|
Natal Chart
A horoscope (or other commonly used names for the horoscope in English include natal chart, astrological chart, astro-chart, celestial map, sky-map, star-chart, cosmogram, vitasphere, radical chart, radix, chart wheel or simply chart) is an astrological chart or diagram representing the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, astrological aspects and angles at the time of an event, such as the moment of a person's birth. The word horoscope is derived from the Greek words ''ōra'' and ''scopos'' meaning "time" and "observer" (''horoskopos'', pl. ''horoskopoi'', or "marker(s) of the hour"). It is claimed by proponents of astrology that a horoscope can be used as a method of divination regarding events relating to the point in time it represents, and it forms the basis of the horoscopic traditions of astrology, although practices surrounding astrology have been recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century. Horoscope columns are often featured in print and online newspaper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions of Celestial objects in astrology, celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in Calendrical calculation, calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindu astrology, Hindus, Chinese astrology, Chinese, and the Maya civilization, Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Sign
In astrology, planets have a meaning different from the astronomical understanding of definition of planet, what a planet is. Before the scientific revolution, age of telescopes, the night sky was thought to consist of two similar components: fixed stars, which remained motionless in relation to each other, and moving objects/"Classical planet, wandering stars" (), which moved relative to the fixed stars over the course of the year(s). To the Ancient Greeks who learned from the Babylonians, the earliest astronomers/astrologers, this group consisted of the five planets visible to the naked eye and excluded Earth, plus the Sun and Moon. Although the Greek term ''planet'' applied mostly to the five 'wandering stars', the ancients included the Sun and Moon as the ''Sacred 7 Luminaires/7 Heavens'' (sometimes referred to as "Lights",) making a total of 7 planets. The ancient Babylonians, Greeks, Persians, Romans, Medieval Christians, and others thought of the 7 Classical Planets, class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Parts
In astrology, the Arabic parts or lots are constructed points based on mathematical calculations of three horoscopic entities such as planets or angles. The distance between two of the points is added to the position of the third (very often the ascendant) to derive the location of the lot. History The lots are a very ancient astrological technique which can be traced back to pre-Hellenistic sources. Their origin is obscure; they could originally be Babylonian, Ancient Egyptian, Magian, Persian or Hermetic, but by the time of Dorotheus of Sidon in the first century A.D. (and probably earlier) they had become an established tenet of Hellenistic astrological practice. One of the best informational sources for the lots is the ''Introduction'' to astrology by fourth-century astrologer Paulus Alexandrinus and the ''Commentary'' on this work by sixth-century philosopher Olympiodorus the Younger. Paulus used a dozen or so major lots for almost every aspect of his analysis. The mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
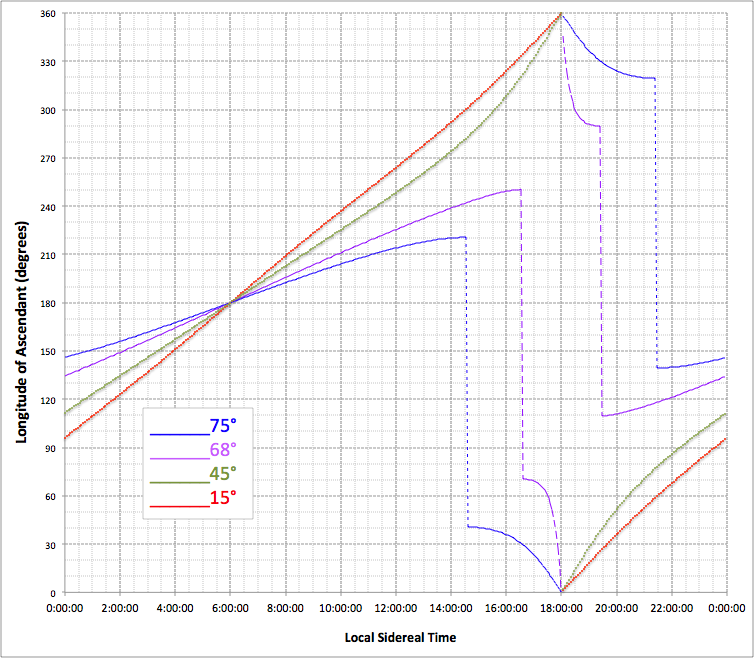
Ascendant
The ascendant (Asc, Asc or As) or rising sign is the astrological sign on the eastern horizon when the person was born. It signifies a person's physical appearance, and awakening consciousness. Because the ascendant is specific to a particular time and place, to astrologers it signifies the individual environment and conditioning that a person receives during their upbringing, and also the circumstances of their childhood. For this reason, astrologers consider that the ascendant is also concerned with how a person has learned to present themself to the world, especially in public and in impersonal situations. History Although Babylonian astronomers observed the actual rising times of the signs, there is no specific mention of the ascendant in the texts that have survived on clay tablets. By the 3rd century BCE, Egyptians looked at the rising of specific asterisms to identify the ascending sign and get an approximate time of night, and that is reflected in the name subsequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midheaven
Most horoscopic traditions of astrology systems divide the horoscope into a number (usually twelve) of houses whose positions depend on time and location rather than on date. The houses of the horoscope represent different fields of experience wherein the energies of the signs and planets operate—described in terms of physical surroundings as well as personal life experiences. Background In astrology, houses are a fundamental component of the birth chart that represent different areas of life. There are 12 houses, each associated with a specific zodiac sign and planetary ruler. The 12 houses in Western astrology represent distinct areas of life experience, shaping how planetary energies manifest in an individual's natal chart. Each house reflects a unique aspect of existence, from personal identity to relationships, career, and spirituality. The interpretation of the houses can vary based on different astrological traditions, psychological frameworks, and philosophical appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House (astrology)
Most Horoscopic astrology, horoscopic traditions of astrology systems divide the horoscope into a number (usually twelve) of houses whose positions depend on time and location rather than on date. The houses of the horoscope represent different fields of experience wherein the energies of the signs and planets operate—described in terms of physical surroundings as well as personal life experiences. Background In Astrology and the classical elements, astrology, houses are a fundamental component of the birth chart that represent different areas of life. There are 12 houses, each associated with a specific Zodiac Sign, zodiac sign and planetary ruler. The 12 houses in Western astrology represent distinct areas of life experience, shaping how planetary energies manifest in an individual's natal chart. Each house reflects a unique aspect of existence, from personal identity to relationships, career, and spirituality. The interpretation of the houses can vary based on different as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Node
A lunar node is either of the two orbital nodes of the Moon; that is, the two points at which the orbit of the Moon intersects the ecliptic. The ''ascending'' (or ''north'') node is where the Moon moves into the northern ecliptic hemisphere, while the ''descending'' (or ''south'') node is where the Moon enters the southern ecliptic hemisphere. Motion The line of nodes, which is also the intersection between the two respective planes, rotates (precesses) with a period of 18.6 years or 19.35° per year. When viewed from the celestial north, the nodes move clockwise around Earth, I.e. with a retrograde motion (opposite to Earth's own spin and its revolution around the Sun). So the time from one node crossing to the next (see eclipse season) is approximately a half-year minus half of 19.1 days -- or about 173 days. Because the orbital plane of the Moon precesses in space, the lunar nodes also precess around the ecliptic, completing one revolution (called a ''draconic period' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliocentric Astrology
Heliocentric astrology is an approach to astrology centered around birth charts cast using the heliocentric model of the Solar System, positioning the Sun at the center. In contrast to geocentric astrology, which places Earth at the center, heliocentric astrology interprets planetary positions from the Sun's vantage point. While geocentric astrology considers elements like the ascendant, midheaven, houses, Sun, Moon, and planetary aspects, heliocentric astrology focuses primarily on planetary aspects and configurations. Astrologers often use this method in conjunction with geocentric astrology to access insights beyond the traditional framework. The roots of heliocentric astrology extend back to Copernicus's 16th-century work on heliocentrism. Early pioneers like Andreas Aurifaber and later practitioners like Joshua Childrey challenged geocentric perspectives during the 17th century. They proposed that astrology could align with contemporary natural philosophy, finding support f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geocentric Model
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded scientific theories, superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric models, the Sun, Moon, stars, and classical planet, planets all orbit Earth. The geocentric model was the predominant description of the cosmos in many European Ancient history, ancient civilizations, such as those of Aristotle in Classical Greece and Ptolemy in Roman Egypt, as well as during the Islamic Golden Age. Two observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. First, from anywhere on Earth, the Sun appears to revolve around Earth diurnal motion, once per day. While the Moon and the planets have their own motions, they also appear to revolve around Earth about once per day. The stars appeared to be fixed stars, fixed on a celestial sphere rotating once each day about celestial pole, an axis through the geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forer Effect
The Barnum effect, also called the Forer effect or, less commonly, the Barnum–Forer effect, is a common psychological phenomenon whereby individuals give high accuracy ratings to descriptions of their personality that supposedly are tailored specifically to them, yet which are in fact vague and general enough to apply to a broad range of people. This effect can provide a partial explanation for the widespread acceptance of some paranormal beliefs and practices, such as astrology, fortune telling, aura reading, and some types of personality tests. It was originally called the "fallacy of personal validation" by psychologist Bertram Forer. The term "Barnum effect" was coined in 1956 by psychologist Paul Meehl in his essay "Wanted – A Good Cookbook", because he relates the vague personality descriptions used in certain "pseudo-successful" psychological tests to those given by showman P. T. Barnum. Overview The Barnum effect is manifested in response to statements that are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopedia, online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest-running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in Edinburgh, Scotland, in three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size; the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810), it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent contributors, and the 9th (1875–1889) and Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, 11th editions (1911) are landmark encyclopaedias for scholarship and literary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claims; reliance on confirmation bias rather than rigorous attempts at refutation; lack of openness to evaluation by other experts; absence of systematic practices when developing hypotheses; and continued adherence long after the pseudoscientific hypotheses have been experimentally discredited. It is not the same as junk science. The demarcation between science and pseudoscience has scientific, philosophical, and political implications. Philosophers debate the nature of science and the general criteria for drawing the line between scientific theories and pseudoscientific beliefs, but there is widespread agreement "that creationism, astrology, homeopathy, Kirlian photography, dowsing, ufology, ancient astronaut theory, Holocaust den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |