|
Music In The Movement Against Apartheid
The apartheid regime in South Africa began in 1948 and lasted until 1994. It involved a system of institutionalized racial segregation and white supremacy, and placed all political power in the hands of a white minority. Opposition to apartheid manifested in a variety of ways, including boycotts, non-violent protests, and armed resistance. Music played a large role in the movement against apartheid within South Africa, as well as in international opposition to apartheid. The impacts of songs opposing apartheid included raising awareness, generating support for the movement against apartheid, building unity within this movement, and "presenting an alternative vision of culture in a future democratic South Africa." The lyrical content and tone of this music reflected the atmosphere that it was composed in. The protest music of the 1950s, soon after apartheid had begun, explicitly addressed peoples' grievances over pass laws and forced relocation. Following the Sharpeville ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miriam Makeba 01
Miriam (, lit. ‘rebellion’) is described in the Hebrew Bible as the daughter of Amram and Jochebed, and the older sister of Moses and Aaron. She was a prophetess and first appears in the Book of Exodus. The Torah refers to her as "Miriam the Prophetess" and the Talmud names her as one of the seven major female prophets of Israel. Scripture describes her alongside of Moses and Aaron as delivering the Jews from exile in Egypt: "For I brought you up out of the land of Egypt and redeemed you from the house of slavery, and I sent before you Moses, Aaron, and Miriam". According to the Midrash, just as Moses led the men out of Egypt and taught them Torah, so too Miriam led the women and taught them Torah. Biblical narrative Miriam was the daughter of Amram and Jochebed and the sister of Aaron and Moses, the leader of the Israelites in ancient Egypt. The narrative of Moses's infancy in the Torah describes an unnamed sister of Moses observing him being placed in the Nile; she is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nelson Mandela 70th Birthday Tribute
The Nelson Mandela 70th Birthday Tribute was a popular-music concert staged on 11 June 1988 at Wembley Stadium, London, and broadcast to 67 countries and an audience of 600 million. Marking the forthcoming 70th birthday (18 July 1988) of the imprisoned anti-apartheid revolutionary Nelson Mandela, the concert was also referred to as ''Freedomfest'', ''Free Nelson Mandela Concert'' and ''Mandela Day''. In the United States, the Fox television network heavily censored the political aspects of the concert.Reed, T.V., ''The Art of Protest'', University of Minnesota Press, 2005, p. 174.Lee, Martin A., and Solomon, Norman, ''Unreliable Sources: A Guide to Detecting Bias in News Media''. . Quoted by Norman Solomon in Shirley, John, "Political and Corporate Censorship in the Land of the Free", ''Gauntlet'' No. 3, 1992.Morse, Steve (13 June 1988), ''The Boston Globe''. The concert is considered a notable example of anti-apartheid music. First of two Mandela events The Birthday Tribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vuyisile Mini
Vuyisile Mini (8 April 1920 – 6 November 1964) was a trade unionist, Umkhonto we Sizwe activist, singer and one of the first African National Congress members to be executed by apartheid South Africa. Early life Mini was born in 1920 in Tsomo in rural Transkei. Mini's father who was born in Tsomo and later moved to Port Elizabeth as a young man was a Port Elizabeth dockworker active in labour and community struggles, which inspired Mini, at 17, to take part in bus fare and rent increase protests. He was also active in campaigns against forced removals of Black people from Korsten (where he lived) to Kwazakhele. After completing elementary school, he worked as a labourer and trade union organiser. Trade union career His union comrades knew Mini as the "organizer of the unorganized", because of his courage and tireless efforts to organize workers across Eastern Cape during the increasingly repressive 1950s. Mini was tasked by the South African Congress of Trade Unions (SAC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorothy Masuka
Dorothy Masuka (3 September 1935 – 23 February 2019) was a Zimbabwe-born South African jazz singer. Music career Masuka's music was popular in South Africa throughout the 1950s, but when her songs became more serious, the government began questioning her. Her song "Dr. Malan," mentioning difficult laws, was banned and in 1961 she sang a song for Patrice Lumumba, which led to her exile. This exile lasted 31 years in total during which she lived in Zambia and worked as a flight attendant. She returned to Zimbabwe in 1980 after independence. In August 2011, Dorothy Masuka and Mfundi Vundla, creator of the popular South African soap opera '' Generations'', confirmed plans to make a film of Masuka's life. The film would concentrate on the years 1952 to 1957. On 27 April 2017 she featured in the concert "The Jazz Epistles featuring Abdullah Ibrahim & Ekaya," at The Town Hall, New York City, opening the show and delivering "one passionate performance after another, warming up and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natives Land Act, 1913
The Natives Land Act, 1913 (subsequently renamed Bantu Land Act, 1913 and Black Land Act, 1913; Act No. 27 of 1913) was an Act of the Parliament of South Africa that was aimed at regulating the acquisition of land. It largely prohibited the sale of land from whites to blacks and vice-versa. Economic interests, political influence and racial prejudices were main contributors to the introduction of the Native's Lands Act. According to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'': www.britannica.com, accessed 29 March 2021 "The Natives' Land Act of 1913 defined less than one-tenth of South Africa as Black "reserves" and prohibited any purchase or lease of land by Blacks outside the reserves. The law also restricted the terms of tenure under which Blacks could live on white-owned farms." Historical conte ...
|
Nkosi Sikelel' IAfrika
"" (, ) is a Christian hymn composed in 1897 by Enoch Sontonga, a Xhosa people, Xhosa clergyman at a Methodism, Methodist mission school near Johannesburg. The song became a pan-African liberation song and versions of it were later adopted as the national anthems of five countries in Africa including Zambia, Tanzania, Namibia and Zimbabwe after independence, and South Africa after the end of apartheid. The song's melody is still used as the Mungu ibariki Afrika, national anthem of Tanzania and the Stand and Sing of Zambia, Proud and Free, national anthem of Zambia (Zimbabwe and Namibia have since changed to new anthems with other melodies). In 1994, Nelson Mandela decreed that the verse of be embraced as a joint national anthem of South Africa; a revised version additionally including elements of "Die Stem van Suid-Afrika, Die Stem" (the then co-state anthem inherited from the previous apartheid government) was adopted in 1997. This new South African national anthem is someti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African National Congress
The African National Congress (ANC) is a political party in South Africa. It originated as a liberation movement known for its opposition to apartheid and has governed the country since 1994, when the 1994 South African general election, first post-apartheid election resulted in Nelson Mandela being elected as President of South Africa. Cyril Ramaphosa, the incumbent national president, has served as president of the ANC since 18 December 2017. Founded on 8 January 1912 in Bloemfontein as the South African Native National Congress, the organisation was formed to advocate for the rights of Bantu peoples of South Africa, black South Africans. When the National Party (South Africa), National Party government came to power 1948 South African general election, in 1948, the ANC's central purpose became to oppose the new government's policy of institutionalised apartheid. To this end, its methods and means of organisation shifted; its adoption of the techniques of mass politics, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
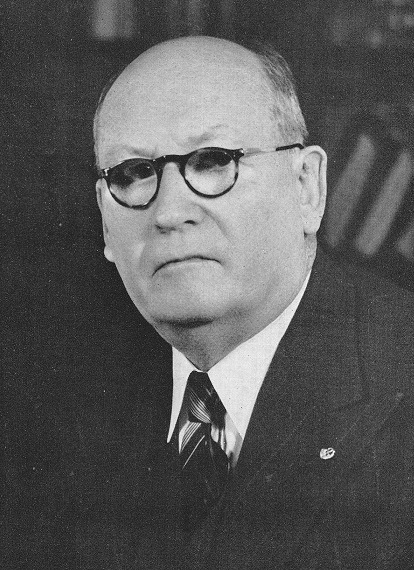
Hendrik Verwoerd
Hendrik Frensch Verwoerd (; 8 September 1901 – 6 September 1966), also known as H. F. Verwoerd, was a Dutch-born South African politician, scholar in applied psychology, philosophy, and sociology, and newspaper editor who was Prime Minister of South Africa from 1958 until his assassination in 1966. He is commonly regarded as the architect of apartheid and nicknamed the "father of apartheid". Verwoerd played a significant role in socially engineering apartheid, the country's system of institutionalized racial segregation and white supremacy, and implementing its policies, as Minister of Native Affairs (1950–1958) and then as prime minister (1958–1966). Furthermore, Verwoerd played a vital role in helping the far-right National Party come to power in 1948, serving as their political strategist and propagandist, becoming party leader upon his premiership. He was the Union of South Africa's last prime minister, from 1958 to 1961, when he proclaimed the founding of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Rights
Human rights are universally recognized Morality, moral principles or Social norm, norms that establish standards of human behavior and are often protected by both Municipal law, national and international laws. These rights are considered inherent and inalienable, meaning they belong to every individual simply by virtue of being human, regardless of characteristics like nationality, ethnicity, religion, or socio-economic status. They encompass a broad range of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights, such as the right to life, freedom of expression, protection against enslavement, and right to education. The modern concept of human rights gained significant prominence after World War II, particularly in response to the atrocities of the Holocaust, leading to the adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) by the United Nations General Assembly in 1948. This document outlined a comprehensive framework of rights that countries are encouraged t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afrikaans
Afrikaans is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language spoken in South Africa, Namibia and to a lesser extent Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe and also Argentina where there is a group in Sarmiento, Chubut, Sarmiento that speaks the Patagonian Afrikaans, Patagonian dialect. It evolved from the Dutch language, Dutch vernacular of South Holland (Hollandic dialect) spoken by the free Burghers, predominantly Dutch settlers and slavery in South Africa#Dutch rule, enslaved population of the Dutch Cape Colony, where it gradually began to develop distinguishing characteristics in the 17th and 18th centuries. Although Afrikaans has adopted words from other languages including German language, German, Malay language, Malay and Khoisan languages, an estimated 90 to 95% of the vocabulary of Afrikaans is of Dutch origin. Differences between Afrikaans and Dutch often lie in the more analytic language, analytic Morphology (linguistics), morphology and grammar of Afrikaans, and differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Party (South Africa)
The National Party (, NP), also known as the Nationalist Party, was a political party in South Africa from 1914 to 1997, which was responsible for the implementation of Apartheid, apartheid rule. The party was an Afrikaner nationalism, Afrikaner ethnic nationalist party, which initially promoted the interests of Afrikaners but later became a stalwart promoter and enactor of white supremacy, for which it is best known. It first became the governing party of the country in 1924. It merged with its rival, the South African Party (SAP), during the Great Depression, 1929-1939 Great Depression, and a splinter faction, the Herenigde Nasionale Party, Re-United National Party became the official opposition during World War II and won power in 1948. With the National Party governing South Africa from 1948 South African general election, 4 June 1948 until 1994 South African general election, 9 May 1994, the country for the bulk of this time was only a ''de jure'' or partial democracy, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afrikaner
Afrikaners () are a Southern African ethnic group descended from predominantly Dutch settlers who first arrived at the Cape of Good Hope in 1652.Entry: Cape Colony. ''Encyclopædia Britannica Volume 4 Part 2: Brain to Casting''. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. 1933. James Louis Garvin, editor. Until 1994, they dominated South Africa's politics as well as the country's commercial agricultural sector. Afrikaans, a language which evolved from the Dutch dialect of South Holland, is the mother tongue of Afrikaners and most Cape Coloureds. According to the South African National Census of 2022, 10.6% of South Africans claimed to speak Afrikaans as a first language at home, making it the country's third-largest home language after Zulu and Xhosa. The arrival of Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama at Calicut, India, in 1498 opened a gateway of free access to Asia from Western Europe around the Cape of Good Hope. This access necessitated the founding and safeguarding of tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |