|
Muslim Conquest Of Northern Persia
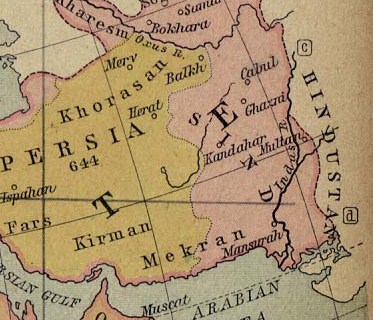
The Muslim Conquest of Northern Iranshahr at the time included Tabaristan, the greater portion of historic Adurbadagan, Armin (Modern day Armenia), Arān (Caucasian Albania), and Wiruzān (In modern day known as eastern Georgia). Each of these territories fell to Muslims at different times throughout the conquest period. The Conquest of Adurbadagan In 651, the Arabs invaded Adurbadagan, which was the domain of the Ispahbudhan brothers Isfandyadh and Bahram. Isfandyadh made a stand against the Arabs, where a battle was fought. He was, however, defeated and captured by the Arabs. While Isfandyadh was in captivity, he told the Arab general Bukayr ibn Abdallah, that if he sought to conquer Adurbadagan easily and peacefully, he should make peace with him. According to Bal'ami, Isfandyadh is known to have said that: "If you ere tokill me all of Adurbadagan illrise in avenging my blood, and will wage war against you." The Arab general accepted Isfandyadh's advice and made peac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign over ancient Iran was second only to the directly preceding Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Founded by Ardashir I, whose rise coincided with the decline of Arsacid influence in the face of both internal and external strife, the House of Sasan was highly determined to restore the legacy of the Achaemenid Empire by expanding and consolidating the Iranian nation's dominions. Most notably, after defeating Artabanus IV of Parthia during the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224, it began competing far more zealously with the neighbouring Roman Empire than the Arsacids had, thus sparking a new phase of the Roman–Iranian Wars. This effort by Ardashir's dynasty ultimately re-established Iran as a major power of late an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of the entire Muslim world (''ummah''). Historically, the caliphates were polities based on Islam which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. During the medieval period, three major caliphates succeeded each other: the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750), and the Abbasid Caliphate (750–1517). In the fourth major caliphate, the Ottoman Caliphate, the rulers of the Ottoman Empire claimed caliphal authority from 1517 until the Ottoman caliphate was Abolition of the Caliphate, formally abolished as part of the Atatürk's reforms, 1924 secularisation of Turkey. An attempt to preserve the title was tried, with the Sharifian Caliphate, but this caliphate fell quickly after its conquest by the Sultanate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khazim Ibn Khuzayma Al-Tamimi
Khazim ibn Khuzayma al-Tamimi () () was a Greater Khorasan, Khurasani Arab military leader. One of the early supporters of the Abbasid ''da'wa'' in Khurasan, he played a major role in the Abbasid Revolution against the Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyads, and then spent the next two decades suppressing revolts across the Caliphate. As one of the main figures of the ''Khurasaniyya'', the main power base of the Abbasid regime, he cemented his family in a position of power and influence: his sons would play an important role in the affairs of the Caliphate over the next decades. Biography His family hailed from the Nahshal branch of the Banu Tamim, which had settled at Marw al-Rudh in Greater Khorasan, Khurasan, probably during the early days of the Muslim conquest of the region. The family had apparently become Persianized to some extent; Khazim is recorded as preferring to use Persian language, Persian to address his followers, and his sister had married an Iranian.Kennedy (2001), p. 100 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Al-Khaṣīb Marzuq
Abu al-Khaṣīb Marzuq was an Abbasid general and administrator during the reign of Abu Ja'far al-Mansur. A ''mawla'' of Mansur in his early life, Abu al-Khasib rose to the position of ''Hajib'' ( chamberlain) in 755. In 760, he was sent by Mansur to conquer Tabaristan from its Dabuyid ruler, Khurshid. After the conquest of Tabaristan, he was appointed as its first Abbasid governor, a position he retained until about 763. Biography Abu al-Khasib was from Sind. According to Ibn Isfandiyar, he had been a client (mawali) of Muthanna ibn al-Hajjaj ibn Qutayba ibn Muslim. He is first mentioned in 755, when he was sent by Abbasid Caliph Mansur as his chamberlain to Abu Muslim Khurasani to calculate what he had acquired by defeating Abdullah ibn Ali, the Caliph's uncle. When Abu Muslim refused to hand over the wealth, Abu al-Khasib returned to Mansur and told him about Abu Muslim's intention. This sowed the seeds of distrust between the caliph and Abu Muslim, ultimately leading to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mansur
Abū Jaʿfar ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad al-Manṣūr (; ; 714 – 6 October 775) usually known simply as by his laqab al-Manṣūr () was the second Abbasid caliph, reigning from 754 to 775 succeeding his brother al-Saffah (). He is known for founding the 'Round City' of Madinat al-Salam, which was to become the core of imperial Baghdad. Modern historians regard al-Mansur as the real founder of the Abbasid Caliphate, one of the largest polities in world history, for his role in stabilizing and institutionalizing the dynasty.''The Cambridge History of Islam, volume 1: The Formation of the Islamic World'', ed. Chase F Robinson, March 2011 Background and early life According to al-Suyuti's ''History of the Caliphs'', al-Mansur lived 95 AH – 158 AH (714 CE – 6 October 775 CE). Al-Mansur was born at the home of the Abbasid family in Humeima (modern-day Jordan) after their emigration from the Hejaz in 714 (95 AH). His mother was Sallamah, a slave woman. Al-Mansur was a brot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 Common Era, CE), from whom the Abbasid dynasty, dynasty takes its name. After overthrowing the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 anno Hegirae, AH), they ruled as caliphs based in modern-day Iraq, with Baghdad being their capital for most of their history. The Abbasid Revolution had its origins and first successes in the easterly region of Greater Khorasan, Khurasan, far from the Levantine center of Umayyad influence. The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad as the new capital. Baghdad became the center of Science in the medieval Islamic world, science, Islamic culture, culture, Abbasid art, arts, and List of invent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate or Umayyad Empire (, ; ) was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member of the clan. The family established dynastic, hereditary rule with Mu'awiya I, the long-time governor of Bilad al-Sham, Greater Syria, who became caliph after the end of the First Fitna in 661. After Mu'awiya's death in 680, conflicts over the succession resulted in the Second Fitna, and power eventually fell to Marwan I, from another branch of the clan. Syria remained the Umayyads' main power base thereafter, with Damascus as their capital. The Umayyads continued the Early Muslim conquests, Muslim conquests, conquering Ifriqiya, Transoxiana, Sind (caliphal province), Sind, the Maghreb and Hispania (al-Andalus). At its greatest extent (661–750), the Umayyad Caliphate covered , making it one of the largest empires in history in terms of ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu'awiya I
Mu'awiya I (–April 680) was the founder and first caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 661 until his death. He became caliph less than thirty years after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and immediately after the four Rashidun Caliphate, Rashidun ('rightly-guided') caliphs. Unlike his predecessors, who had been close, early companions of Muhammad, Mu'awiya was a relatively late follower of Muhammad. Mu'awiya and his father Abu Sufyan had opposed Muhammad, their distant Qurayshite kinsman and later Mu'awiya's brother-in-law, until Muhammad conquest of Mecca, captured Mecca in 630. Afterward, Mu'awiya became one of Muhammad's katib, scribes. He was appointed by Caliph Abu Bakr () as a deputy commander in the Muslim conquest of the Levant, conquest of Syria. He moved up the ranks through Umar's caliphate () until becoming governor of Bilad al-Sham, Syria during the reign of his Umayyad dynasty#Empowerment by Caliph Uthman, Umayyad kinsman, Caliph Uthman (). He a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurgan
Gorgan (; ) is a city in the Central District of Gorgan County, Golestan province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. It lies approximately to the northeast of the national capital Tehran, and some away from the Caspian Sea. History There are several archaeological sites near Gorgan, including Tureng Tepe and Shah Tepe, in which remains dating from the Neolithic and Chalcolithic eras. Some other important Neolithic sites in the area are Yarim Tepe, and Sange Chaxmaq. The nearby Shahroud Plain has many such sites. More than 50 are on the Gorgan Plain. According to the Greek historian Arrian, Zadracarta was the largest city of Hyrcania and the site of the "royal palace". The term means "the yellow city", and it was given to it from the great number of oranges, lemons, and other fruit trees which grew in the outskirts of that city. Hyrcania became part of the Achaemenid Empire during the reign of Cyrus the Great (559–530 BC), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
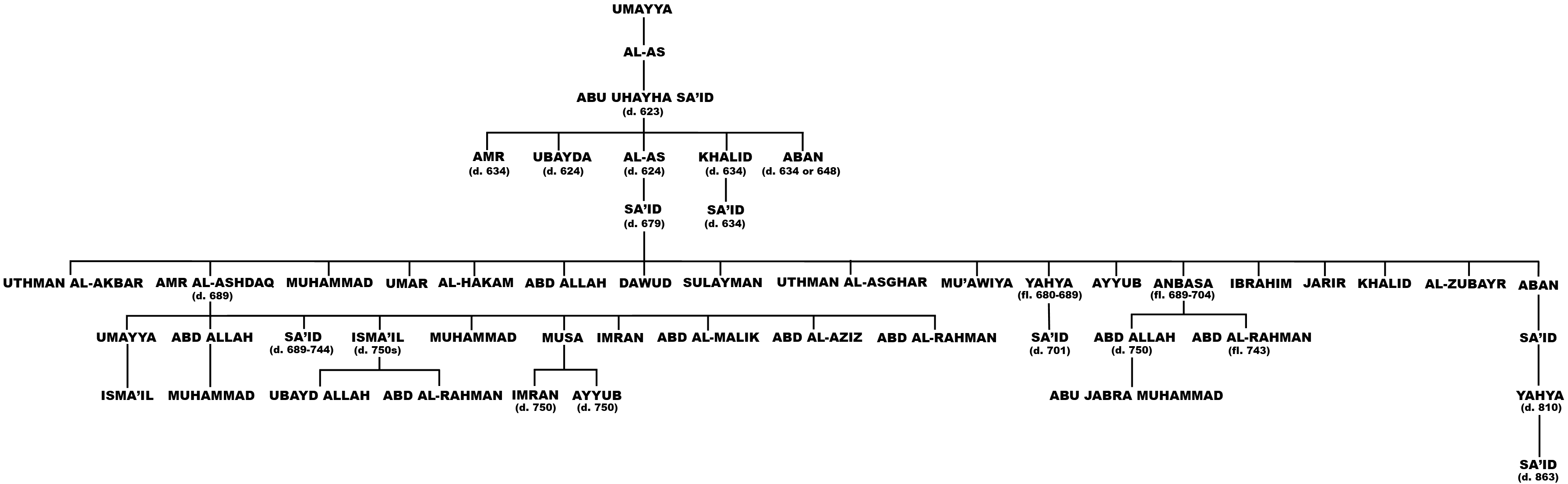
Sa'id Ibn Al-As
Sa'id ibn al-As ibn Abi Uhayha (; died 678/679) was the Arab Muslim governor of Kufa under Caliph Uthman () and governor of Medina under Caliph Mu'awiya I (). Like the aforementioned caliphs, Sa'id belonged to the Umayyad clan of the Quraysh. During his governorship of Kufa, Sa'id led military campaigns in Azerbaijan and near the Caspian Sea. However, he had to contend with dissent from some of the Kufan elite, led by Malik ibn al-Harith. The dissent was largely driven by Sa'id and Uthman's policy of consolidating ownership of the productive Sawad lands of Iraq into the hands of the Quraysh and Muslim veterans from Medina. Sa'id had the dissidents exiled, but during a visit to Medina, rebels in Kufa led by Yazid ibn Qays al-Arhabi took control of the city. After his ouster from Kufa, Sa'id aided in the defense of Uthman's house from attack by Egyptian rebels, but Uthman was killed nonetheless and Sa'id was wounded. He declined to fight alongside the Banu Umayya and A'isha agains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uthman Ibn Affan
Uthman ibn Affan (17 June 656) was the third caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruling from 644 until Assassination of Uthman, his assassination in 656. Uthman, a second cousin, son-in-law, and notable Companions of the Prophet, companion of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad, played a major role in History of Islam, early Islamic history. During his reign as caliph, he was known for ordering the official compilation of the standardized version of the Quran, known as Uthman's Quran, that is still being used today. Before his predecessor, Caliph Umar (), died in office, he appointed a committee of trustees to elect a successor. Uthman, who was then aged 68–71 years, was elected to succeed him and became the oldest person to hold such a high position. During his premiership, the Caliphate expanded further into Persia in 650 and reached as far as the provinces of Greater Khorasan, Khorasan in 651. Uthman instituted Centralized government, centralized reforms in order to create a mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emirate Of Tbilisi
The Emirate of Tbilisi ( ka, თბილისის საამირო ', ') was a Islam, Muslim emirate in Transcaucasia. The Emirs of Tbilisi ruled over the parts of today's eastern Georgia (country), Georgia from their base in the city of Tbilisi, from 736 to 1080 (nominally to 1122). Established by the Arabs during their rule of Georgian lands, the emirate was an important outpost of the Muslim rule in the Caucasus until Siege of Tbilisi (1122), recaptured by the Georgians under King David IV of Georgia, David IV in 1122. History The Arabs first appeared in Georgia, namely in Kartli (Principality of Iberia, Iberia) in 645. It was not, however, until 735 that they succeeded in establishing firm control over a large portion of the country. In that year, Marwan II Marwan ibn Muhammad's invasion of Georgia, took hold of Tbilisi and much of the neighbouring lands and installed there an Arab emir, who was to be confirmed by the Caliph or, occasionally, by the ''ostikan'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |