|
Musculocutaneous Nerve
The musculocutaneous nerve is a Mixed nerve, mixed branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus derived from cervical spinal nerves C5-C7. It arises opposite the lower border of the pectoralis minor. It provides motor innervation to the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm: the Coracobrachialis muscle, coracobrachialis, Biceps brachi, biceps brachii, and Brachialis muscle, brachialis. It provides sensory innervation to the lateral forearm (via its Lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm, terminal branch). It courses through the anterior part of the arm, terminating 2 cm above elbow; after passing the lateral edge of the tendon of Biceps brachi, biceps brachii it is becomes known as the Lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm, lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm. Structure Course Musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus with root value of C5 to C7 of the spinal cord. It follows the course of the third part of the axillary artery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musculocutaneous Nerve 2
The musculocutaneous nerve is a mixed branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus derived from cervical spinal nerves C5-C7. It arises opposite the lower border of the pectoralis minor. It provides motor innervation to the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm: the coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, and brachialis. It provides sensory innervation to the lateral forearm (via its terminal branch). It courses through the anterior part of the arm, terminating 2 cm above elbow; after passing the lateral edge of the tendon of biceps brachii it is becomes known as the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm. Structure Course Musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus with root value of C5 to C7 of the spinal cord. It follows the course of the third part of the axillary artery (part of the axillary artery distal to the pectoralis minor) laterally and enters the frontal aspect of the arm where it penetrates the coracobrachialis mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Compartment Of The Arm
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Terminolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biceps Brachii
The biceps or biceps brachii (, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join to form a single muscle belly which is attached to the upper forearm. While the long head of the biceps crosses both the shoulder and elbow joints, its main function is at the elbow where it flexes and supinates the forearm. Both these movements are used when opening a bottle with a corkscrew: first biceps screws in the cork (supination), then it pulls the cork out (flexion). Structure The biceps is one of three muscles in the anterior compartment of the upper arm, along with the brachialis muscle and the coracobrachialis muscle, with which the biceps shares a nerve supply. The biceps muscle has two heads, the short head and the long head, distinguished according to their origin at the coracoid process and supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, respectively. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abduction (anatomy)
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Point Of Neck
The nerve point of the neck, also known as Erb's point, is a site at the upper trunk of the brachial plexus located 2–3 cm above the clavicle. It is named for Wilhelm Heinrich Erb. Taken together, there are six types of nerves that meet at this point. "Erb's point" is also a term used in head and neck surgery to describe the point on the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, approximately 2-3cm above the clavicle, overlying the transverse process of the sixth cervical vertebra, where the four superficial branches of the cervical plexus—the greater auricular nerve, greater auricular, lesser occipital nerve, lesser occipital, transverse cervical nerve, transverse cervical, and supraclavicular nerves—emerge from behind the muscle. This point is located approximately at the junction of the upper and middle thirds of this muscle. From here, the accessory nerve courses through the posterior triangle of the neck to enter the anterior border of the trapezius mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electric potential generated by muscle cells when these cells are electrically or neurologically activated. The signals can be analyzed to detect abnormalities, activation level, or recruitment order, or to analyze the biomechanics of human or animal movement. Needle EMG is an electrodiagnostic medicine technique commonly used by neurologists. Surface EMG is a non-medical procedure used to assess muscle activation by several professionals, including physiotherapists, kinesiologists and biomedical engineers. In computer science, EMG is also used as middleware in gesture recognition towards allowing the input of physical action to a computer as a form of human-computer interaction. Clinical uses EMG testing has a varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
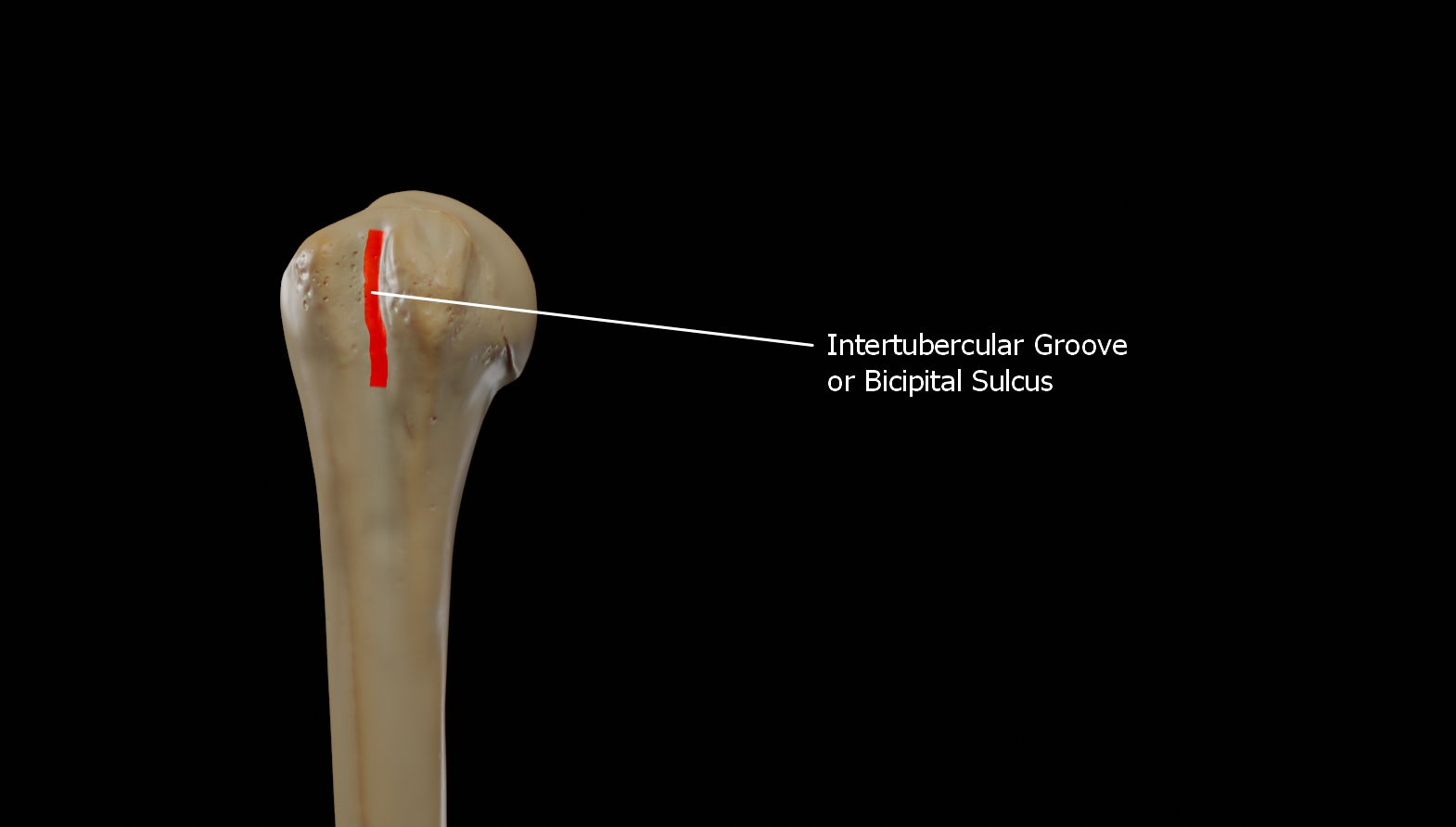
Bicipital Groove
The bicipital groove (intertubercular groove, sulcus intertubercularis) is a deep groove on the humerus that separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle. It allows for the long tendon of the biceps brachii muscle to pass. Structure The bicipital groove separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle. It is usually around 8 cm long and 1 cm wide in adults. The groove lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii muscle, positioned between the tendon of the pectoralis major muscle on the lateral lip and the tendon of the teres major muscle on the medial lip. It also transmits a branch of the anterior humeral circumflex artery to the shoulder joint. The insertion of the latissimus dorsi muscle is found along the floor of the bicipital groove. The teres major muscle inserts on the medial lip of the groove. It runs obliquely downward, and ends near the junction of the upper with the middle third of the bone. It is the lateral wall of the axilla. Function The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinel's Sign
Tinel's sign (also Hoffmann-Tinel sign) is a way to detect irritated nerves. It is performed by lightly tapping ( percussing) over the nerve to elicit a sensation of tingling or "pins and needles" in the distribution of the nerve. Percussion is usually performed moving distal to proximal. It is named after Jules Tinel.Tinel, J. (1978) The "tingling sign" in peripheral nerve lesions (Translated by EB Kaplan). In: M. Spinner M (Ed.), Injuries to the Ma jor Branches of Peripheral Nerves of the Forearm. (2nd ed.) (pp 8–13). Philadelphia: WD Saunders CoTinel, J. (1915) Le signe du fourmillement dans les lésions des nerfs périphériques. Presse médicale, 47, 388–389Tinel, J., Nerve wounds. London: Baillère, Tindall and Cox, 1917 It is a potential sign of carpal tunnel syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a nerve compression syndrome associated with the collected signs and symptoms of Pathophysiology of nerve entrapment#Compression, compression of the median nerve at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracoid Process
The coracoid process (from Greek κόραξ, raven) is a small hook-like structure on the lateral edge of the superior anterior portion of the scapula (hence: coracoid, or "like a raven's beak"). Pointing laterally forward, it, together with the acromion, serves to stabilize the shoulder joint. It is palpable in the deltopectoral groove between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles. Structure The coracoid process is a thick curved process attached by a broad base to the upper part of the neck of the scapula; it runs at first upward and medially; then, becoming smaller, it changes its direction, and projects forward and laterally. The component parts of the process are the base; angle; shaft; and apex of the coracoid process, respectively. The coracoglenoid notch is an indentation localized between the coracoid process and the glenoid. As the coracoid process projects laterally, it defines the subcoracoid space beneath. The ''ascending portion'', flattened from the fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronator Teres
The pronator teres is a muscle (located mainly in the forearm) that, along with the pronator quadratus, serves to pronate the forearm (turning it so that the palm faces posteriorly when from the anatomical position). It has two origins, at the medial humeral supracondylar ridge and the medial side of the coronoid process of the ulna and inserts near the middle of the radius. Structure The pronator teres has two heads—humeral and ulnar. * The humeral head, the larger and more superficial, arises from the medial supracondylar ridge immediately superior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus, and from the common flexor tendon (which arises from the medial epicondyle). * The ulnar head (or ulnar tuberosity) is a thin fasciculus, which arises from the medial side of the coronoid process of the ulna, and joins the preceding at an acute angle. The median nerve enters the forearm between the two heads of the muscle, and is separated from the ulnar artery by the ulnar head. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Nerve
The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus. The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has contributions from ventral roots of C6-C7 (lateral cord) and C8 and T1 (medial cord). The median nerve is the only nerve that passes through the carpal tunnel. Carpal tunnel syndrome is the disability that results from the median nerve being pressed in the carpal tunnel. Structure The median nerve arises from the branches from lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, courses through the anterior part of arm, forearm, and hand, and terminates by supplying the muscles of the hand. Arm After receiving inputs from both the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, the median nerve enters the arm from the axilla at the inferior margin of the teres major muscle. It then passes vertically down and courses lateral to the brac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
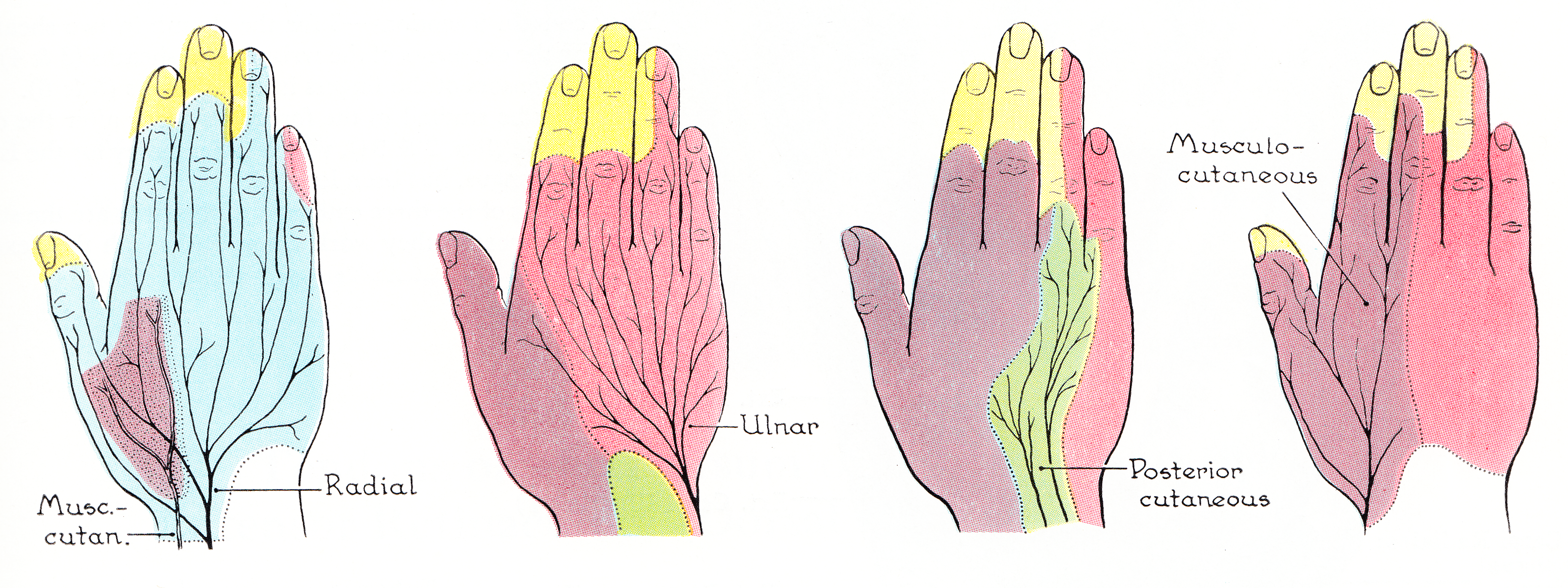
Lateral Cutaneous Nerve Of The Forearm
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to: Biology and healthcare * Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side" * Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx * Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure to release tight capsular structures Other uses * ''Lateral'', a digital journal and production of the Cultural Studies Association * ''Lateral'', a podcast by English YouTuber and web developer Tom Scott * Lateral canal, a canal built along the same right-of-way as an existing stream * Lateral consonant, a consonant in which the airstream proceeds along one or both of the sides of the tongue * Lateral mark, a sea mark used in maritime pilotage to indicate the edge of a channel * Lateral modes, an aspect of dynamic stability and control in the field of aircraft flight dynamics * Lateral pass, a non-advancing move in gridiron football * Lateral release (phonetics), the release of a plosive consonant into a lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |