|
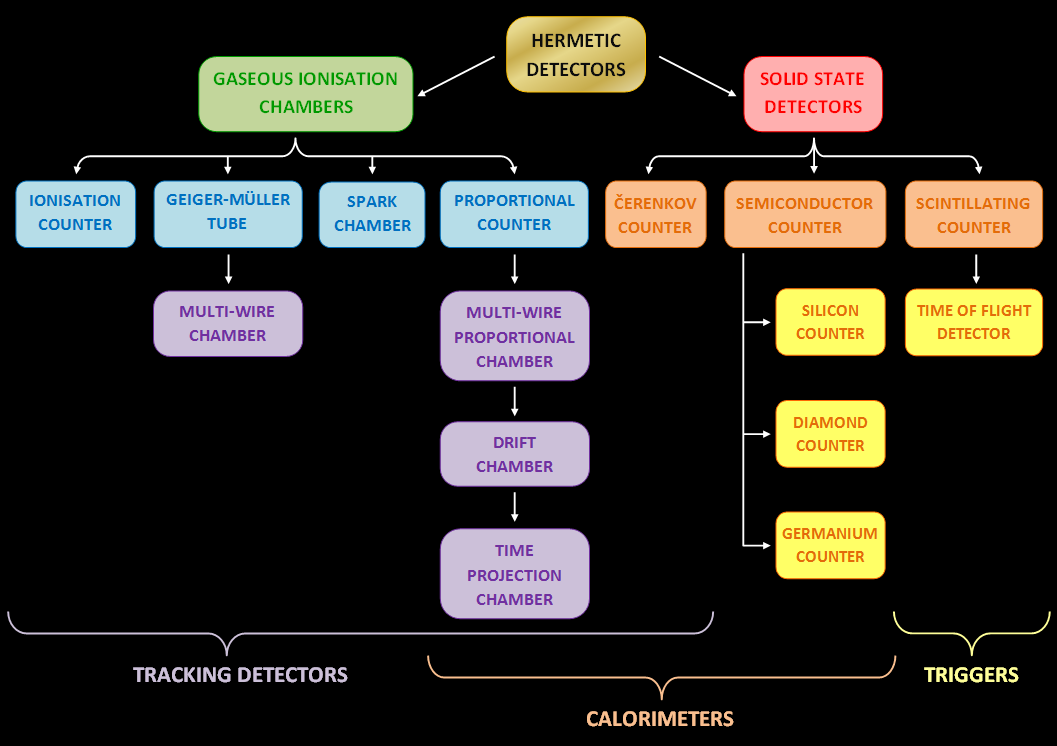
Multiwire Proportional Chamber
A wire chamber or multi-wire proportional chamber is a type of proportional counter that detects charged particles and photons and can give positional information on their trajectory, by tracking the trails of gaseous ionization. was located via Dr. C.N. BootPHY304 Particle Physics Sheffield University The technique was an improvement over the bubble chamber particle detection method, which used photographic techniques, as it allowed high speed electronics to track the particle path. Description The multi-wire chamber uses an array of wires at a positive dc voltage (anode)s, which run through a chamber with conductive walls held at a lower potential (cathode). The chamber is filled with gas, such as an argon/methane mix, so that any ionizing particle that passes through the tube will ionize surrounding gaseous atoms and produce ion pairs, consisting of positive ions and electrons. These are accelerated by the electric field across the chamber, preventing recombination; the elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportional Counter
The proportional counter is a type of gaseous ionization detector device used to measure Charged particle, particles of ionizing radiation. The key feature is its ability to measure the Electronvolt, energy of incident radiation, by producing a detector output pulse that is ''proportional'' to the radiation energy absorbed by the detector due to an ionizing event; hence the detector's name. It is widely used where energy levels of incident radiation must be known, such as in the discrimination between alpha particle, alpha and beta particles, or accurate measurement of X-ray radiation absorbed dose, dose. A proportional counter uses a combination of the mechanisms of a Geiger–Müller tube and an ionization chamber, and operates in an intermediate voltage region between these. The accompanying plot shows the proportional counter operating voltage region for a co-axial cylinder arrangement. Operation In a proportional counter the fill gas of the chamber is an inert gas which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized. Xenon is used in flash lamps and arc lamps, and as a general anesthetic. The first excimer laser design used a xenon dimer molecule (Xe2) as the lasing medium, and the earliest laser designs used xenon flash lamps as pumps. Xenon is also used to search for hypothetical weakly interacting massive particles and as a propellant for ion thrusters in spacecraft. Naturally occurring xenon consists of seven stable isotopes and two long-lived radioactive isotopes. More than 40 unstable xenon isotopes undergo radioactive decay, and the isotope ratios of xenon are an important tool for studying the early history of the Solar System. Radioactive xe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaseous Ionization Detector
Gaseous ionization detectors are radiation detection instruments used in particle physics to detect the presence of ionizing particles, and in radiation protection applications to measure ionizing radiation. They use the ionising effect of radiation upon a gas-filled sensor. If a particle has enough energy to ionize a gas atom or molecule, the resulting electrons and ions cause a current flow which can be measured. Gaseous ionisation detectors form an important group of instruments used for radiation detection and measurement. This article gives a quick overview of the principal types, and more detailed information can be found in the articles on each instrument. The accompanying plot shows the variation of ion pair generation with varying applied voltage for constant incident radiation. There are three main practical operating regions, one of which each type utilises. Types The three basic types of gaseous ionization detectors are 1) ionization chambers, 2) proportional count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubble Chamber
A bubble chamber is a vessel filled with a superheated transparent liquid (most often liquid hydrogen) used to detect electrically charged particles moving through it. It was invented in 1952 by Donald A. Glaser, for which he was awarded the 1960 Nobel Prize in Physics. Supposedly, Glaser was inspired by the bubbles in a glass of beer; however, in a 2006 talk, he refuted this story, although saying that while beer was not the inspiration for the bubble chamber, he did experiments using beer to fill early prototypes. While bubble chambers were extensively used in the past, they have now mostly been supplanted by wire chambers, spark chambers, drift chambers, and silicon detectors. Notable bubble chambers include the Big European Bubble Chamber (BEBC) and Gargamelle. __TOC__ Function and use The bubble chamber is similar to a cloud chamber, both in application and in basic principle. It is normally made by filling a large cylinder with a liquid heated to just below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée Des Arts Et Métiers
The Musée des Arts et Métiers (; English: Museum of Arts and Crafts) is an industrial design museum in Paris that houses the collection of the Conservatoire national des arts et métiers, which was founded in 1794 as a repository for the preservation of scientific instruments and inventions. History Since its foundation, the museum has been housed in the deserted priory of Saint-Martin-des-Champs on the Rue Réaumur in the 3rd arrondissement of Paris. Today the museum, which underwent major renovations in 1990, includes an additional building adjacent to the abbey, with larger objects remaining in the abbey itself. Collection The museum has over 80,000 objects and 15,000 drawings in its collection, of which about 2,500 are on display in Paris. The rest of the collection is preserved in a storehouse in Saint-Denis, Seine-Saint-Denis, Saint-Denis. Among its collection is an original version of the Foucault pendulum, the original model of ''Liberty Enlightening the World'' (commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drift Velocity
Drift or Drifts may refer to: Geography * Drift or ford (crossing) of a river * Drift (navigation), difference between heading and course of a vessel * Drift, Kentucky, unincorporated community in the United States * In Cornwall, England: ** Drift, Cornwall, village ** Drift Reservoir, associated with the village Science, technology, and physics * Directional Recoil Identification from Tracks, a dark-matter experiment * Drift (video gaming), a typical game-controller malfunction * Drift pin, metalworking tool for localizing hammer blows and for aligning holes * Drift (geology), deposited material of glacial origin * drift (in mining), a roughly horizontal passage; an adit * Drift, linear term of a stochastic process * Drift (motorsport), the controlled sliding of a vehicle through a sharp turn, either via over-steering with sudden sharp braking, or counter-steering with a sudden "clutch kick" acceleration * Incremental changes: ** Drift (linguistics), a type of language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogonal
In mathematics, orthogonality (mathematics), orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. Although many authors use the two terms ''perpendicular'' and ''orthogonal'' interchangeably, the term ''perpendicular'' is more specifically used for lines and planes that intersect to form a right angle, whereas ''orthogonal'' is used in generalizations, such as ''orthogonal vectors'' or ''orthogonal curves''. ''Orthogonality'' is also used with various meanings that are often weakly related or not related at all with the mathematical meanings. Etymology The word comes from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "upright", and ('), meaning "angle". The Ancient Greek (') and Classical Latin ' originally denoted a rectangle. Later, they came to mean a right triangle. In the 12th century, the post-classical Latin word ''orthogonalis'' came to mean a right angle or something related to a right angle. Mathematics Physics Optics In optics, polarization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Outer Tracker (COT)
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object. Central may also refer to: Directions and generalised locations * Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as Middle Africa * Central America, a region in the centre of America continent * Central Asia, a region in the centre of Eurasian continent * Central Australia, a region of the Australian continent * Central Belt, an area in the centre of Scotland * Central Europe, a region of the European continent * Central London, the centre of London * Central Region (other) * Central United States, a region of the United States of America Specific locations Countries * Central African Republic, a country in Africa States and provinces * Blue Nile (state) or Central, a state in Sudan * Central Department, Paraguay * Central Province (Kenya) * Central Province (Papua New Guinea) * Central Province (Solomon Islands) * Central Province, Sri Lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geiger Counter
A Geiger counter (, ; also known as a Geiger–Müller counter or G-M counter) is an electronic instrument for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation with the use of a Geiger–Müller tube. It is widely used in applications such as radiation dosimetry, radiological protection, experimental physics and the nuclear industry. "Geiger counter" is often used generically to refer to any form of dosimeter (or, ''radiation-measuring device''), but scientifically, a Geiger counter is only one specific type of dosimeter. It detects ionizing radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays using the ionization effect produced in a Geiger–Müller tube, which gives its name to the instrument. In wide and prominent use as a hand-held radiation survey instrument, it is perhaps one of the world's best-known radiation detection instruments. The original detection principle was realized in 1908 at the University of Manchester, but it was not until the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photograph
A photograph (also known as a photo, or more generically referred to as an ''image'' or ''picture'') is an image created by light falling on a photosensitivity, photosensitive surface, usually photographic film or an electronic image sensor. The process and practice of creating such images is called photography. Most photographs are now created using a smartphone or camera, which uses a photographic lens, lens to focus the scene's visible spectrum, visible wavelengths of light into a reproduction of what the human eye would perceive. Etymology The word ''photograph'' was coined in 1839 by Sir John Herschel and is based on the Greek language, Greek φῶς ('':el:phos, phos''), meaning "light", and γραφή (''graphê''), meaning "drawing, writing", together meaning "drawing with light". History The first permanent photograph, a contact-exposed copy of an engraving, was made in 1822 using the Bitumen of Judea, bitumen-based "heliography" process developed by Nicéphore Niép ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield of physics and electrical engineering which uses Passivity (engineering), active devices such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits to control and amplify the flow of electric current and to convert it from one form to another, such as from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or from analog signal, analog signals to digital signal, digital signals. Electronic devices have significantly influenced the development of many aspects of modern society, such as telecommunications, entertainment, education, health care, industry, and security. The main driving force behind the advancement of electronics is the semiconductor industry, which continually produces ever-more sophisticated electronic devices and circuits in respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |