|
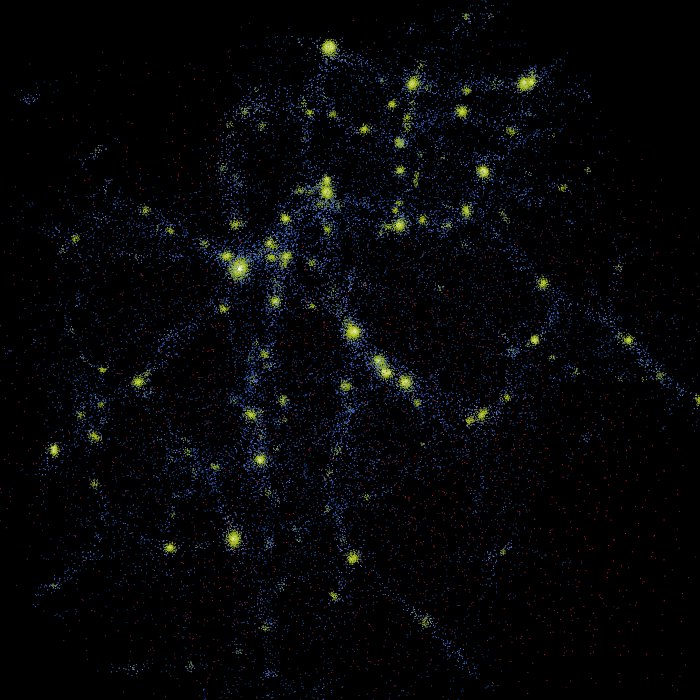
N-body
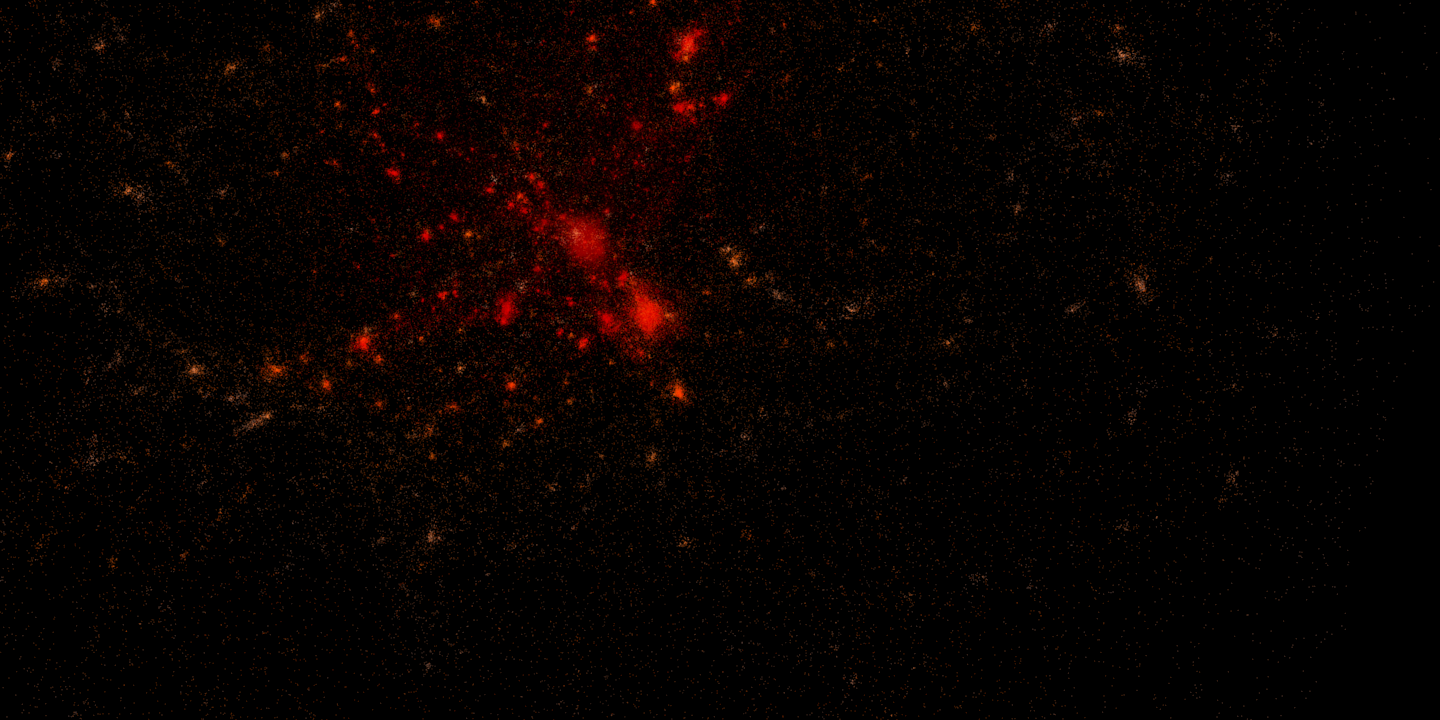
In physics and astronomy, an ''N''-body simulation is a simulation of a dynamical system of particles, usually under the influence of physical forces, such as gravity (see ''n''-body problem for other applications). ''N''-body simulations are widely used tools in astrophysics, from investigating the dynamics of few-body systems like the Earth-Moon The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...-Sun system to understanding the evolution of the large-scale structure of the universe. In physical cosmology, ''N''-body simulations are used to study processes of non-linear structure formation such as galaxy filaments and galaxy halos from the influence of dark matter. Direct ''N''-body simulations are used to study the dynamical evolution of star clusters. Nature of the particles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-body Simulation
In physics and astronomy, an ''N''-body simulation is a simulation of a dynamical system of particles, usually under the influence of physical forces, such as gravity (see n-body problem, ''n''-body problem for other applications). ''N''-body simulations are widely used tools in astrophysics, from investigating the dynamics of few-body systems like the Earth-Moon-Sun system to understanding the evolution of the large-scale structure of the universe. In physical cosmology, ''N''-body simulations are used to study processes of non-linear structure formation such as galaxy filaments and galaxy halos from the influence of dark matter. Direct ''N''-body simulations are used to study the dynamical evolution of star clusters. Nature of the particles The 'particles' treated by the simulation may or may not correspond to physical objects which are particulate in nature. For example, an N-body simulation of a star cluster might have a particle per star, so each particle has some physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-body Problem
In physics, the -body problem is the problem of predicting the individual motions of a group of astronomical object, celestial objects interacting with each other gravitationally.Leimanis and Minorsky: Our interest is with Leimanis, who first discusses some history about the -body problem, especially Ms. Kovalevskaya's 1868–1888 twenty-year complex-variables approach, failure; Section 1: "The Dynamics of Rigid Bodies and Mathematical Exterior Ballistics" (Chapter 1, "The motion of a rigid body about a fixed point (Euler and Poisson equations)"; Chapter 2, "Mathematical Exterior Ballistics"), good precursor background to the -body problem; Section 2: "Celestial Mechanics" (Chapter 1, "The Uniformization of the Three-body Problem (Restricted Three-body Problem)"; Chapter 2, "Capture in the Three-Body Problem"; Chapter 3, "Generalized -body Problem"). Solving this problem has been motivated by the desire to understand the motions of the Sun, Moon, planets, and visible stars. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erik Holmberg (astronomer)
Erik Holmberg (13 November 1908 – 1 February 2000) was a Swedish astronomer and cosmologist. He is most famous for his work in the effects of interacting galaxies. This research showed that galaxies that came near each other would likely combine to form a larger galaxy. In 1908, Holmberg was born to Malcolm and Anna Holmberg in Skillingaryd, Sweden. In 1947 he married Martha Asdahl. They had one daughter named Osa, who was born in 1953. He died on 1 February 2000 in Gothenburg, at the age of 91. Scientific work In 1941, Holmberg performed arguably the first N-body simulation on the dynamics of interacting galaxies. In order to simulate the effect, he constructed an array of 37 lightbulbs. Using photocells, he was able to measure the simulated force of gravity - because both gravity and light would follow an inverse square law. He concluded that, over time, the 'galaxies' would move closer toward each other. He also concluded in a later experiment that elliptical galaxies are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multibody System
Multibody system is the study of the dynamics (physics), dynamic behavior of interconnected rigid body, rigid or flexible body, flexible bodies, each of which may undergo large Translation (physics), translational and rotational displacements. Introduction The systematic treatment of the dynamic behavior of interconnected bodies has led to a large number of important multibody formalisms in the field of mechanics. The simplest bodies or elements of a multibody system were treated by Isaac Newton, Newton (free particle) and Leonhard Euler, Euler (rigid body). Euler introduced reaction forces between bodies. Later, a series of formalisms were derived, only to mention Joseph Louis Lagrange, Lagrange’s formalisms based on minimal coordinates and a second formulation that introduces constraints. Basically, the motion of bodies is described by their kinematic behavior. The Analytical dynamics, dynamic behavior results from the equilibrium of applied forces and the rate of change of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics
Smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) is a computational method used for simulating the mechanics of continuum media, such as solid mechanics and fluid flows. It was developed by Gingold and Monaghan and Lucy in 1977, initially for astrophysical problems. It has been used in many fields of research, including astrophysics, ballistics, volcanology, and oceanography. It is a meshfree Lagrangian method (where the co-ordinates move with the fluid), and the resolution of the method can easily be adjusted with respect to variables such as density. Method Advantages * By construction, SPH is a meshfree method, which makes it ideally suited to simulate problems dominated by complex boundary dynamics, like free surface flows, or large boundary displacement. * The lack of a mesh significantly simplifies the model implementation and its parallelization, even for many-core architectures. * SPH can be easily extended to a wide variety of fields, and hybridized with some other mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structure Formation
In physical cosmology, structure formation describes the creation of galaxies, galaxy clusters, and larger structures starting from small fluctuations in mass density resulting from processes that created matter. The universe, as is now known from observations of the cosmic microwave background radiation, began in a hot, dense, nearly uniform state approximately 13.8 billion years ago. However, looking at the night sky today, structures on all scales can be seen, from stars and planets to galaxies. On even larger scales, galaxy clusters and sheet-like structures of galaxies are separated by enormous voids containing few galaxies. Structure formation models gravitational instability of small ripples in mass density to predict these shapes, confirming the consistency of the physical model. The modern Lambda-CDM model is successful at predicting the observed large-scale distribution of galaxies, clusters and voids; but on the scale of individual galaxies there are many complicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Few-body Systems
In physics, a few-body system consists of a small number of well-defined structures or point particles. It is usually in-between the two-body and the many-body systems with large ''N''. Quantum mechanics In quantum mechanics, examples of few-body systems include light nuclear systems (that is, few-nucleon bound and scattering states), small molecules, light atoms (such as helium in an external electric field), atomic collisions, and quantum dots. A fundamental difficulty in describing few-body systems is that the Schrödinger equation and the classical equations of motion are not analytically solvable for more than two mutually interacting particles even when the underlying forces are precisely known. This is known as the few-body problem. For some three-body systems an exact solution can be obtained iteratively through the Faddeev equations. It can be shown that under certain conditions Faddeev equations should lead to the Efimov effect. Most three-body systems are amenable to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Calculation Institute (University Of Heidelberg)
The Astronomical Calculation Institute (; ARI) is a research institute in Heidelberg, Germany, with origins dating back from the 1700s. Beginning in 2005, the ARI became part of the Center of Astronomy (University of Heidelberg), Center for Astronomy at Heidelberg University (', ). Previously, the institute directly belonged to the state of Baden-Württemberg. Description The ARI has a rich history. It was founded in 1700 in Dahlem (Berlin), Berlin-Dahlem by Gottfried Kirch. It had its origin in a patent application by Frederick I of Prussia, who introduced a monopoly on publishing star catalogs in Prussia. In 1945 the Institute was moved by the Americans nearer to the United States Army Garrison Heidelberg. On January 1, 2005 the combined Center for Astronomy institute formed by combining ARI, with the Institute of Theoretical Astrophysics (University of Heidelberg), Institute of Theoretical Astrophysics (', ITA) and the Landessternwarte Heidelberg-Königstuhl ("Heidelberg- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline, James Keeler, said, astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the heavenly bodies, rather than their positions or motions in space—''what'' they are, rather than ''where'' they are", which is studied in celestial mechanics. Among the subjects studied are the Sun ( solar physics), other stars, galaxies, extrasolar planets, the interstellar medium, and the cosmic microwave background. Emissions from these objects are examined across all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, and the properties examined include luminosity, density, temperature, and chemical composition. Because astrophysics is a very broad subject, ''astrophysicists'' apply concepts and methods from many disciplines of physics, including classical mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, thermodynamics, quantum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebastian Von Hoerner
Sebastian Rudolf Karl von Hoerner (15 April 1919 – 7 January 2003) was a German astrophysicist and radio astronomer. He was born in Görlitz, Lower Silesia. During WW II, Von Hoerner served in the German Army on the Eastern Front. A bullet struck a pair of binoculars he was wearing on a strap around his neck, ricocheted up and blinded him in one eye. He was sent to Germany to recover and was there when the Front collapsed. After the end of World War II he studied physics at University of Göttingen. He obtained his doctorate at the same university in 1951 as Carl Friedrich von Weizsäcker. Together they conducted simulations that studied the formation of stars and globular clusters. He continued this work at Astronomical Calculation Institute (University of Heidelberg) with Walter Fricke. He obtained his habilitation in 1959 at the University of Heidelberg. In 1962 he moved to National Radio Astronomy Observatory ( Green Bank, West Virginia), where he collaborated, inter al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lund Observatory
Lund Observatory was the official English name for the astronomy department at Lund University, and is currently used as a network of researchers within astronomy or other space related research projects, administered by the Department of Physics. Between 1867-2001 "Lund Observatory" was also the name of the Observatory building, which is now referred to as the "Lund Old Observatory". Prior to 2023, Lund Observatory was part of the Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics at Lund University until 2023, when that department was dissolved and its staff mostly transferred to the Department of Physics. It is located in Lund, Sweden. History The institution was founded in 1749, but was preceded by an observatory built by astronomy professor Anders Spole (the grandfather of Anders Celsius) in 1672, which was destroyed at the Battle of Lund in 1676. The now old observatory from 1867 is located in a cultural-heritage protected observatory park just outside the medieval city boun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |