|
Musical Analysis
Musical analysis is the study of musical structure in either compositions or performances. According to music theorist Ian Bent, music analysis "is the means of answering directly the question 'How does it work?'". The method employed to answer this question, and indeed exactly what is meant by the question, differs from analyst to analyst, and according to the purpose of the analysis. According to Bent, "its emergence as an approach and method can be traced back to the 1750s. However it existed as a scholarly tool, albeit an auxiliary one, from the Middle Ages onwards." The principle of analysis has been variously criticized, especially by composers, such as Edgard Varèse's claim that, "to explain by means of nalysisis to decompose, to mutilate the spirit of a work". Analyses Some analysts, such as Donald Tovey (whose '' Essays in Musical Analysis'' are among the most accessible musical analyses) have presented their analyses in prose. Others, such as Hans Keller (who d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Analysis Shape
Musical is the adjective of music. Musical may also refer to: * Musical theatre, a performance art that combines songs, spoken dialogue, acting and dance * Musical film and television, a genre of film and television that incorporates into the narrative songs sung by the characters * MusicAL, an Albanian television channel * Musical isomorphism, the canonical isomorphism between the tangent and cotangent bundles See also * Lists of musicals * Music (other) * Musica (other) * Musicality, the ability to perceive music or to create music * {{Music disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolph Réti
Rudolph Reti, also Réti (; November 27, 1885 – February 7, 1957), was a musical analyst, composer and pianist. He was the older brother of the chess master Richard Réti, but unlike his brother, Reti did not write his surname with an acute accent on the 'e'. Biography Reti was born in Užice in the Kingdom of Serbia and studied music theory, musicology and piano in Vienna. Among his teachers was the pianist Eduard Steuermann, an eminent champion of Schoenberg and a supporter of modern music. Reti was in contact with Schoenberg at the time of that composer's earliest atonal works, and in 1911 gave the first performance of his Drei Klavierstücke Op.11. Reti's compositions have not remained in the repertoire, but he was an active composer and received a number of high-profile performances. At the end of the first International Festival of Modern Music in Salzburg, in 1922, his 'Six Songs' were performed alongside Schoenberg's Second Quartet; three years later, at the 3rd I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Jacques Nattiez
Jean-Jacques Nattiez (; born December 30, 1945) is a French musicologist and ethnomusicologist active in Canada, who is seminal figure in music semiology. Professor of musicology at the Université de Montréal since 1972,. he studied semiology with Georges Mounin and Jean Molino and music semiology (doctoral) with Nicolas Ruwet. Life and career Jean-Jacques Nattiez was born on December 30, 1945, in Amiens, France. He is a noted specialist on the writings of the composer and conductor Pierre Boulez. In 1990, he was made a Member of the Order of Canada. In 2001, he was made a Knight of the National Order of Quebec. Awards *1988, Dent Medal of the Royal Musical Association *1989, Prix André-Laurendeau pour les sciences humaines from the Association canadienne française pour l'avancement des sciences *1990, Molson Prize from the Canada Council *1994, prix Léon-Gérin pour les sciences sociales du Gouvernement du Québec *1996, Fumio Koizumi Prize for Ethnomusicol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discretization
In applied mathematics, discretization is the process of transferring continuous functions, models, variables, and equations into discrete counterparts. This process is usually carried out as a first step toward making them suitable for numerical evaluation and implementation on digital computers. Dichotomization is the special case of discretization in which the number of discrete classes is 2, which can approximate a continuous variable as a binary variable (creating a dichotomy for modeling purposes, as in binary classification). Discretization is also related to discrete mathematics, and is an important component of granular computing. In this context, ''discretization'' may also refer to modification of variable or category ''granularity'', as when multiple discrete variables are aggregated or multiple discrete categories fused. Whenever continuous data is discretized, there is always some amount of discretization error. The goal is to reduce the amount to a level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Note
Note, notes, or NOTE may refer to: Music and entertainment * Musical note, a pitched sound (or a symbol for a sound) in music * ''Notes'' (album), a 1987 album by Paul Bley and Paul Motian * ''Notes'', a common (yet unofficial) shortened version of the title of the American TV situation comedy, ''Notes from the Underbelly'' * ''Notes'' (film), a short by John McPhail * ''Notes'' (journal), the quarterly journal of the Music Library Association Finance * Banknote, a form of cash currency, also known as ''bill'' in the United States and Canada * Promissory note, a contract binding one party to pay money to a second party * Note, a security (finance), a type of bond Technology and science * IBM Notes, (formerly Lotus Notes), a client-server, collaborative application owned by IBM Software Group * Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES), a type of minimally invasive surgery * Notes (Apple), a note-taking application bundled with macOS and iOS * Notes, another n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Music
Absolute music (sometimes abstract music) is music that is not explicitly "about" anything; in contrast to program music, it is non- representational.M. C. Horowitz (ed.), ''New Dictionary of the History of Ideas'', , Vol. 1, p. 5 The idea of absolute music developed at the end of the 18th century in the writings of authors of early German Romanticism, such as Wilhelm Heinrich Wackenroder, Ludwig Tieck and E. T. A. Hoffmann but the term was not coined until 1846 where it was first used by Richard Wagner in a programme to Beethoven's Ninth Symphony. The aesthetic ideas underlying absolute music derive from debates over the relative value of what was known in the early years of aesthetic theory as the fine arts. Kant, in his ''Critique of Judgment'', dismissed music as "more a matter of enjoyment than culture" and "less worth in the judgement of reason than any other of the fine arts" because of its lack of conceptual content, thus treating as a deficit the very feature of music ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide, or obscure, clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are usually meant to create a likeness or an Analogy, analogy. Analysts group metaphors with other types of figurative language, such as antithesis, hyperbole, metonymy, and simile. According to Grammarly, "Figurative language examples include similes, metaphors, personification, hyperbole, allusions, and idioms." One of the most commonly cited examples of a metaphor in English literature comes from the "All the world's a stage" monologue from ''As You Like It'': All the world's a stage, And all the men and women merely players; They have their exits and their entrances And one man in his time plays many parts, His Acts being seven ages. At first, the infant... :—William Shakespeare, ''As You Like It'', 2/7 This quotation expresses a metaphor because the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
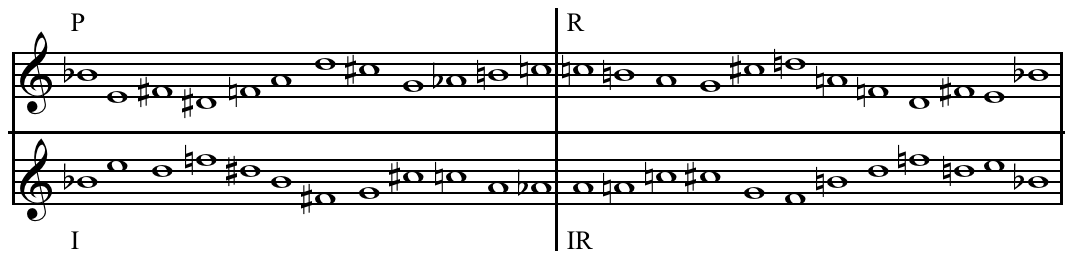
Tone-row
In music, a tone row or note row ( or '), also series or set, is a non-repetitive ordering of a set of pitch-classes, typically of the twelve notes in musical set theory of the chromatic scale, though both larger and smaller sets are sometimes found. History and usage Tone rows are the basis of Arnold Schoenberg's twelve-tone technique and most types of serial music. Tone rows were widely used in 20th-century contemporary music, like Dmitri Shostakovich's use of twelve-tone rows, "without dodecaphonic transformations." A tone row has been identified in the A minor prelude, BWV 889, from book II of J.S. Bach's '' The Well-Tempered Clavier'' (1742) and by the late eighteenth century it is found in works such as Mozart's C major String Quartet, K. 157 (1772), String Quartet in E-flat major, K. 428, String Quintet in G minor, K. 516 (1790), and the Symphony in G minor, K. 550 (1788). Beethoven also used the technique but, on the whole, "Mozart seems to have employed serial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Numeral Analysis
In music theory, Roman numeral analysis is a type of Harmony, harmonic analysis in which chord (music), chords are represented by Roman numerals, which encode the chord's Degree (music), degree and Function_(music), harmonic function within a given musical key. Specific notation conventions vary: some theorists use uppercase numerals (e.g. I, IV, V) to represent Major chord, major chords, and lowercase numerals (e.g. ii, iii, vi) to represent Minor chord, minor chords. Others use uppercase numerals for all chords regardless of their chord quality, quality.Roger Sessions (1951). ''Harmonic Practice''. New York: Harcourt, Brace. . p. 7. (As the II, III, and VI chords always are minor chords and the VII always diminished, a further distinguishment is thought unneeded, see table for Major Diatonic scale below) Roman numerals can be used to notate and analyze the harmonic progression of a composition independent of its specific Key (music), key. For example, the ubiquitous twelve-bar bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward T
Edward is an English male name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortunate; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”. History The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Saxon England, but the rule of the Norman and Plantagenet dynasties had effectively ended its use amongst the upper classes. The popularity of the name was revived when Henry III named his firstborn son, the future Edward I, as part of his efforts to promote a cult around Edward the Confessor, for whom Henry had a deep admiration. Variant forms The name has been adopted in the Iberian peninsula since the 15th century, due to Edward, King of Portugal, whose mother was English. The Spanish/Portuguese forms of the name are Eduardo and Duarte. Other variant forms include French Édouard, Italian Edoardo and Odoardo, German, Dutch, Czech and Romanian Eduard and Scandinavian Edvard. Short forms include Ed, Eddy, Eddie, Ted, Teddy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historically Informed Performance
Historically informed performance (also referred to as period performance, authentic performance, or HIP) is an approach to the performance of Western classical music, classical music which aims to be faithful to the approach, manner and style of the musical era in which a work was originally conceived. It is based on two key aspects: the application of the stylistic and technical aspects of performance, known as performance practice; and the use of #Early instruments, period instruments which may be reproductions of historical instruments that were in use at the time of the original composition, and which usually have different timbre and temperament (music), temperament from their modern equivalents. A further area of study, that of changing listener expectations, is increasingly under investigation. Given no Sound recording and reproduction, sound recordings exist of music before the late 19th century, historically informed performance is largely derived from Musicology, musico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Musicology
New musicology is a wide body of musicology since the 1980s with a focus upon the cultural study, aesthetics, criticism, and hermeneutics of music. It began in part a reaction against the traditional positivist musicology—focused on primary research—of the early 20th century and postwar era. Many of the procedures of new musicology are considered standard, although the name more often refers to the historical turn rather than to any single set of ideas or principles. Indeed, although it was notably influenced by feminism, gender studies, queer theory, postcolonial studies, and critical theory, new musicology has primarily been characterized by a wide-ranging eclecticism. Definitions and history New musicology seeks to question the research methods of traditional musicology by displacing positivism, working in partnership with outside disciplines, including the humanities and social sciences, and by questioning accepted musical knowledge. New musicologists seek ways to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |