2021 election, being run by a coalition of the Conservative Party (UK), Conservatives, Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrats, Derwentside Independents, Green Party of England and Wales, Green Party, and most of the Independent politician, independents, led by Liberal Democrat councillor Amanda Hopgood. It had previously been under the control of the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party continuously since 1925. On 1 May 2025 the Council c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
County Durham
County Durham, officially simply Durham, is a ceremonial county in North East England.UK General Acts 1997 c. 23Lieutenancies Act 1997 Schedule 1(3). From legislation.gov.uk, retrieved 6 April 2022. The county borders Northumberland and Tyne and Wear to the north, the North Sea to the east, North Yorkshire to the south, and Cumbria to the west. The largest settlement is Darlington. The county has an area of and a population of . The latter is concentrated in the east; the south-east is part of the Teesside urban area, which extends into North Yorkshire. After Darlington, the largest settlements are Hartlepool, Stockton-on-Tees, and Durham, England, Durham. For Local government in England, local government purposes the county consists of the Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority areas of County Durham (district), County Durham, Borough of Darlington, Darlington, Borough of Hartlepool, Hartlepool, and part of Borough of Stockton-on-Tees, Stockton-on-Tees. Durham Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Shildon
Shildon is a town and civil parish in County Durham (district), County Durham, in England. The population taken at the 2011 Census was 9,976. The town has the Locomotion Museum, due to it having the first , built in 1825, and locomotive works on the Stockton and Darlington Railway. History The name Shildon comes from the Old English word ''sceld'', This translates as 'shelf shaped hill' or 'shield/refuge'. Another possibility is the Old English word ''scylfe'' meaning 'shelf' and the suffix ''dun'' meaning 'hill'. This refers to the town's location on a limestone escarpment.Shildon County Durham Conservation Area Prepared for Sedgefield Borough Council Conservation Area Character Appraisal December 2008 ''Report No: 0055/1-08'' Report by Archaeo-Environment Ltd The earliest inhabitants of the area were most likely present from the Mesolithic period some 6,000 years ago. Although no evidence of settlement has been found in Shildon itself a small Stone tool, flint tool disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
National Railway Museum Shildon
Locomotion, previously known as Locomotion the National Railway Museum at Shildon, is a railway museum in Shildon, County Durham, England. The museum was renamed in 2017 when it became part of the Science Museum Group. Overview The museum was opened on 22 October 2004 by then Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister and local MP Tony Blair. Built at a cost of £11.3 million, it is based on the former "Timothy Hackworth Victorian Railway Museum". The museum is operated in partnership with Durham County Council and was expected to bring 60,000 visitors a year to the small town. It exceeded expectations, and during its first six months, the museum attracted 94,000 visits. Locomotion was shortlisted as one of the final five contenders in the Gulbenkian Prize, which is the largest arts prize in the United Kingdom. As part of the 2025 plans for the National Railway Museum, a second building has been built to house more of the national collection. In addition, parts of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
York Park And Ride
The York park and ride is a park and ride network in the cathedral city of York, England, with sites operated by the City of York Council and bus services operated by First York. It is the largest park and ride network in the United Kingdom, with 4,970 car spaces across six sites: Askham Bar, Grimston Bar, Monks Cross, Poppleton Bar, Rawcliffe Bar and York Designer Outlet. History Bus services have been operated by First York, under contract to the City of York Council, since the late 1990s. In June 2016, the park and ride contract was put up for tender. However, as none of the bids met the council's criteria, First York was granted a twelve-month extension, until January 2018, with the intention of commencing a fresh tender process. In January 2018, First York was awarded a further seven-year contract to operate the park and ride network. In June 1990, the first permanent park and ride site opened at Askham Bar. Four years later, a second site was opened at Grimston Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |