|
Music Of Turkmenistan
The music of contemporary nomadic and rural Turkmen people is closely related other Central Asian folk forms and is descended from Arab and Persian forms of the Middle Ages. Important musical traditions in Turkmen music include traveling singers and shamans called '' bagshy'', who act as healers and magicians and sing either a cappella or accompanied by the dutar, a two-stringed lute. The Central Asian classical music tradition, mugam, is also present in Turkmenistan under the name mukamlar. Classical Turkmen folk music According to Soviet musicologist Viktor Belyayev, Turkmen classical folk music is directly descended from Arabic music as taught and performed in Khorezm, particularly in Bukhara, which was the musical center of the Islamic world in the 13th century. The Turkic tribes of Central Asia, including the predecessors of today's Turkmen, abandoned their own culture in the 9th century and shifted to Arab culture, including music, with their adoption of Islam.The Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pastoral tribes slowly decreased, reaching an estimated 30–40 million nomads in the world . Nomadic hunting and gathering—following seasonally available wild plants and game—is by far the oldest human subsistence method known. Pastoralists raise herds of domesticated livestock, driving or accompanying them in patterns that normally avoid depleting pastures beyond their ability to recover. Nomadism is also a lifestyle adapted to infertile regions such as steppe, tundra, or ice and sand, where mobility is the most efficient strategy for exploiting scarce resources. For example, many groups living in the tundra are reindeer herders and are semi-nomadic, following forage for their animals. Sometimes also described as "nomadic" are vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khorezm
Khwarazm (; ; , ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the east by the Kyzylkum Desert, on the south by the Karakum Desert, and on the west by the Ustyurt Plateau. It was the center of the Iranian Khwarezmian civilization, and a series of kingdoms such as the Afrighid dynasty and the Anushtegin dynasty, whose capitals were (among others) Kath, Gurganj (now Konye-Urgench) andfrom the 16th century onKhiva. Today Khwarazm belongs partly to Uzbekistan and partly to Turkmenistan. Names and etymology Names Khwarazm has been known also as ''Chorasmia'', ''Khaurism'', ''Khwarezm'', ''Khwarezmia'', ''Khwarizm'', ''Khwarazm'', ''Khorezm'', ''Khoresm'', ''Khorasam'', ''Kharazm'', ''Harezm'', ''Horezm'', and ''Chorezm''. In Avestan the name is '; in Old Persian 𐎢𐎺𐎠𐎼𐏀𐎷𐎡𐏁 or 𐎢𐎺𐎠𐎼𐏀𐎷𐎡𐎹 (/hUvārazmī ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilli Tuiduk
The dilli tuiduk is a Turkmen musical instrument in the clarinet-family that uses a single reed to produce the instrument's sound. It is used mainly in Turkmen folk music. The woodwind instrument is also transcribed '' dilli düdük'', '' dilli tuyduk '', ''dili tüidük'', ''dilli tüidük'', ''dili tuiduk'', and дилли туйдук. Construction The instrument has a body made from the stem of a bulrush, and a reed cut into the tube at the top (a split that forms a flexible edge that vibrates when blown). A variant was photographed (bülban) in 1869-1872, in which the bulrush body has been replaced by a carved wooden body. The split reed was retained as a tip, the same style of mouthpiece as on the ghoshmeh. Dilli-tuiduk come in two kinds. In one, the reed end of the instrument is closed and in the other it is open. A reed is cut in the upper part of the pipe and 3 or 4 finger holes are cut on the upper part, at intervals of some 5-6mm. Its range is a 6th or 7th, from ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghijak
The ''ghijak'' (also spelled ''ghidjak'', ''ghichak'', ''gidzhak'', ''gijak'', ''g'ijjak'', ', or ''ghijek'' (, or occasionally ; Chinese: 艾捷克 ''aijieke'' or 吉孜哈克 ''jizihake''; ), is a group of related spike fiddles, used by Afghans, Uzbeks, Uyghurs, Tajiks, Turkmens, Qaraqalpaks and in the Xinjiang province of western China. Despite the similarity of the name, it is more closely related to the Persian kamancheh than the ghaychak. History The instrument name appears in 10th-century manuscripts, which indicate that the bridge (''harrak'') was made of almond shells. The ghidjak as depicted in 15th-century Persian miniatures resembles the modern instrument in its construction. Xinjiang The ghijek as it is used in Xinjiang has four strings, either with a bowl soundbox (similar to the ''kamancheh''), or with a box soundbox often made from a tin can. One of Xinjiang's most prominent ''ghijek'' players is Akram Omar (艾克热木·吾买尔 / ئەكرەم ئۆمەر ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uzbeks
The Uzbeks () are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia, being among the largest Turkic ethnic groups in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to Kazakhs, Kazakh and Karakalpaks, Karakalpak minorities, and also form minority groups in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Russia, and China. Uzbek diaspora communities also exist in Uzbeks in Turkey, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, Uzbek Americans, United States, Ukraine, Uzbeks in Pakistan, Pakistan, and other countries. Etymology The origin of the word ''Uzbek'' is disputed. One view holds that it is eponymously named after Oghuz Khagan, also known as ''Oghuz Beg'', became the word ''Uzbeg'' or ''Uzbek''.A. H. Keane, A. Hingston Quiggin, A. C. Haddon, Man: Past and Present, p.312, Cambridge University Press, 2011, Google Books, quoted: "Who take their name from a mythical Uz-beg, Prince Uz (beg in Turki=a chief, or hereditary ruler)." Another theory states th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dastan
Dastan () is an ornate form of oral history, an epic, from Central Asia, Iran, Turkey and Azerbaijan. A dastan is generally centered on one individual who protects his tribe or his people from an outside invader or enemy, although only occasionally can this figure be traced back to a historical person. This main character sets an example of how one should act, and the dastan becomes a teaching tool — for example the Sufi master and Turkic poet Ahmed Yesevi said "Let the scholars hear my wisdom, treating my words like a dastan". Alongside the wisdom, each dastan is rich with cultural history of interest to scholars. During the Russian conquest of Central Asia, many new dastans were created to protest the Russian occupation. It is possible that they came into contact and influenced each other. According to Turkish historian Hasan Bülent Paksoy, the Bolsheviks tried to destroy these symbols of culture by only publishing them in insufficiently large quantities and in a distorted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Dede Korkut
The ''Book of Dede Korkut'' or ''Book of Korkut Ata'' (, ; ; ) is the most famous among the dastans or epic stories of the Oghuz Turks. The stories carry morals and values significant to the social lifestyle of the nomadic Turkic peoples and their pre-Islamic beliefs. The book's mythic narrative is part of the cultural heritage of the peoples of Oghuz origin, mainly of Azerbaijan, Turkey and Turkmenistan. Only two manuscripts of the text, one in the Vatican and one in Dresden, Germany, were known before a third manuscript was discovered in a private collection in Gonbad-e Kavus, Iran, in 2018. The epic tales of ''Dede Korkut'' are some of the best-known Turkic dastans from among a total of well over 1000 recorded epics among the Turkic and Mongolian language families. Origin and synopsis of the epic ''Dede Korkut'' is a heroic dastan, also known as the ''Oghuznama'' among the Oghuz, which starts in Central Asia, continues in Anatolia, and centers most of its action in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dastgāh
''Dastgāh'' (; , , ) is the standard musical system in Persian traditional music, Persian art music, standardised in the 19th century following the transition of Persian music from the Persian maqam, Maqam modal system. A consists of a collection of musical Melody, melodies, . In a song played in a given , a musician starts with an introductory , and then meanders through various different , evoking different Easy listening, moods. Many in a given are related to an equivalent Mode (music), musical mode in Western culture#Music, Western music. For example, most in Dastgāh-e Māhur correspond to the Ionian mode in the Major scale, whilst most in Dastgāh-e Šur, Dastgāh-e Shur correspond to the Phrygian mode. In spite of 50 or more Ancient literature, extant , 12 are most commonly played, with Dastgāh-e Šur and Dastgāh-e Māhur being referred to as the mothers of all . Summary Each consists of seven basic Musical note, notes, plus several variable notes used fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
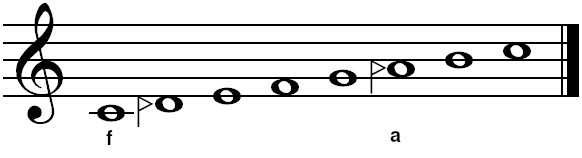
Augmented Second
In Western classical music, an augmented second is an interval created by widening a major second by a chromatic semitone, spanning three semitones and enharmonically equivalent to a minor third in 12-tone equal temperament.Benward & Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I'', p.54. . Specific example of an A2 not given but general example of major intervals described. For instance, the interval from C to D is a major second, two semitones wide, and the interval from C to D is an augmented second, spanning three semitones. Usage Augmented seconds occur in many scales, including the various modes of the harmonic minor and double harmonic scales. In harmonic minor, the augmented second occurs between the sixth and seventh scale degrees. For example, in the scale of A harmonic minor, the notes F and G form the interval of an augmented second. This distinguishing feature of harmonic minor scales occurs as a consequence of the seventh scale degree having been chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merv
Merv (, ', ; ), also known as the Merve Oasis, was a major Iranian peoples, Iranian city in Central Asia, on the historical Silk Road, near today's Mary, Turkmenistan. Human settlements on the site of Merv existed from the 3rd millennium BC until the 18th century AD. It changed hands repeatedly throughout history. Under the Achaemenid Empire, it was the center of the satrapy of Margiana. It was subsequently ruled by Hellenistic Period, Hellenistic Kings, Parthians, Sasanian Empire, Sasanians, Arabs, Ghaznavids, Seljuk Turks, Seljuqs, Khwarazmian dynasty, Khwarazmians and Timurids, among others. Merv was the capital city of several polity, polities throughout its history. In the beginning of the 9th century, Merv was the seat of the caliph al-Ma'mun and the capital of the entire Abbasid caliphate, Islamic caliphate. It served later as the seat of the Tahirid dynasty, Tahirid governors of Greater Khorasan, Khorasan. In the 11th–12th centuries, Merv was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
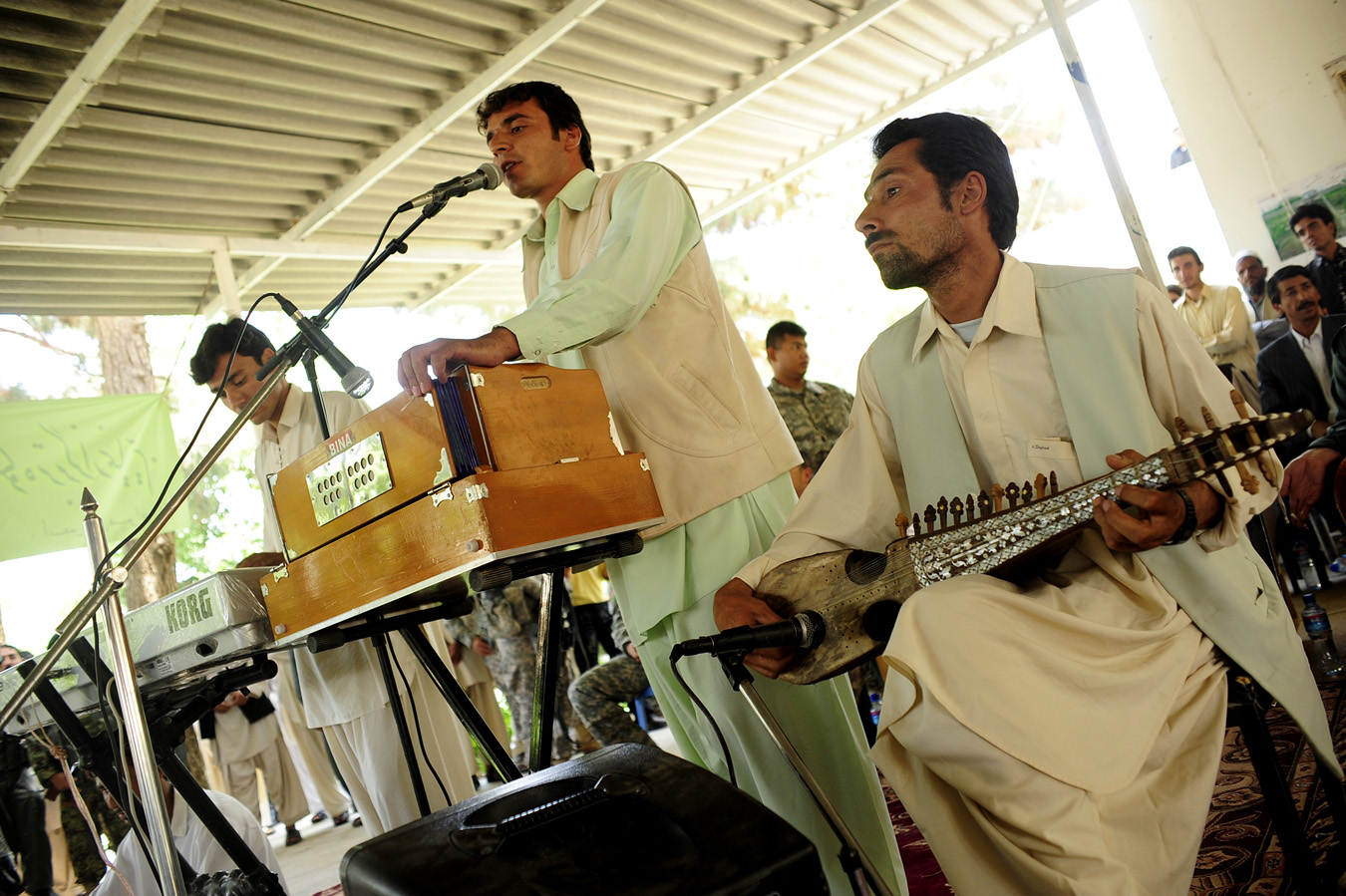
Music Of Afghanistan
The music of Afghanistan comprises many varieties of classical music, folk music, and modern popular music. Afghanistan has a rich musical heritage and features a mix of Persian melodies, Indian compositional principles, and sounds from ethnic groups such as the Pashtuns, Tajiks and Hazaras. Instruments used range from Indian tablas to long-necked lutes. Afghanistan's classical music is closely related to Hindustani classical music while sourcing much of its lyrics directly from classical Persian poetry such as Mawlana Balkhi (Rumi) and the Iranian tradition indigenous to central Asia. Lyrics throughout most of Afghanistan are typically in Dari (Persian) and Pashto. The multi-ethnic city of Kabul has long been the regional cultural capital, but outsiders have tended to focus on the city of Herat, which is home to traditions more closely related to Iranian music than in the rest of the country.Doubleday, pg. 4 Under the rule of the Taliban, both from 1996 to 2001 and again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |