|
Naos Of The Decades
Naos of the Decades, also known as the Saft el-Hinna Naos, is a black granite cella, naos preserved in several parts that have been discovered almost two centuries apart. The naos is dedicated to the god Shu (Egyptian god), Shu-Sopdu and dates to the reign of Nectanebo I. An astrological calendar is engraved on its sides depicting 36 decades, or 10-day periods marked by small constellations of stars called decans. Discovery The upper part of the monument, known as the pyramidion, has been on display in the Louvre Museum since 1817, and it was discovered and brought back by French explorers. The rest of the naos consists of many pieces. One large piece was found in 1940 by Prince Omar Toussoun and is held at the Graeco-Roman Museum in Alexandria. Other pieces were discovered in 2001 by Franck Goddio during the underwater archaeology, underwater excavations he organized in search of the sunken cities of Canopus, Egypt, Canopus and Heracleion. All of these pieces were found in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
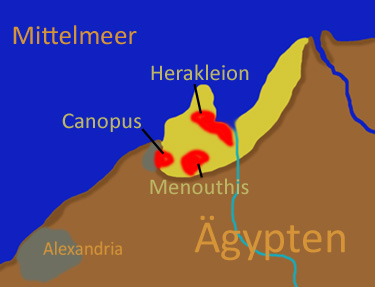
Canopus, Egypt
Canopus ( , , ; , ), also known as Canobus (, ), was an ancient Egyptian coastal town, located in the Nile Delta. Its site is in the eastern outskirts of modern-day Alexandria, around from the center of that city. Canopus was located on the western bank at the mouth of the westernmost branch of the Delta – known as the Canopic or Heracleotic branch. It belonged to the seventh Egyptian Nome (Egypt), Nome, known as ''Menelaites'', and later as ''Canopites'', after it. It was the principal port in Egypt for Greek trade before the foundation of Alexandria, along with Naucratis and Heracleion. Its ruins lie near the present Egyptian town of Abu Qir. Land in the area of Canopus was subject to rising sea levels, earthquakes, tsunamis, and large parts of it seem to have succumbed to liquefaction sometime at the end of the 2nd century BC. The eastern suburbs of Canopus collapsed, their remains being today submerged in the sea, with the western suburbs being buried beneath the modern c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naos Des Décades - Musée Du Louvre Antiquités Egyptiennes N 389 ; D 37 ; LL 91
Naos may refer to: * A naós or cella, the inner chamber in Greek and Roman temples * An ancient Greek temple, called a ''naos'' in Koine Greek * Naos (hieroglyph), an Egyptian hieroglyph * Zeta Puppis Zeta Puppis (ζ Puppis, abbreviated Zeta Pup, ζ Pup), formally named Naos , is the brightest star in the constellation of Puppis. The spectral class of O4 means this is one of the hottest, and most luminous, stars ..., a star See also * Naus (other) {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graeco-Roman Museum
The Graeco-Roman Museum is an archaeological museum located in Alexandria, Egypt. Its collection of over 40,000 objects includes sculptures, mosaics, woodwork, and coins. History Erected in 1892, it was first built in a five-room apartment, inside one small building on Rosetta Street (later Avenue Canope and now Horriya). In 1895, it was transferred to another, larger building near Gamal Abdul Nasser Street. Its first director was . From 1904 to 1932 he was followed by Evaristo Breccia and then Achille Adriani. The museum was inaugurated in 1895 by Khedive Abbas II of Egypt, Abbas II. The museum edited the ''Bulletin of the Alexandria Archaeological Society''. The museum contains several pieces dating from the Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman (Ptolemaic Kingdom, Ptolemaic) era in the 3rd century BC, such as a sculpture of Apis (god), Apis in black granite, the sacred bull of the Egyptians, mummy, mummies, sarcophagus, tapestry, tapestries, and other objects offering a view of Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1940 Archaeological Discoveries
Year 194 ( CXCIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Septimius and Septimius (or, less frequently, year 947 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 194 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Decimus Clodius Septimius Albinus Caesar became a Roman Consul. * Battle of Issus: Septimius Severus marches with his army (12 legions) to Cilicia, and defeats Pescennius Niger, Roman governor of Syria. Pescennius retreats to Antioch, and is executed by Severus' troops. * Septimius Severus besieges Byzantium (194–196); the city walls suffer extensive damage. Asia * Battle of Yan Province: Warlords Cao Cao and Lü Bu fight for control over Yan Province; the battle lasts for over 100 days. * First year of the ''Xingping'' era during the Han Dynasty in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Temples
Egyptian temples were built for the official worship of the ancient Egyptian deities, gods and in commemoration of the pharaohs in ancient Egypt and regions under Egyptian control. Temples were seen as houses for the gods or kings to whom they were dedicated. Within them, the Egyptians performed the central rituals of Ancient Egyptian religion, Egyptian religion: giving Sacrifice, offerings to the gods, reenacting their Egyptian mythology, mythology through festivals, and warding off the forces of chaos. These rituals were seen as necessary for the gods to continue to uphold ''maat'', the divine order of the universe. Caring for the gods was the obligations of pharaohs, who dedicated prodigious resources to temple construction and maintenance. Pharaohs delegated most of their ritual duties to priests, but most of the populace was excluded from direct participation in ceremonies and forbidden to enter a temple's most sacred areas. Nevertheless, a temple was an important religious s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Qir Bay
The Abū Qīr Bay (sometimes transliterated Abukir Bay or Aboukir Bay) (; transliterated: Khalīj Abū Qīr) is a spacious bay on the Mediterranean Sea near Alexandria in Egypt, lying between the Rosetta mouth of the Nile and the town of Abu Qir. The ancient cities of Canopus, Heracleion and Menouthis lie submerged beneath the waters of the bay. In 1798 it was the site of the Battle of the Nile, a naval battle fought between the British Royal Navy and the navy of the French First Republic. The bay contains a natural gas field, discovered in the 1970s. Geography Abu Qir Bay lies approximately east of Alexandria, bounded to the southwest by the Abu Qir headland, on which lies the town of Abu Qir, and to the northeast by the Rosetta mouth of the Nile. The bay is a highly fertile Egyptian coastal region but suffers from acute eutrophication and pollution from untreated industrial and domestic waste. The ABU QIR Fertilizers and Chemicals Industries Company, a large producer of ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heracleion
Heracleion (Ancient Greek: ), also known as Thonis (Ancient Greek: ; from the Egyptian language, Ancient Egyptian: ; ) and sometimes called Thonis-Heracleion, was an ancient Egyptian port city located near the Canopic Mouth of the Nile, about northeast of Alexandria on the Mediterranean Sea. It became inundated and its remains are located in Abu Qir Bay, currently off the coast, under ca. of water, and near Abukir. The sanctuary of Neith of Sais was located in Thonis. A stele found on the site indicates that late in its history the city was known by both its Egyptian and Greek names. The legendary beginnings of Thonis go back to as early as the 12th century BC, and it is mentioned by ancient Greeks, Greek historians. Its importance grew particularly during the Late Period of ancient Egypt, waning days of the pharaohs. History Thonis was originally built on some adjoining islands in the Nile Delta. The city was built around a central temple, and was intersected by canals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underwater Archaeology
Underwater archaeology is archaeology practiced underwater. As with all other branches of archaeology, it evolved from its roots in pre-history and in the classical era to include sites from the historical and industrial eras. Its acceptance has been a relatively late development due to the difficulties of accessing and working underwater sites, and because the application of archaeology to underwater sites initially emerged from the skills and tools developed by shipwreck salvagers. As a result, underwater archaeology initially struggled to establish itself as actual archaeological research. This changed when universities began teaching the subject and a theoretical and practical base for the sub-discipline was firmly established in the late 1980s. Underwater archaeology now has a number of branches including, maritime archaeology: the scientifically based study of past human life, behaviors and cultures and their activities in, on, around and (lately) under the sea, estuarie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franck Goddio
Franck Goddio (born 1947 in Casablanca, Morocco) is a French underwater archaeologist who, in 2000, discovered the city of Thonis-Heracleion off the Egyptian shore in Aboukir Bay. He led the excavation of the submerged site of Canopus and of the ancient harbour of Alexandria (''Portus Magnus''), including Antirhodos Island. He has also excavated ships in the waters of the Philippines, significantly the Spanish galleon ''San Diego''. Biography Goddio received degrees in mathematics and statistics from the École Nationale de la Statistique et de l'Administration Économique in Paris. He was employed as an advisor to national and international organizations and various governments for over 15 years. In the early 1980s, he decided to focus on underwater archaeology. In 1987, he founded the Institut Européen d'Archéologie Sous-Marine (IEASM) in Paris. In his work in detecting and recovering ancient shipwrecks and searching for the remains of sunken cities, Goddio developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Omar Toussoun
Prince Mohamed Omar Toussoun (1872–1944) was an Egyptian prince of the Muhammad Ali dynasty. He is one of the most admired princes of the Muhammad Ali family. He was famous for his excellence in many fields, his charitable works, his discoveries and his writings in geography, history and archaeology. He published many books and maps in Arabic and French, and he was the first to suggest sending a delegation from Egypt to the Versailles conference to demand its independence, a task later accomplished by Saad Zaghloul.Daily News EgyptOmar Toussoun: Enlightened Prince and National Geographer Atef Moatamed (27 October 2020) Biography Prince Omar Toussoun was born in Alexandria on 8 September 1872 to Princess Bahshat Hour and Prince Mohamed Toussoun Pasha, son of the Wāli of Egypt, Muhammad Sa'id Pasha. He lost his father when he was four years old, and his paternal grandmother, Princess Melek Per, took care of his upbringing. In his youth he travelled extensively in Europe. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saft El-Hinna
Saft el-Hinna (), also written as Saft el-Hinneh, Saft el-Henna, Saft el-Henneh, is a village and an archaeological site in Egypt. It is located in the modern Al Sharqia Governorate, in the Nile Delta, about 7 km southeast of Zagazig. The 1885 Census of Egypt recorded Saft el-Hinna as a nahiyah in the district of Bilbeis in Sharqia Governorate; at that time, the population of the town was 664 (306 men and 358 women). Name The modern village of Saft el-Hinna lies on the ancient Egyptian town of Per-Sopdu or Pi-Sopt, meaning "House of Sopdu", which was the capital of the 20th Nome (Egypt), nome of Lower Egypt and one of the most important cult centers during the Late Period of ancient Egypt. As the ancient name implies, the town was consecrated to Sopdu, god of the eastern borders of Egypt. During the late Third Intermediate Period, Per-Sopdu – called ''Pishaptu'' or ''Pisapti'', in Akkadian language, Akkadian, by the Neo-Assyrian invaders – was the seat of one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louvre Museum
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is a national art museum in Paris, France, and one of the most famous museums in the world. It is located on the Rive Droite, Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement of Paris, 1st arrondissement (district or ward) and home to some of the most Western canon, canonical works of Art of Europe, Western art, including the ''Mona Lisa,'' ''Venus de Milo,'' and ''Winged Victory''. The museum is housed in the Louvre Palace, originally built in the late 12th to 13th century under Philip II of France, Philip II. Remnants of the Medieval Louvre fortress are visible in the basement of the museum. Due to urban expansion, the fortress eventually lost its defensive function, and in 1546 Francis I of France, Francis I converted it into the primary residence of the French kings. The building was redesigned and extended many times to form the present Louvre Palace. In 1682, Louis XIV chose the Palace of Versailles for his househ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |