|
National Institute For The Promotion Of Science
The National Institution for the Promotion of Science organization was established in Washington, D.C., in May 1840, and was heir to the mantle of the earlier ''Columbian Institute for the Promotion of Arts and Sciences''. The National Institution for the Promotion of Science was later renamed the ''National Institute'' and eventually became a part of the Smithsonian Institution. The National Institute was the initial repository for collections of artifacts brought to the US by the United States Exploring Expedition, as well as various other object accumulated by the government, such as items owned by early American politicians, patent models, and natural objects. Housed in the Patent Office Building, these were the precursor to the Smithsonian Institution collection. The cabinet was managed by a group of scientists in 1840 and others to secure control of the Smithson bequest and create a National Museum in Washington. Among those who were elected as corresponding members wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the Federal government of the United States#branches, three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967. The Smithsonian Institution has historical holdings of over 157 million items, 21 museums, 21 libraries, 14 education and research centers, a zoo, and historical and architectural landmarks, mostly located in Washington, D.C. Additional facilities are located in Maryland, New York (state), New York, and Virg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
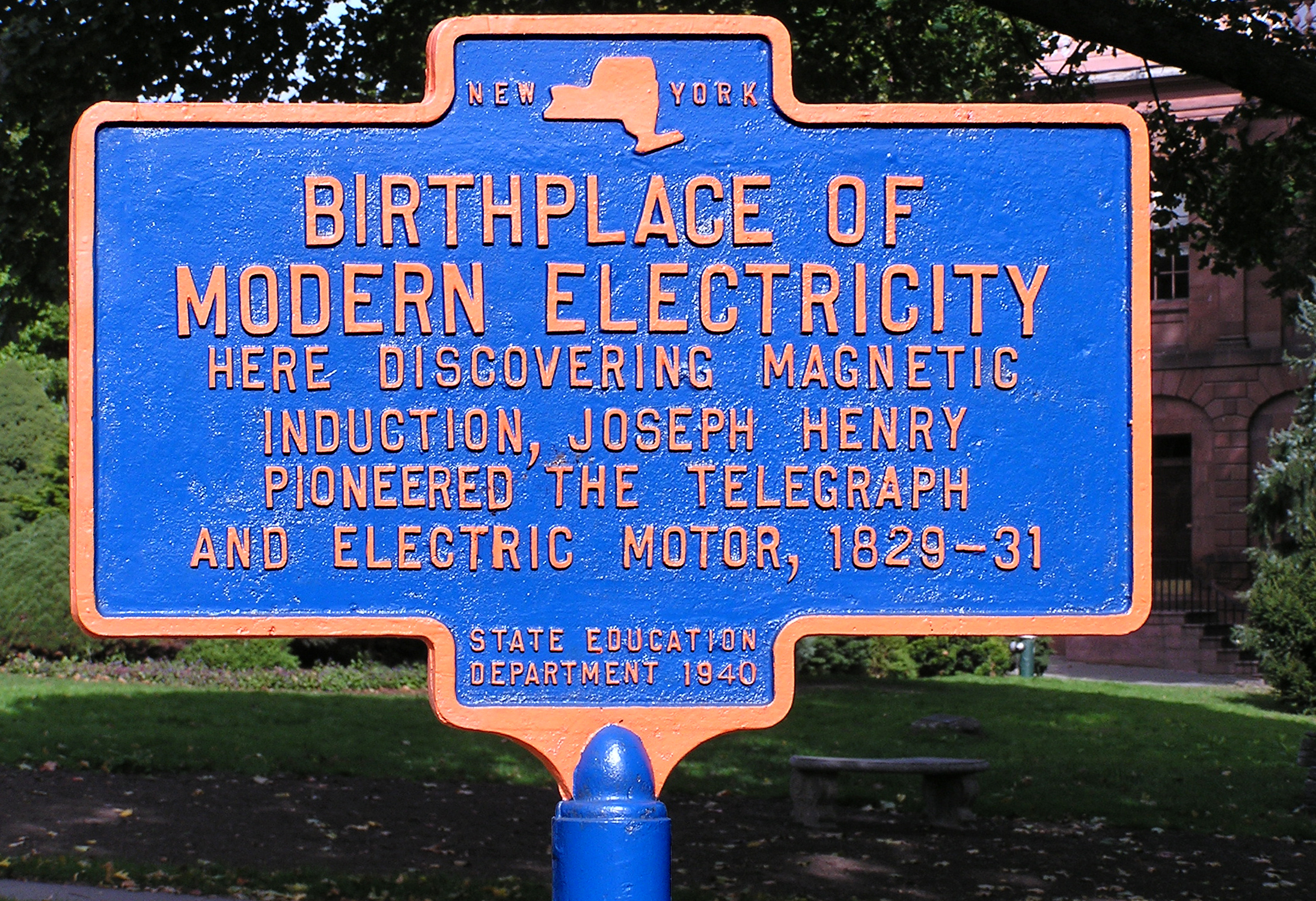
Joseph Henry
Joseph Henry (December 17, 1797– May 13, 1878) was an American physicist and inventor who served as the first secretary of the Smithsonian Institution. He was the secretary for the National Institute for the Promotion of Science, a precursor of the Smithsonian Institution. He also served as president of the National Academy of Sciences from 1868 to 1878. While building electromagnets, Henry discovered the electromagnetism, electromagnetic phenomenon of self-inductance. He also discovered mutual inductance independently of Michael Faraday, though Faraday was the first to make the discovery and publish his results. Henry developed the electromagnet into a practical device. He invented a precursor to the electric doorbell (specifically a bell that could be rung at a distance via an electric wire, 1831) and electric relay (1835). His work on the electromagnetic relay was the basis of the practical electrical telegraph, invented separately by Samuel Morse, Samuel F. B. Morse and Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Georg Wilhelm Von Struve
Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve (, trans. ''Vasily Yakovlevich Struve''; 15 April 1793 – ) was a Baltic German astronomer and geodesist. He is best known for studying double stars and initiating a triangulation survey later named Struve Geodetic Arc in his honor. Life He was born to the aristocratic Struve family at Altona, Duchy of Holstein (then a part of the Denmark–Norway kingdoms), the son of Jacob Struve (1755–1841). To avoid military service during the French occupation of Holstein, his family moved to the Russian Empire,V. K. Abalkin ''et al.'Struve dynasty (in Russian), St. Petersburg University equipped with Danish passports. In 1808 he entered the University of Tartu ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolphe Quetelet
Lambert Adolphe Jacques Quetelet FRSF or FRSE (; 22 February 1796 – 17 February 1874) was a Belgian- French astronomer, mathematician, statistician and sociologist who founded and directed the Brussels Observatory and was influential in introducing statistical methods to the social sciences. His name is sometimes spelled with an accent as ''Quételet''. He also founded the science of anthropometry and developed the body mass index (BMI) scale, originally called the Quetelet Index. His work on measuring human characteristic to determine the ideal ''l'homme moyen'' ("the average man"), played a key role in the origins of eugenics. Biography Adolphe was born in Ghent (which, at the time was a part of the new French Republic). He was the son of François-Augustin-Jacques-Henri Quetelet, a Frenchman and Anne Françoise Vandervelde, a Flemish woman. His father was born at Ham, Picardy, and being of a somewhat adventurous spirit, he crossed the English Channel and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's College London
King's College London (informally King's or KCL) is a public university, public research university in London, England. King's was established by royal charter in 1829 under the patronage of George IV of the United Kingdom, King George IV and the Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Duke of Wellington. In 1836, King's became one of the two founding colleges of the University of London. It is one of the Third-oldest university in England debate, oldest university-level institutions in England. In the late 20th century, King's grew through a series of mergers, including with Queen Elizabeth College and Chelsea College of Science and Technology (1985), the Institute of Psychiatry (1997), the United Medical and Dental Schools of Guy's and St Thomas' Hospitals and the Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery (in 1998). King's operates across five main campuses: the historic Strand Campus in central London, three other Thames-side campuses (Guy's, St Thomas' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Wheatstone
Sir Charles Wheatstone (; 6 February 1802 – 19 October 1875) was an English physicist and inventor best known for his contributions to the development of the Wheatstone bridge, originally invented by Samuel Hunter Christie, which is used to measure an unknown electrical resistance, and as a major figure in the development of telegraphy. His other contributions include the English concertina, the stereoscope (a device for displaying three-dimensional images) and the Playfair cipher (an encryption technique). Life Charles Wheatstone was born in Barnwood, Gloucestershire. His father, W. Wheatstone, was a music-seller in the town, who moved to 128 Pall Mall, London, four years later, becoming a teacher of the flute. Charles, the second son, went to a village school, near Gloucester, and afterwards to several institutions in London. One of them was in Kennington, and kept by a Mrs. Castlemaine, who was astonished at his rapid progress. From another he ran away, but was captured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denison Olmsted
Denison Olmsted (June 18, 1791 – May 13, 1859) was an American physicist and astronomer. Professor Olmsted is credited with giving birth to meteor science after the 1833 Leonid meteor shower over North America spurred him to study this phenomenon. Biography Olmsted was born June 18, 1791, in East Hartford, Connecticut. In 1813, he graduated from Yale College, where he acted as college tutor from 1815 to 1817. In the latter year, he was appointed to the chair of chemistry, mineralogy and geology in the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. A gold rush in North Carolina spurred the state legislature to sponsor the first state geological survey that was ever attempted in the United States. Olmsted traveled by horseback across the state collecting minerals and fossils, publishing his geological map in 1825. In 1825, he became professor of mathematics and natural philosophy at Yale. He published an elaborate theory of hail-stones in 1830, which caused much discussion, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Dallas Bache
Alexander Dallas Bache (July 19, 1806 – February 17, 1867) was an American physicist, scientist, and surveyor who erected coastal fortifications and conducted a detailed survey to map the mideastern United States coastline. Originally an army engineer, he later became Superintendent of the United States Coast Survey, and built it into the foremost scientific institution in the country before the American Civil War. Early life and education Bache was born in Philadelphia, the son of Richard Bache, Jr., and Sophia Burrell Dallas Bache. He came from a family prominent in American politics. He was the nephew of Vice-President George M. Dallas and naval hero Alexander J. Dallas, the grandson of Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Dallas, and the great-grandson of Benjamin Franklin. Career United States Army After graduating from the United States Military Academy at West Point in 1825, as first in his class, he was an assistant professor of engineering there for some time. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Point
The United States Military Academy (USMA), commonly known as West Point, is a United States service academies, United States service academy in West Point, New York that educates cadets for service as Officer_(armed_forces)#United_States, commissioned officers in the United States Army. The academy was founded in 1802, and it is the oldest of the five United States service academies, American service academies. The Army has occupied the site since establishing a fort there in 1780 during the American Revolutionary War, as it sits on strategic high ground overlooking the Hudson River north of New York City. West Point's academic program grants the Bachelor of Science degree with a curriculum that grades cadets' performance upon a broad academic program, military leadership performance, and mandatory participation in competitive athletics. Candidates for admission must apply directly to the academy and receive a nomination, usually from a member of United States Congress, Congr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Exploring Expedition
The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the Pacific Ocean and surrounding lands conducted by the United States. The original appointed commanding officer was Commodore Thomas ap Catesby Jones. Funding for the original expedition was requested by President John Quincy Adams in 1828; however, Congress would not implement funding until eight years later. In May 1836, the oceanic exploration voyage was finally authorized by Congress and created by President Andrew Jackson. The expedition is sometimes called the U.S. Ex. Ex. for short, or the Wilkes Expedition in honor of its next appointed commanding officer, United States Navy Lieutenant Charles Wilkes. The expedition was of major importance to the growth of science in the United States, in particular the then-young field of oceanography. During the event, armed conflict between Pacific islanders and the expedition was common and dozens of natives were killed in action ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical mineralogy, optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifact (archaeology), artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the processes of mineral origin and formation, classification of minerals, their geographical distribution, as well as their utilization. History Early writing on mineralogy, especially on gemstones, comes from ancient Babylonia, the ancient Greco-Roman world, ancient and medieval History of China, China, and Sanskrit texts from History of India, ancient India and the ancient Islamic world. Books on the subject included the ''Naturalis Historia, Natural History'' of Pliny the Elder, which not only described many different minerals but also explained many of their properties, and Kitab al Jawahir (Book of Precious Stones) by Persian scientist Al-Biruni. The German Renaissance specialist Georgius Agricola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during chemical reaction, reactions with other chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |