|
Nasiruddin Mahmud (eldest Son Of Iltutmish)
Nāṣir ad-Dīn Maḥmūd () was the eldest son of the Delhi Sultan Shamsuddin Iltutmish and his chief consort Turkan Khatun, (as the court historian Minhaj-i Siraj Juzjani clearly mentioned in the Tabaqat-i Nasiri, the only contemporary source of history of that time), the daughter of Qutb ud-Din Aibak. He was, in all probabilities, the full brother of Razia Sultan. He was the governor of Awadh and later served as the governor of Bengal (Preceded by Iwaz Khalji) until his death in 1229. Then in 1230 the son of Ali Sher Khalji, Balka Khalji declared himself as independent king of Bengal. Thus in 1231 Iltutmish marched against him and defeated him and made Alauddin Jani as the next governor of Bengal. History When Iwaz Khalji rebelled against Delhi Sultan Iltutmish, he sent his son Nasiruddin Mahmud along with Alauddin Jani to lead an invasion against Iwaz. Iwaz was defeated and killed, and Nasiruddin became the governor of Bengal. He received the title ''Malik ush-Shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
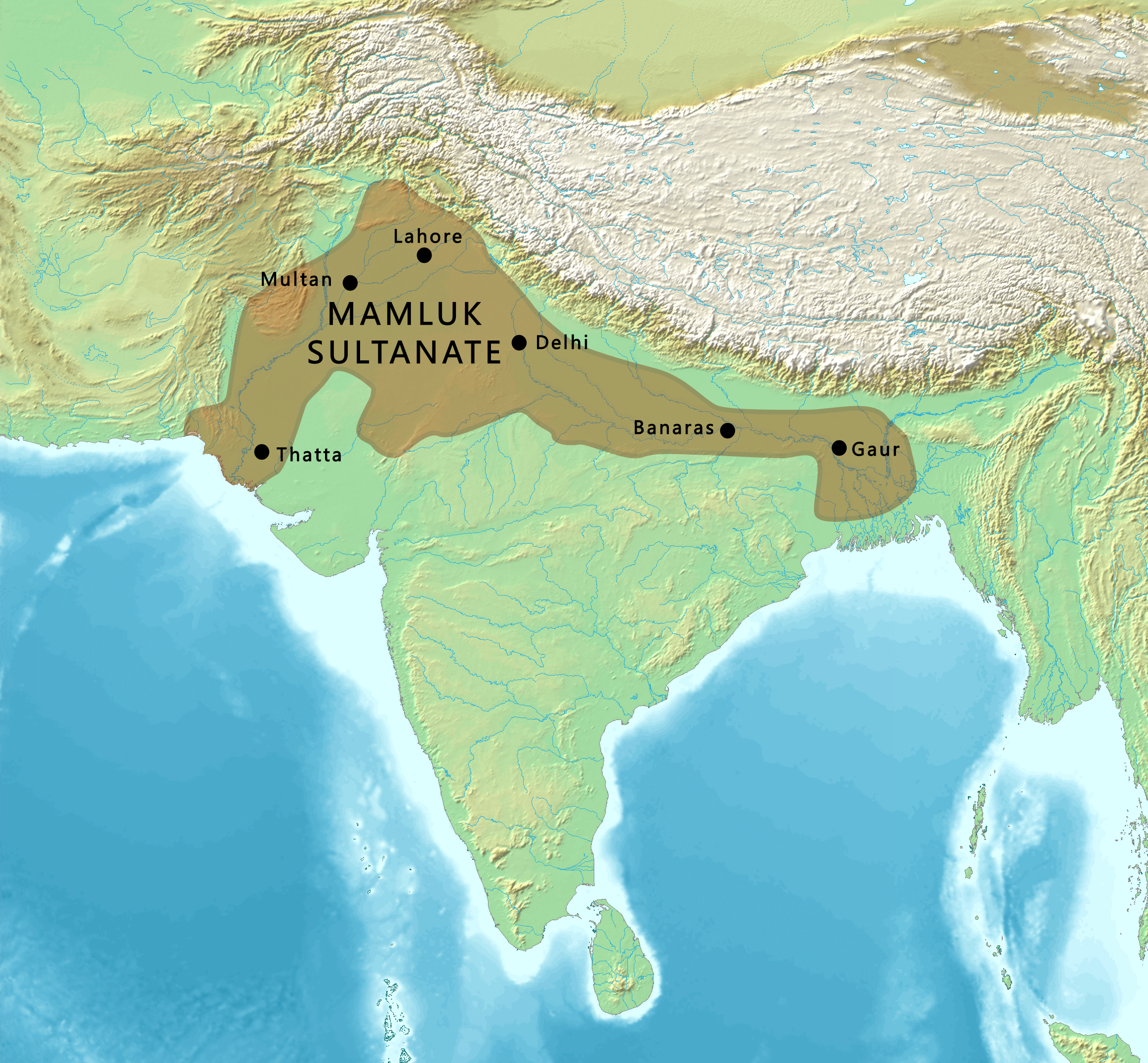
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica The sultanate was established around in the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk (1206–1290), Khalji dynasty, Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq dynasty, Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid dynasty, Sayyid (1414–1451), and Lodi dynasty, Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, as well as some parts of southern Nepal. The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups such as Mongols, Monpa people, Monpa, Tamang people, Tamang, Qiang people, Qiang, Sherpa people, Sherpa, Lhoba people, Lhoba, and since the 20th century Han Chinese and Hui people, Hui. Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of . Located in the Himalayas, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain, rising above sea level. The Tibetan Empire emerged in the 7th century. At its height in the 9th century, the Tibetan Empire extended far beyond the Tibetan Plateau, from the Tarim Basin and Pamirs in the west, to Yunnan and Bengal in the southeast. It then divided into a variety of territories. The bulk of western and central Tibet (Ü-Tsang) was often at least nominally unified under a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governors Of Bengal
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the type of political region or polity, a ''governor'' may be either appointed or elected, and the governor's powers can vary significantly, depending on the public laws in place locally. The adjective pertaining to a governor is gubernatorial, from the Latin root ''gubernare''. In a federated state, the governor may serve as head of state and head of government for their regional polity, while still operating under the laws of the federation, which has its own head of state for the entire federation. Ancient empires Pre-Roman empires Though the legal and administrative framework of provinces, each administered by a governor, was created by the Romans, the term ''governor'' has been a convenient term for historians to describe similar systems in antiquity. Indeed, many regions of the pre-Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1229 Deaths
Year 1229 ( MCCXXIX) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. Events By place Sixth Crusade * February 18 – Treaty of Jaffa: Emperor Frederick II signs a 10-year truce together with Sultan Al-Kamil and his representatives; he manages to regain many parts of the Holy Land through political negotiation, rather than by resorting to military force or directly confronting the Muslim army. Frederick's achievements, including the control of Jerusalem (without the Temple Mount) and Bethlehem, with a corridor running through Lydda to the sea of Jaffa, as well as Nazareth and western Galilee, including Montfort Castle and Toron, and the remaining Muslim districts around Sidon. All Muslims are to be allowed the right of entry in Jerusalem and freedom of worship. * March 17 – Frederick II enters Jerusalem, escorted by German and Italian troops. Of the Military Orders only the Teutonic Knights are represented and some clergy. He receives the forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khalji Dynasty Of Bengal
The Khalji dynasty (, ) was the first Muslim dynasty to rule the Bengal region in the Indian subcontinent. The dynasty, which hailed from the Garmsir District, Garmsir region of present-day Afghanistan, was founded in 1204 by Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khalji, Muhammad Bakhtiyar Khalji, a Muslim Turko-Afghan general of the Ghurid Empire. The Khaljis initially pledged allegiance to Sultan Muhammad of Ghor until his death in 1206, though their rule in Bengal was mostly independent. Under the rule of Iwaz Khalji, Bengal experienced major developments such as its first naval force, flood defence systems and linkage with the Grand Trunk Road. The dynasty was based in the city of Gauḍa (city), Lakhnauti in north Bengal, northern Bengal, later expanding eastwards and southwards. Nasiruddin Mahmud (eldest son of Iltutmish), Nasiruddin Mahmud, the son of Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk sultan Iltutmish of Delhi managed to conquer Bengal in 1227; although the Khaljis briefly reasserted their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rulers Of Bengal
This is a list of rulers of Bengal. For much of History of Bengal, its history, Bengal was split up into several independent kingdoms, completely unifying only several times. In Kingdoms of Ancient India, ancient times, Bengal consisted of the kingdoms of Pundra kingdom, Pundra, Suhma kingdom, Suhma, Vanga kingdom, Vanga, Samatata and Harikela. In the 4th century BCE, during the reign of the Nanda Empire, the powerful rulers of Gangaridai sent their forces consisting of war elephants which led to the withdrawal of Alexander the Great from the Indian subcontinent. With the rise of Gopala in 750 AD, Bengal was united once more under the Buddhist and Shaivism, Shaivite Pala Empire. The Pala period is considered as one of golden eras of Bengali history as it brought stability and prosperity to Bengal after centuries of Civil war, Civil War, created outstanding works of art and architecture, proto-Bengali language developed under them including its first literary work, the Charyapa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muiz Ud Din Bahram
Muiz ud-Din Bahram (; 9 July 1212 – 15 May 1242) was the sixth sultan of the Mamluk Dynasty. Life He was the son of Shams ud din Iltutmish (1211–36) and the half-brother of Razia Sultan (1236–40). While his sister was imprisoned in Bathinda by subedar Malik Altunia (both Altunia and Bahram Shah planned conspiracy against Razia Sultan) he declared himself the king with the support of forty chiefs. Even so, during Muiz ud din Bahram's two years as king, the chiefs that had originally supported him became disordered and constantly bickered among each other. It was during this period of unrest that he was murdered by his own army in 1242 (died 15 May 1242). After his death, he was succeeded by his nephew Ala ud din Masud, a son of his half-brother Rukn ud din Firuz. Ögedei Khan of the Mongol Empire appointed Dayir commander of Ghazni and Menggetu commander in Kunduz. In winter 1241 the Mongol force invaded the Indus valley and besieged Lahore. Dayir died storming th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruknuddin Firuz
Rukn-ud-din Firuz (), further transliterated as Rukn al-Din Firoz and also known as Firuz I (1211 – 19 November 1236), was the Sultan of Delhi for less than seven months in 1236. As a prince, he had administered the Badaun and Lahore provinces of the Sultanate. He ascended the throne after the death of his father Iltutmish, a powerful Mamluk ruler who had established the Sultanate as the most powerful kingdom in northern India. However, he pursued pleasure, wine, women, and left his mother Shah Turkan in control of the administration. The misadministration led to rebellions against Ruknuddin and his mother, both of whom were arrested and imprisoned. The nobles and the army subsequently appointed his half-sister Razia on the throne. Early life Ruknuddin was born to the Delhi Sultan Iltutmish and his wife ''Khudawanda-i-Jahan'' Shah Turkan, who was a hand-maid of Turkic origin. As a prince, he was assigned the iqta' of Badaun in 1228. He administered Badaun with the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qutb Minar Complex
The Qutb Minar complex are monuments and buildings from the Delhi Sultanate at Mehrauli in Delhi, India. Construction of the Qutub Minar "victory tower" in the complex, named after the religious figure Sufi Saint Khwaja Qutbuddin Bakhtiar Kaki, was begun by Qutb-ud-din Aibak, who later became the first Sultan of Delhi of the Mamluk dynasty (Gulam Vansh). It was continued by his successor Iltutmish (a.k.a. Altamash), and finally completed much later by Firoz Shah Tughlaq, a Sultan of Delhi from the Tughlaq dynasty (1320–1412) in 1368 AD. The Qubbat-ul-Islam Mosque (Dome of Islam), later corrupted into Quwwat-ul Islam, stands next to the Qutb Minar.Epigraphia Indo Moslemica, 1911–12, p. 13. Many subsequent rulers, including the Tughlaqs, Alauddin Khalji and the British added structures to the complex. Apart from the Qutb Minar and the Quwwat ul-Islam Mosque, other structures in the complex include the Alai Darwaza gate, the Alai Minar and the Iron pillar. Inside the comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be considered a type of tomb, or the tomb may be considered to be within the mausoleum. Overview The word ''mausoleum'' (from the ) derives from the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus (near modern-day Bodrum in Turkey), the grave of King Mausolus, the Persian satrap of Caria, whose large tomb was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Mausolea were historically, and still may be, large and impressive constructions for a deceased leader or other person of importance. However, smaller mausolea soon became popular with the gentry and nobility in many countries. In the Roman Empire, these were often in necropoles or along roadsides: the via Appia Antica retains the ruins of many private mausolea for kilometres outside Rome. When Christianity became domin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world's Major religious groups, second-largest religious population after Christians. Muslims believe that Islam is the complete and universal version of a Fitra, primordial faith that was revealed many times through earlier Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets and messengers, including Adam in Islam, Adam, Noah in Islam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, and Jesus in Islam, Jesus. Muslims consider the Quran to be the verbatim word of God in Islam, God and the unaltered, final revelation. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Torah in Islam, Tawrat (the Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Gospel in Islam, Injil (Gospel). They believe that Muhammad in Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |