|
Name Of Toronto
The name of Toronto has a history distinct from that of the city itself. Originally, the term "''Tkaronto''" referred to a channel of water between Lake Simcoe and Lake Couchiching, at what is now the city of Orillia, on maps as early as 1675 but in time the name passed southward, and was eventually applied to a new fort at the mouth of the Humber River. Fort Toronto was the first European settlement in the area, and lent its name to what became the city of Toronto. John Graves Simcoe identified the area as a strategic location to base a new capital for Upper Canada, believing Newark to be susceptible to American invasion. A garrison was established at Garrison Creek, on the western entrance to the docks of Toronto Harbour, in 1793; this later became Fort York. The settlement it defended was renamed York on August 26, 1793, as Simcoe favoured English names over those of First Nations languages, in honour of Prince Frederick, Duke of York. Residents petitioned to change the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toronto
Toronto ( , locally pronounced or ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada. It is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the List of North American cities by population, fourth-most populous city in North America. The city is the anchor of the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration of 9,765,188 people (as of 2021) surrounding the western end of Lake Ontario, while the Greater Toronto Area proper had a 2021 population of 6,712,341. As of 2024, the census metropolitan area had an estimated population of 7,106,379. Toronto is an international centre of business, finance, arts, sports, and culture, and is recognized as one of the most multiculturalism, multicultural and cosmopolitanism, cosmopolitan cities in the world. Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous peoples have travelled through and inhabited the Toronto area, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yorkville, Toronto
Yorkville is a neighbourhood and former village in Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is roughly bounded by Bloor Street to the south, Davenport Road to the north, Yonge Street to the east and Avenue Road, Toronto, Avenue Road to the west, and it is part of The Annex neighbourhood. Established as a separate community in 1830, it was annexed into Toronto in 1883. Yorkville comprises residential areas, office space, and retail shopping. The Mink Mile shopping district on Bloor Street is located in Yorkville. History Yorkville was funded in 1830 by the entrepreneur Joseph Bloor (after whom Bloor Street, one of Toronto's main thoroughfares, is named) and William Botsford Jarvis of Rosedale, Toronto, Rosedale and began as a residential suburb. Bloore operated a brewery northeast of today's Bloor and Church Street intersection, and Jarvis was Sheriff of the Home District. The two purchased land in the Yorkville area and subdivided it into smaller lots on new side streets for those i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toronto Carrying-Place Trail
The Toronto Carrying-Place Trail, also known as the Humber Portage and the Toronto Passage, was a major portage route in Ontario, Canada, linking Lake Ontario with Lake Simcoe and the northern Great Lakes (North America), Great Lakes. The name comes from the Mohawk language, Mohawk term ''toron-ten'', meaning "the place where the trees grow over the water", an important landmark on Lake Simcoe through which the trail passed. Route From Lake Ontario, the trail ran northward along the eastern bank of the Humber River (Ontario), Humber River. It forked at Woodbridge, Ontario, Woodbridge, with one path crossing the east branch of the Humber and running along the west side of the river to the vicinity of Kleinburg, Ontario, Kleinburg, where it crossed the river again. This trail was probably used during the seasons when the water was low enough to ford. The other path of the fork followed the east side of the river and angled cross-country to King Creek, Ontario, King Creek, joining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
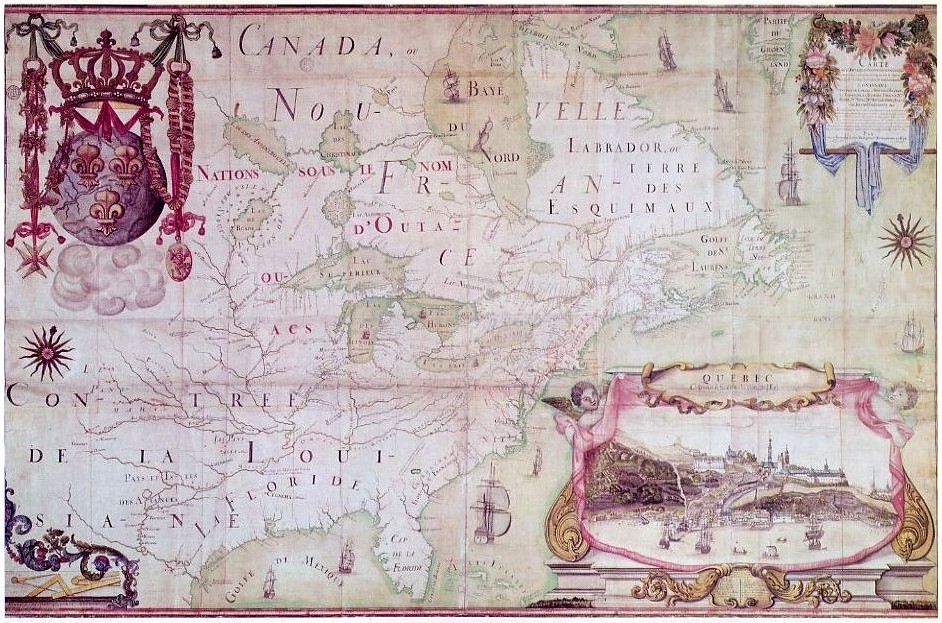
Jean-Baptiste-Louis Franquelin
Jean-Baptiste-Louis Franquelin (; 1650-c.1712) was a French trader who was appointed in the early 1670s as the first Cartography, cartographer in ''Nouvelle France'' (Canada) by the colony's governor. He was appointed in 1688 as a royal Hydrography, hydrographer by Louis XIV. Franquelin was born in the commune of Pallauau-sur-Indre in central France. He migrated to New France in 1671 where he was soon appointed as the colony's cartographer. He documented a decade of Louis Jolliet and René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle, René-Robert Cavelier de La Salle's explorations in North America. He also completed other projects for the Crown and served the king's military engineer. After returning to France in 1692, he never lived in Canada again. Biography Born at Palluau-sur-Indre, Saint-Michel de Villebernin, he grew up in the village in the small commune of Palluau-sur-Indre in central France. Having developed drawing and mapmaking skills, Franquelin migrated in 1671 from the Indr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and History of Spain (1700–1808), Spain in 1763 under the Treaty of Paris (1763), Treaty of Paris. A vast viceroyalty, New France consisted of five colonies at its peak in 1712, each with its own administration: Canada (New France), Canada, the most developed colony, which was divided into the districts of Quebec (around what is now called Quebec City), Trois-Rivières, and Montreal; Hudson Bay; Acadia in the northeast; Terre-Neuve (New France), Terre-Neuve on the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland; and Louisiana (New France), Louisiana. It extended from Newfoundland to the Canadian Prairies and from Hudson Bay to the Gulf of Mexico, including all the Great Lakes of North America. The continent-traversing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Raffeix
Pierre Raffeix (1633–1724) was a French Jesuit missionary in Canada. Biography He was born at Clermont-Ferrand, entered the Society of Jesus in 1653, and came to Canada in 1663. In 1668 he established near Montreal a settlement for converted Iroquois (now Kahnawake). In 1671 he replaced Étienne de Carheil in the Cayuga mission, and afterwards went to the Seneca Indians until 1680. Raffeix was a cartographer, as the following surviving maps bear witness: *"Carte des regions les plus occidentales du Canada", dated 1676, and bearing a legend relating to the voyage of discovery of Jacques Marquette and Louis Joliet; *"Le lac Ontario avec les pays adjacents et surtout les cinq nations iroquoises"; *"La Nouvelle-France, de l'Océan au lac Erié, et, au sud, jusqu'à la Nouvelle-Angleterre". After his return to Quebec he acted as procurator to the mission. He spent two years at Jeune-Lorette (1699–1700), shortly after the final migration of the remnants of the Huron nation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyandot Language
Wyandot (also Wyandotte, Wendat, Quendat or Huron) is the Iroquoian language traditionally spoken by the people known as Wyandot or Wyandotte, descended from the Tionontati. It is considered a sister to the Wendat language, spoken by descendants of the Huron-Wendat Confederacy. It was last spoken, before its revival, by members located primarily in Oklahoma, United States, and Quebec, Canada. Linguists have traditionally considered Wyandot as a dialect or modern form of Wendat, even though the two are no longer mutually intelligible. Wyandot essentially died out as a spoken language with the death of the last native speaker in 1972, though there are now attempts at revitalization: *The Wyandotte Nation is offering Wyandot language classes in the Wyandotte Public Schools grades K–4, at the Wyandotte Nation's preschool "Turtle-Tots" program in Oklahoma and has created online language lessons for self-study. *The Huron-Wendat Nation of Quebec is offering adult and children's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyandot People
The Wyandot people (also Wyandotte, Wendat, Waⁿdát, or Huron) are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of the present-day United States and Canada. Their Wyandot language belongs to the Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian language family. In Canada, the Huron-Wendat Nation has two First Nations in Canada, First Nations Indian reserve, reserves at Wendake, Quebec. In the United States, the Wyandotte Nation is a federally recognized tribe headquartered in Wyandotte, Oklahoma. There are also List of organizations that self-identify as Native American tribes, organizations that self-identify as Wyandot. The Wendat emerged as a confederacy of five nations in the St. Lawrence River Valley, especially in Southern Ontario, including the north shore of Lake Ontario. Their original homeland extended to the Georgian Bay of Lake Huron and Lake Simcoe in Ontario, Canada and occupied territory around the western part of the lake. The Wyandotte Nation (the U.S. Tribe) descends f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mnjikaning Fish Weirs
The Mnjikaning Fish Weirs are one of the oldest human developments in Canada. These fishing weirs were built by the first nations people well before recorded history, dating to around 4500 BP during the Archaic period in North America, according to carbon dating done on some of the wooden remnants. The weirs were built in the narrows between Lake Couchiching and Lake Simcoe, now known as Atherley Narrows, over which Ontario Highway 12 passes today. They were preserved by the water and layers of protective silt. The weirs were built as fences using local wood species, including eastern white cedar, sugar maple, and white birch for the stakes. The weirs were used to trap the various fish species swimming through them. The early fishermen wove brush and vegetation among the weirs to make net-like fencing where the fish were guided to be speared, netted or kept for later use, particularly for consumption during the winter. The weirs – historically called ''ouentaronk'' (Huron) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel De Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; 13 August 1574#Fichier]For a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see #Ritch, RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December 1635) was a French explorer, navigator, cartographer, draftsman, soldier, geographer, ethnologist, diplomat, and chronicler. He made between 21 and 29 trips across the Atlantic Ocean, and founded Quebec City, and New France, on 3 July 1608. An important figure in history of Canada, Canadian history, Champlain created the first accurate coastal map during his explorations and founded various colonial settlements. Born into a family of sailors, Champlain began exploring North America in 1603, under the guidance of his uncle, François Gravé Du Pont.#Davignon, d'Avignon (2008) After 1603, Champlain's life and career consolidated into the path he would follow for the rest of his life. From 1604 to 1607, he participated in the exploration an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohawk People
The Mohawk, also known by their own name, (), are an Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous people of North America and the easternmost nation of the Haudenosaunee, or Iroquois Confederacy (also known as the Five Nations or later the Six Nations). Mohawk are an Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian-speaking people with communities in southeastern Canada and northern New York (state), New York State, primarily around Lake Ontario and the St. Lawrence River. As one of the five original members of the Iroquois Confederacy, the Mohawk are known as the Keepers of the Eastern Door who are the guardians of the confederation against invasions from the east. Today, Mohawk people belong to the Mohawk Council of Akwesasne, Mohawks of the Bay of Quinte First Nation, Mohawks of Kahnawà:ke, Mohawks of Kanesatake, Six Nations of the Grand River, and Saint Regis Mohawk Tribe, a federally recognized tribe in the United States. At the time of European contact, Mohawk people were based in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Canada And The Iroquois Confederacy
Upper may refer to: * Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot * Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both * ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found footage film ''The Upper Footage'' * Dmitri Upper Dmitri Sergeyevich Upper (; born July 27, 1978) is a Kazakhstani former professional ice hockey center. He also holds Russian citizenship. Career Upper was selected by the New York Islanders in the 5th round (136th overall) of the 2000 NHL ... (born 1978), Kazakhstani ice hockey player See also * Uppers (video game), a video game by Marvelous {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |