|
Museum Of The Polish Army
Museum of the Polish Army () is a museum in Warsaw documenting the military history of Poland. Established in 1920 under the Second Polish Republic, it formerly occupied a wing of the building of the Polish National Museum and now occupies a building of its own at the Warsaw Citadel, as well as several branches in Poland. It is Warsaw's second largest museum and the largest collection of military objects in Poland. The collection illustrates a thousand years of Polish military history, from the 10th century to the Second World War. Establishment Opened in 1920, the museum expanded in 1993 with the Museum of Katyn and the Museum of Polish Military Technology opened in the 9th Czerniakowski Fort. Collections The forecourt of the museum houses several dozen armoured vehicles, artillery pieces and aircraft, an eclectic mix of Soviet, western and Polish equipment, mostly from the World War II era. The indoor galleries concentrate on the military history of Poland since the 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a Warsaw metropolitan area, greater metropolitan area of 3.27 million residents, which makes Warsaw the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 6th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises List of districts and neighbourhoods of Warsaw, 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is classified as an Globalization and World Cities Research Network#Alpha 2, alpha global city, a major political, economic and cultural hub, and the country's seat of government. It is also the capital of the Masovian Voivodeship. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010 Polish Air Force Tu-154 Crash
On 10 April 2010, a Tupolev Tu-154 aircraft operating Polish Air Force Flight 101 crashed near the Russian city of Smolensk, killing List of casualties of the Smolensk air disaster, all 96 people on board. Among the victims were the president of Poland, Lech Kaczyński, and his wife, Maria Kaczyńska, Maria; the former Polish government-in-exile, president of Poland-in-exile, Ryszard Kaczorowski; the chief of the Polish General Staff and other senior Polish military officers; the president of the National Bank of Poland; Polish government officials; 18 members of the Polish parliament; senior members of the Polish clergy; and relatives of victims of the Katyn massacre. The group was arriving from Warsaw to attend an event commemorating the 70th anniversary of the massacre, which took place not far from Smolensk. The pilots were attempting to land at Smolensk North Airport — a former military airbase — in thick fog, with visibility reduced to about . The aircraft descended f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Olszynka Grochowska
The Battle of Olszynka Grochowska, or the battle of Grochów, was fought on 25 February 1831 in the woods near Grochów, on the eastern outskirts of Warsaw. The Polish army, commanded by Józef Chłopicki, succeeded in preventing its Russian counterpart, under Hans Karl von Diebitsch, from crushing the uprising. However, the battle has also been described as an inconclusive bloodbath. Prelude The first months after the outbreak of the November Uprising saw no hostilities between Poland and Russia. Both the Polish commander Józef Chłopicki and Russian Tsar Nicholas I were hoping for a peaceful solution to the conflict. However, neither side could propose a satisfactory compromise, and on 25 January 1831 Nicholas was deposed from the Polish throne. This was seen as a de facto declaration of war and the Russian Army under Hans Karl von Diebitsch was ordered to enter Poland and crush the rebellion. The Russian army entered Poland on 4 February and started a fast advance t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum, Warsaw
The National Museum in Warsaw (, MNW) is a national museum in Warsaw, one of the largest museums in Poland and the largest in the capital. It comprises a rich collection of ancient art (Art of ancient Egypt, Egyptian, Art in ancient Greece, Greek, Roman art, Roman), counting about 11,000 pieces, an extensive gallery of Culture of Poland#Art, Polish painting since the 16th century and a collection of foreign painting (Art of Italy, Italian, French art, French, Flemish Baroque painting, Flemish, Dutch School (painting), Dutch, German art, German and Russian culture, Russian) including some paintings from Adolf Hitler's private collection, ceded to the museum by the Allied-occupied Germany, American authorities in post-war Germany. The museum is also home to Numismatics, numismatic collections, a gallery of applied arts and a department of oriental art, with the largest collection of Chinese art in Poland, comprising some 5,000 objects. The museum boasts the Faras Gallery at the Natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Uprising Museum
The Warsaw Rising Museum (), in the Wola district of Warsaw, Poland, is dedicated to the Warsaw Uprising of 1944. The institution of the museum was established in 1983, but no construction work took place for many years. It opened on July 31, 2004, marking the 60th anniversary of the uprising. The museum sponsors research into the history of the uprising, and the history and possessions of the Polish Underground State. It collects and maintains hundreds of artifact (archaeology), artifacts – ranging from weapons used by the insurgents to love letters – to present a full picture of the people involved. The museum's stated goals include the creation of an archive of historical information on the uprising and the recording of the stories and memories of living participants. Its director is Jan Ołdakowski, with historian Dariusz Gawin from the Polish Academy of Sciences as his deputy. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Żoliborz
Żoliborz () is one of the northern dzielnica, districts of the city of Warsaw. It is located directly to the north of the Warszawa-Śródmieście, City Centre, on the left bank of the Vistula river. It has approximately 50,000 inhabitants and is one of the smallest boroughs of Warsaw. Despite its small size, the district has many green areas and mostly consists of low-rise architecture. Historically an upscale neighborhood and home to Warsaw's intelligentsia prior to World War II, Żoliborz is the second most expensive residential district in Warsaw after Śródmieście, Warsaw, Śródmieście. History In the 18th century the area belonged to the Piarists of a monastery in the nearby city of Warsaw. The monks started to parcel the grounds and allowed for the creation of various settlements on their fields, which were parceled between several villages. One of them was named ''Joli Bord'' (''Beautiful Embankment'' in French, which was later transcribed to Polish language as Żoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Peacekeeping
Peacekeeping by the United Nations is a role of the United Nations's Department of Peace Operations and an "instrument developed by the organization as a way to help countries torn by conflict to create the conditions for lasting peace". It is distinguished from peacebuilding, peacemaking, and peace enforcement although the UN does acknowledge that all activities are "mutually reinforcing" and that overlap between them is frequent in practice. Peacekeeping, Peacekeepers monitor and observe peace processes in post-conflict areas and assist ex-combatants in implementing the peace agreements they may have signed. Such assistance comes in many forms, including separating former combatants, confidence-building measures, power-sharing arrangements, electoral assistance, strengthening the rule of law, and economic and social development. Accordingly, UN peacekeepers (often referred to as Blue Berets or Blue Helmets because of their light blue berets or helmets) can include soldiers, po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
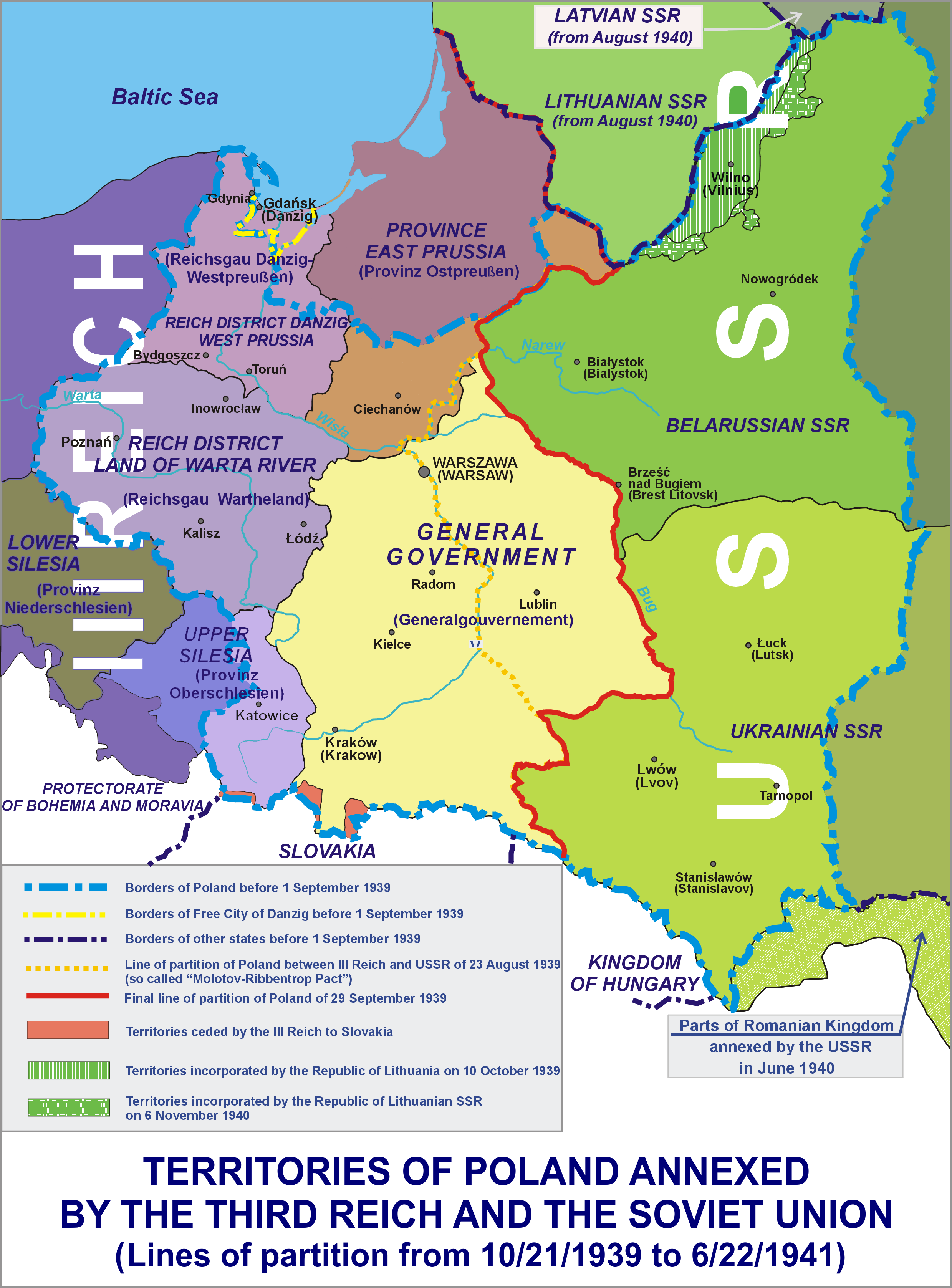
Occupation Of Poland (1939–1945)
During World War II, Poland was occupied by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union following the invasion in September 1939, and it was formally concluded with the defeat of Germany by the Allies in May 1945. Throughout the entire course of the occupation, the territory of Poland was divided between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union (USSR), both of which intended to eradicate Poland's culture and subjugate its people. In the summer-autumn of 1941, the lands which were annexed by the Soviets were overrun by Germany in the course of the initially successful German attack on the USSR. After a few years of fighting, the Red Army drove the German forces out of the USSR and crossed into Poland from the rest of Central and Eastern Europe. Sociologist Tadeusz Piotrowski argues that both occupying powers were hostile to the existence of Poland's sovereignty, people, and the culture and aimed to destroy them. Before Operation Barbarossa, Germany and the Soviet Union coordinated th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic, and the Soviet Union, which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviet invasion of Poland, Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The aim of the invasion was to disestablish Poland as a sovereign country, with its citizens destined for The Holocaust, extermination. German and Field Army Bernolák, Slovak forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
January Uprising
The January Uprising was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at putting an end to Russian occupation of part of Poland and regaining independence. It began on 22 January 1863 and continued until the last insurgents were captured by the Russian forces in 1864. It was the longest-lasting insurgency in partitioned Poland. The conflict engaged all levels of society and arguably had profound repercussions on contemporary international relations and ultimately transformed Polish society. A confluence of factors rendered the uprising inevitable in early 1863. The Polish nobility and urban bourgeois circles longed for the semi-autonomous status they had enjoyed in Congress Poland before the previous insurgency, a generation earlier in 1830, and youth encouraged by the success of the Italian independence movement urgently desired the same outcome. Russia had been weakened by its Crimean adventure and had introduced a more liberal attitude in its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31) (), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution, was an armed rebellion in Russian Partition, the heartland of Partitions of Poland, partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The uprising began on 29 November 1830 in Warsaw when young Polish officers from the military academy of the Army of Congress Poland revolted, led by Lieutenant Piotr Wysocki. Large segments of the peoples of Lithuania, Belarus, and Right-bank Ukraine soon joined the uprising. Although the insurgents achieved local successes, a numerically superior Imperial Russian Army under Ivan Paskevich eventually crushed the uprising. "Polish Uprising of 1830–31." ''The Great Soviet Encycloped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Poland
Congress Poland or Congress Kingdom of Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It was established when the French ceded a part of Polish territory to the Russian Empire following France's defeat in the Napoleonic Wars. In 1915, during World War I, it was replaced by the German-controlled nominal Regency Kingdom until Poland regained independence in 1918. Following the partitions of Poland at the end of the 18th century, Poland ceased to exist as an independent nation for 123 years. The territory, with its native population, was split among the Habsburg monarchy, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire. After 1804, an equivalent to Congress Poland within the Austrian Empire was the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, also commonly referred to as " Austrian Poland". The area incorporated into Prussia initially also held autonomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |