|
Mutesa II Of Buganda
Sir Edward Frederick William David Walugembe Mutebi Luwangula Mutesa II (19 November 1924 – 21 November 1969) was a Ugandan royal and statesman who served as the first president of Uganda from 1962 to 1966, when he was overthrown by Milton Obote. Mutesa was also the Kabaka of Buganda, Kabaka (king) of the Non-sovereign monarchy, traditional kingdom of Buganda in Uganda from 22 November 1939 until his death in 1969. He was often referred as King Freddie by the foreign press, a name rarely used in Uganda. An ardent defender of Buganda's interests, especially its traditional autonomy, he often threatened to make the kingdom independent both before and after Uganda's independence to preserve it. These firm convictions also later led to conflicts with his erstwhile political ally Milton Obote, who would eventually overthrow him. Mutesa was crowned Kabaka on his 18th birthday in 1942, three years after the death of his father Daudi Cwa II, Daudi Cwa II of Buganda during Uganda Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabaka Of Buganda
Kabaka is the title of the monarch, king of the Buganda, Kingdom of Buganda.Stanley, H.M., 1899, Through the Dark Continent, London: G. Newnes, According to the traditions of the Baganda, they are ruled by two kings, one spiritual and the other secular. The spiritual, or supernatural, king is represented by the Royal Drums, regalia called ''Mujaguzo''. As they always exist, Buganda will always have a king. ''Mujaguzo'', like any other king, has his own palace, officials, servants and palace guards. The material, human prince has to perform special cultural rites on the Royal Drums before he can be declared king of Buganda. Upon the birth of a royal prince or princess, the Royal Drums are sounded by drummers specially selected from a specified clan as a means of informing the subjects of the kingdom of the birth of a new member of the royal family. The same Royal Drums are sounded upon the death of a reigning king to officially announce the death of the material king. According ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
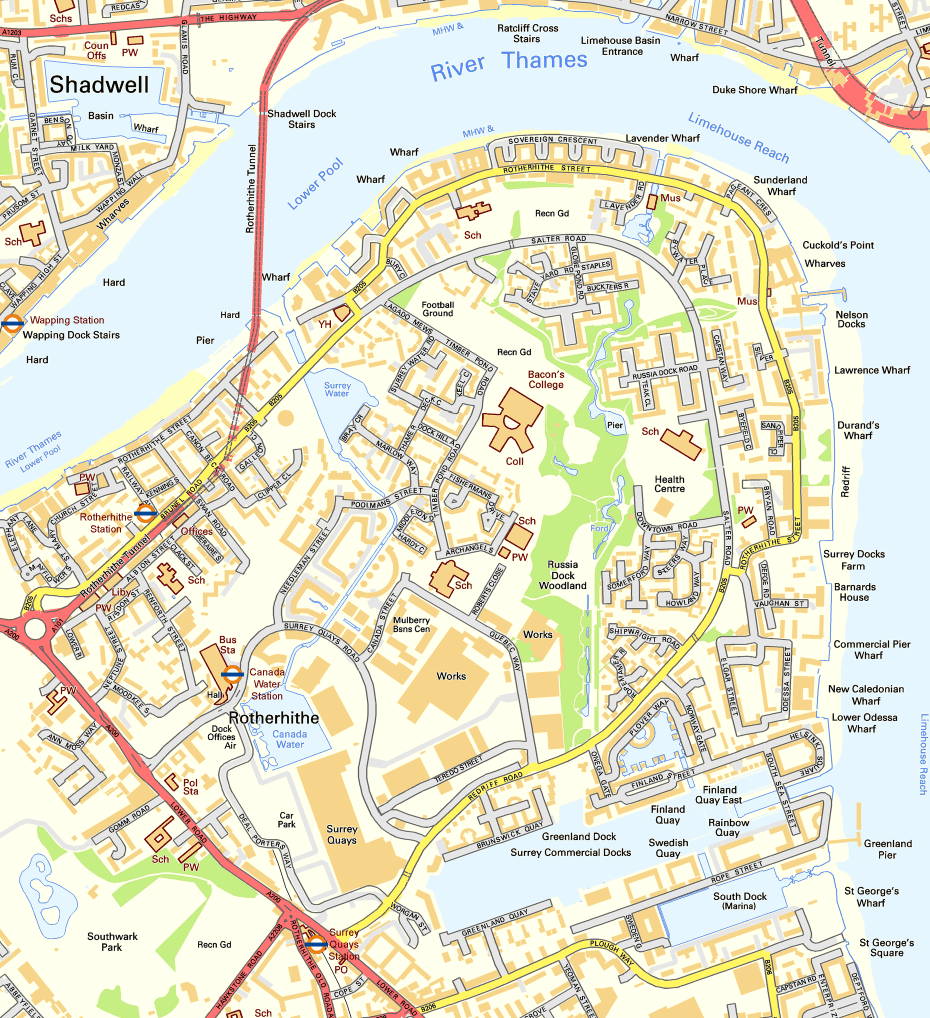
Rotherhithe
Rotherhithe ( ) is a district of South London, England, and part of the London Borough of Southwark. It is on a peninsula on the south bank of the Thames, facing Wapping, Shadwell and Limehouse on the north bank, with the Isle of Dogs to the east. It borders Bermondsey to the west and Deptford to the south-east. The district is a part of the London Docklands, Docklands area. Rotherhithe has a long history as a port, with Elizabethan era, Elizabethan shipyards and working docks until the 1970s. In the 1980s, the area along the river was redeveloped as housing through a mix of warehouse conversions and new-build developments. The Jubilee line was extended to the area in 1999, giving fast connections to the West End of London, West End and to Canary Wharf; the East London Line, East London London Underground, underground line was converted to part of the London Overground network in 2010, which provides easy access to the City of London. As a result, Rotherhithe is now a gentrifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabaka Yekka
Kabaka Yekka, commonly abbreviated as KY, was a monarchist political movement and party in Uganda. ''Kabaka Yekka'' means 'king only' in the Ganda language, Kabaka being the title of the King in the kingdom of Buganda. History Formation In 1960, Milton Obote helped to establish a political party in Uganda, known as the Uganda People's Congress (UPC). The UPC aimed to erode the power and influence of the "Mengo Establishment", a group of traditionalist Baganda that led the sub-national kingdom of Buganda. The Mengo Establishment was plagued by rivalries and infighting, but most of its members, as Protestant Christians, were united by their dislike of the Democratic Party (DP), which was dominated by Catholics. The DP won a majority of the seats in the National Assembly in Uganda's first free national elections in 1961, and formed a government. The UPC and the traditionalist Baganda both disliked the Catholic orientation of the DP, but were diametrically opposed to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buganda Agreement (1955)
The Buganda Agreement (1955) was made on 18 October 1955 between Andrew Cohen, the governor of the Uganda Protectorate, and Mutesa II, Kabaka of Buganda. The agreement facilitated Mutesa II's return as a constitutional monarch of Buganda, ending the Kabaka crisis that began when the Kabaka was exiled to England by Cohen in 1953. It amended the earlier Buganda Agreement (1900). The final text reflected the agreed outcomes of the Namirembe Conference. Background Between 1953 and 1955 there was major unrest and discontent in Uganda, part of the British-administered Uganda Protectorate, following a speech in which the British Secretary of State for the Colonies made a "passing reference" to the possibility of East African federation. The incident prompted widespread calls for Bugandan independence as the only protection against British overreach. In order to force a resolution to the deepening political crisis, the Governor of Uganda, Sir Andrew Cohen, invoked the Uganda Agree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Cohen (colonial Administrator)
Sir Andrew Benjamin Cohen (7 October 1909 – 17 June 1968) was Governor of Uganda from 1952 to 1957. Early life and education Cohen was from a distinguished Anglo-Jewish family. He was a descendant of Levy Barent Cohen. He was educated at Malvern College and Trinity College, Cambridge, receiving a degree in Classics. He was a Cambridge Apostle. Gold Coast In 1947, Cohen was appointed Assistant Under-Secretary for the Colonial Office's Africa division. This same year, he issued the Cohen Report which recommended the gradual devolution of power to Africans. However, only the Gold Coast was deemed to be capable of self-government "within a generation". In 1948, a British inquiry was launched by the Labour government into the causes of a series of riots in the Gold Coast. Colonial Secretary Arthur Creech Jones and Cohen sent Aiken Watson, a support of the Fabian Society who had previously stood as a Labour candidate in the 1935 election, to tour the colony and que ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daudi Cwa II
Daudi Cwa II was the 34th Kabaka of the Kingdom of Buganda who ruled from 1897, when he was an infant, until his death in 1939. Life He was born on 8 August 1896, at Mengo Palace. He was the fifth son of Kabaka Danieri Basammula-Ekkere Mwanga II Mukasa, Kabaka of Buganda, between 1884 and 1888 and between 1889 and 1897. His mother was Abakyala Evalini Kulabako, of the Ngabi Clan, the fourth of his father's sixteen wives. He ascended to the throne in August 1897 following the deposition of his father by British Forces. At the time of his coronation, he was only one year old. He maintained his capital at Mengo Hill. He was educated at Kings College Budo, which was founded in 1906 alongside Daudi, by the British Commissioner and commander in chief of the then Uganda protectorate, George Wilson. On 8 August 1914, he received an honorary commission as a lieutenant in the British Army, and was appointed an honorary captain on 22 September 1917. He was appointed an honorary Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The southern part includes a substantial portion of Lake Victoria, shared with Kenya and Tanzania. Uganda is in the African Great Lakes region, lies within the Nile basin, and has a varied equatorial climate. , it has a population of 49.3 million, of whom 8.5 million live in the capital and largest city, Kampala. Uganda is named after the Buganda, Buganda kingdom, which encompasses a large portion of the south, including Kampala, and whose language Luganda is widely spoken; the official language is English. The region was populated by various ethnic groups, before Bantu and Nilotic groups arrived around 3,000 years ago. These groups established influential kingdoms such as the Empire of Kitara. The arrival of Arab trade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buganda
Buganda is a Bantu peoples, Bantu kingdom within Uganda. The kingdom of the Baganda, Baganda people, Buganda is the largest of the List of current non-sovereign African monarchs, traditional kingdoms in present-day East Africa, consisting of Uganda's Districts of Uganda, Central Region, including the Ugandan capital Kampala. The 14 million ''Baganda'' (singular ''Muganda''; often referred to simply by the root word and adjective, Ganda) make up the largest Ugandan region, representing approximately 16% of Demographics of Uganda, Uganda's population. History of Buganda, Buganda's history includes unification during the 13th century by the first king, Kato Kintu, the founder of Buganda's Kintu dynasty, Buganda grew to become one of the largest and most powerful states in East Africa during the 18th and the 19th centuries. During the Scramble for Africa, and following unsuccessful attempts to retain its independence against British Empire, British imperialism, Buganda became the ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-sovereign Monarchy
A non-sovereign monarchy, subnational monarchy or constituent monarchy is one in which the head of the Monarchy, monarchical polity (whether a geographic territory or an ethnic group), and the polity itself, are subject to a temporal authority higher than their own. The constituent states of the German Empire or the princely states of the British Indian Empire, Indian Empire during British rule provide historical examples; while the List of Zulu kings, Zulu king, whose power derives from the Constitution of South Africa, is a contemporary one. Structure and forms This situation can exist in a formal capacity, such as in the United Arab Emirates (in which seven historically independent emirates now serve as constituent states of a federation, the president of which is chosen from among the emirs), or in a more informal one, in which theoretically independent territories are in feudal suzerainty to stronger neighbors or foreign powers (the position of the princely states of Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Uganda
The president of the Republic of Uganda is the head of state and the head of government of Uganda. The President (government title), president leads the Executive (government), executive branch of the government of Uganda and is the commander-in-chief of the Uganda People's Defence Force. Background The office of the president of Uganda was formed on 9th October 1963 to replace the queen of Uganda (which was last held by Elizabeth II) as head of state. It was entirely a ceremonial role i.e without executive powers during the time of the first holder Mutesa II of Bugandauntil the end of the Mengo Crisis in 1967 when Milton Obote took over ending the alliance between the Uganda People’s Congress and the Kabaka Yekka parties combining the roles of prime minister and president and therefore creating the first president of Uganda with executive powers. The office has been held by 9 people, 8 of whom (besides Edward Muteesa) came into power through military coups and civil war. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Monument Of Sir Edward Mutesa II
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is '' a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, '' a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest known ancestor of A is ''aleph''—the first letter of the Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |