|
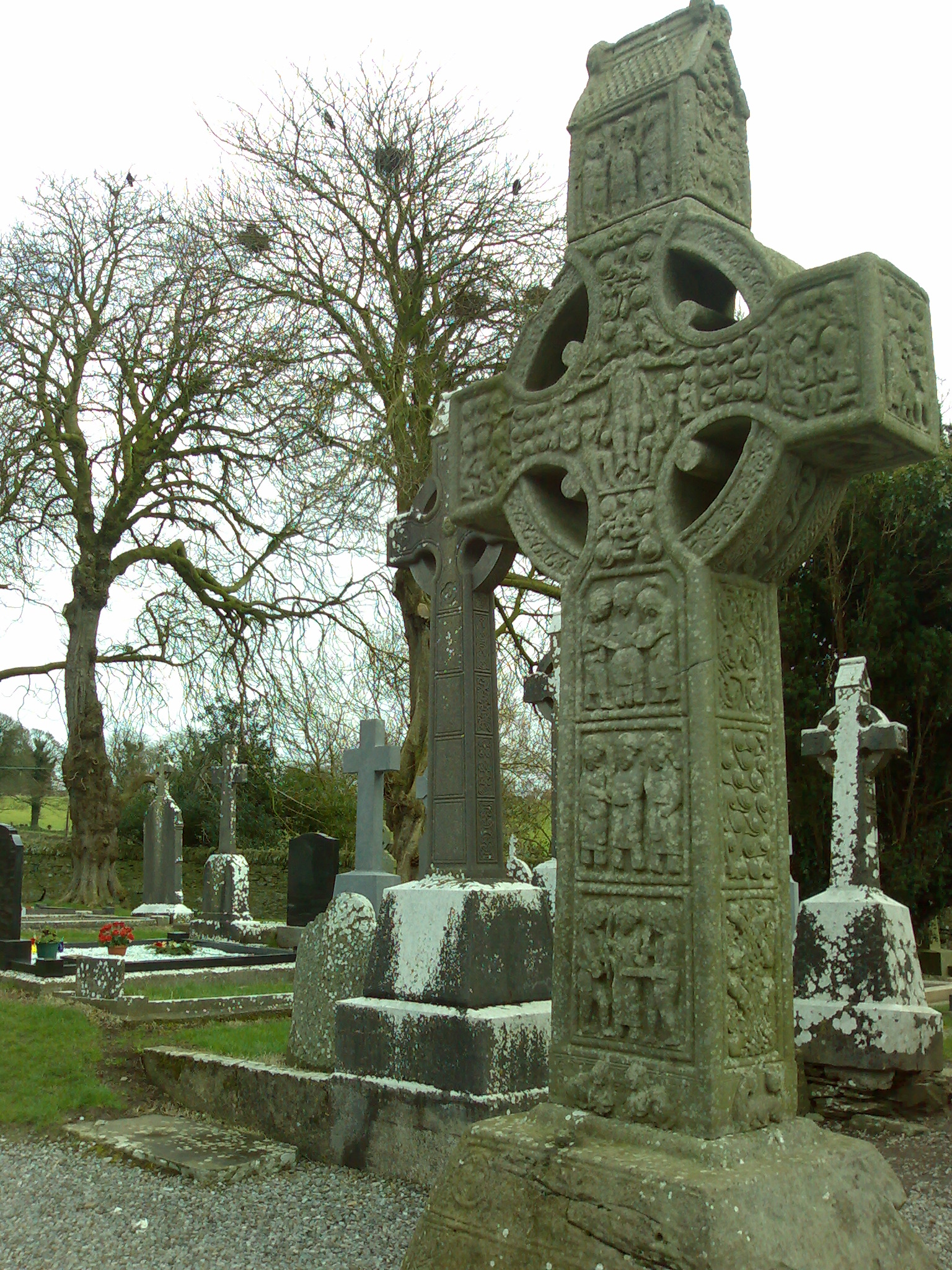
Muiredach's High Cross
Muiredach's High Cross is a high cross from the 10th or possibly 9th century, located at the ruined monastic site of Monasterboice, in County Louth, Ireland. There are two other high crosses at Monasterboice; in local terms Muiredach's cross is also known as the South Cross. Muiredach's cross is the most impressive surviving example of early medieval Irish stonework, and the crosses at Monasterboice have been said to be Ireland's greatest contribution to European sculpture. Background: high crosses in Ireland Irish high crosses are internationally recognised icons of early medieval Ireland. They are usually found on early church sites and can be either plain or decorated. High crosses served a variety of functions including, liturgical, ceremonial, and symbolic uses. They were also used as markers for an area of sanctuary around a church; as well as focal points for markets, which grew around church sites. The "greatest", or "classic", Irish high crosses can be found at Durro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Offaly
County Offaly (; ga, Contae Uíbh Fhailí) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is named after the ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in honour of Philip II of Spain. Offaly County Council is the local authority for the county. The county population was 82,668 at the 2022 census. Central Statistics Office figures Geography and political subdivisions Offaly is the 18th largest of Ireland's 32 counties by area and the 24th largest in terms of population. It is the fifth largest of Leinster's 12 counties by size and the 10th largest by population.Physical geography [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Alexander Stewart Macalister
Robert Alexander Stewart Macalister (8 July 1870 – 26 April 1950) was an Irish archaeologist. Biography Macalister was born in Dublin, Ireland, the son of Alexander Macalister, then Professor of Zoology, University of Dublin. His father was appointed professor of anatomy at Cambridge University in 1883, and he was educated at The Perse School, and then studied at Cambridge University. Although his earliest interest was in the archaeology of Ireland, he soon developed a strong interest in biblical archaeology. Along with Frederick J. Bliss, he excavated several towns in the Shephelah region of Ottoman Palestine from 1898 to 1900. Using advances in stratigraphy building on the work of Flinders Petrie, they developed a chronology for the region using ceramic typology. Upon Bliss' retirement, Macalister became director of excavations for the Palestine Exploration Fund (PEF) in 1901. From 1902 to 1909 he was responsible for the excavations at Gezer, in the modern state o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeologist
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
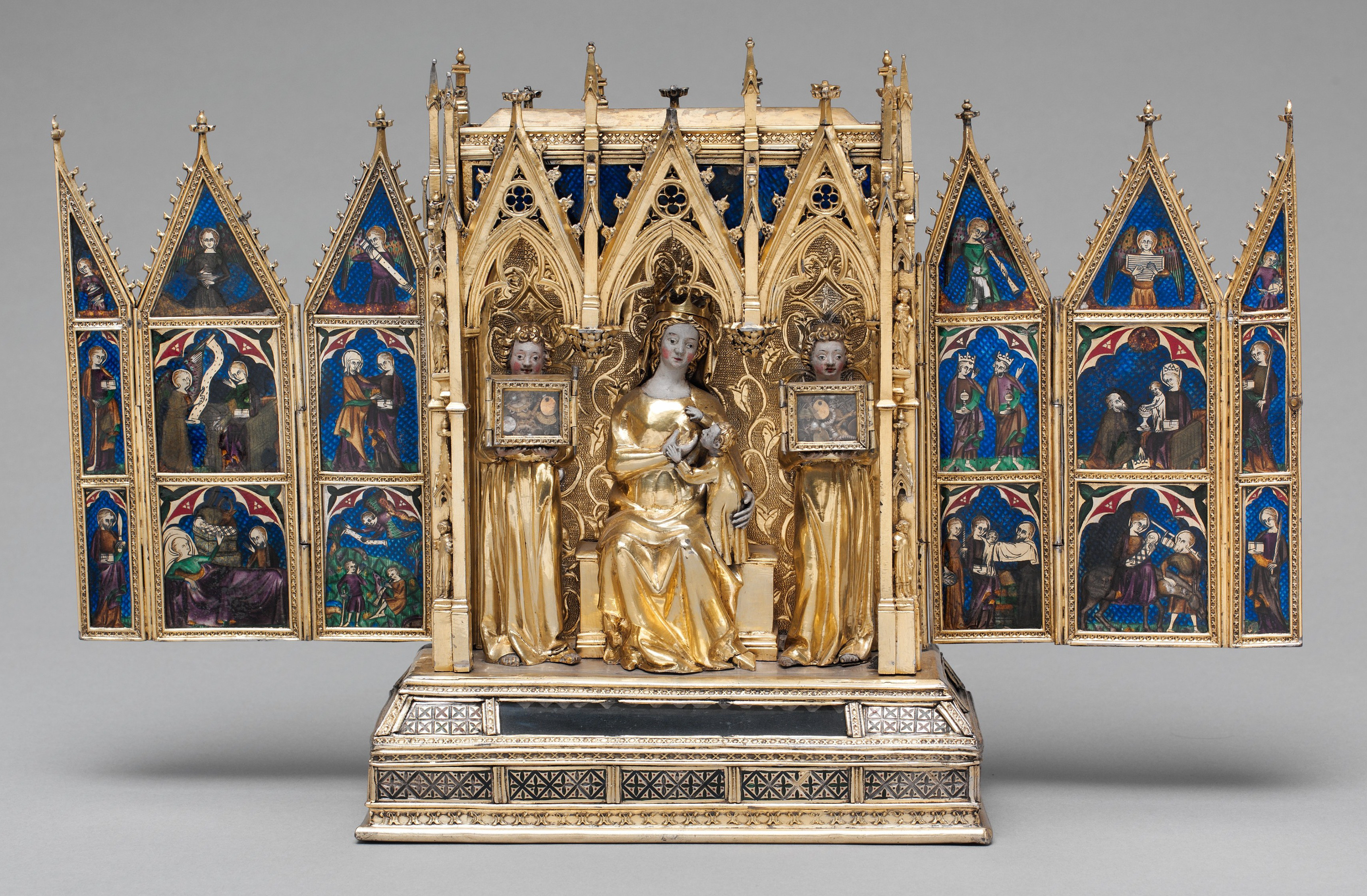
Monymusk Reliquary
The Monymusk Reliquary is an eighth century Scottish house-shape reliquaryMoss (2014), p. 286 made of wood and metal characterised by an Insular fusion of Gaelic and Pictish design and Anglo-Saxon metalworking, probably by Ionan monks. It is now in the National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh. It is an early example of the house-shaped shrine that became popular across Europe later in the Middle Ages, perhaps influenced by Insular styles. The Monymusk Reliquary is now empty. Its dimensions are W 112mm x D 51mm x H 89mm. Past scholars suggested that Monymusk Reliquary was the Brecbennach of St. Columba ( modern Gaelic ''Breac Bannoch'' or "embossed peaked-thing"), a sacred battle ensign of the Scottish army, used for saintly assistance, and mentioned in various charters associated with Arbroath Abbey. However, this identification of the Monymusk Reliquary with the ''Brecbennach'' is unlikely, and the Monymusk Reliquary is therefore not the object mentioned in historical rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliquaries
A reliquary (also referred to as a ''shrine'', by the French term ''châsse'', and historically including ''phylacteries'') is a container for relics. A portable reliquary may be called a ''fereter'', and a chapel in which it is housed a ''feretory''. Relics may be the purported or actual physical remains of saints, such as bones, pieces of clothing, or some object associated with saints or other religious figures. The authenticity of any given relic is often a matter of debate; it is for that reason, some churches require documentation of the relic's provenance. Relics have long been important to Buddhists, Christians, Hindus and to followers of many other religions. In these cultures, reliquaries are often presented in shrines, churches, or temples to which the faithful make pilgrimages in order to gain blessings. The term is sometimes used loosely of containers for the body parts of non-religious figures; in particular the Kings of France often specified that their hearts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
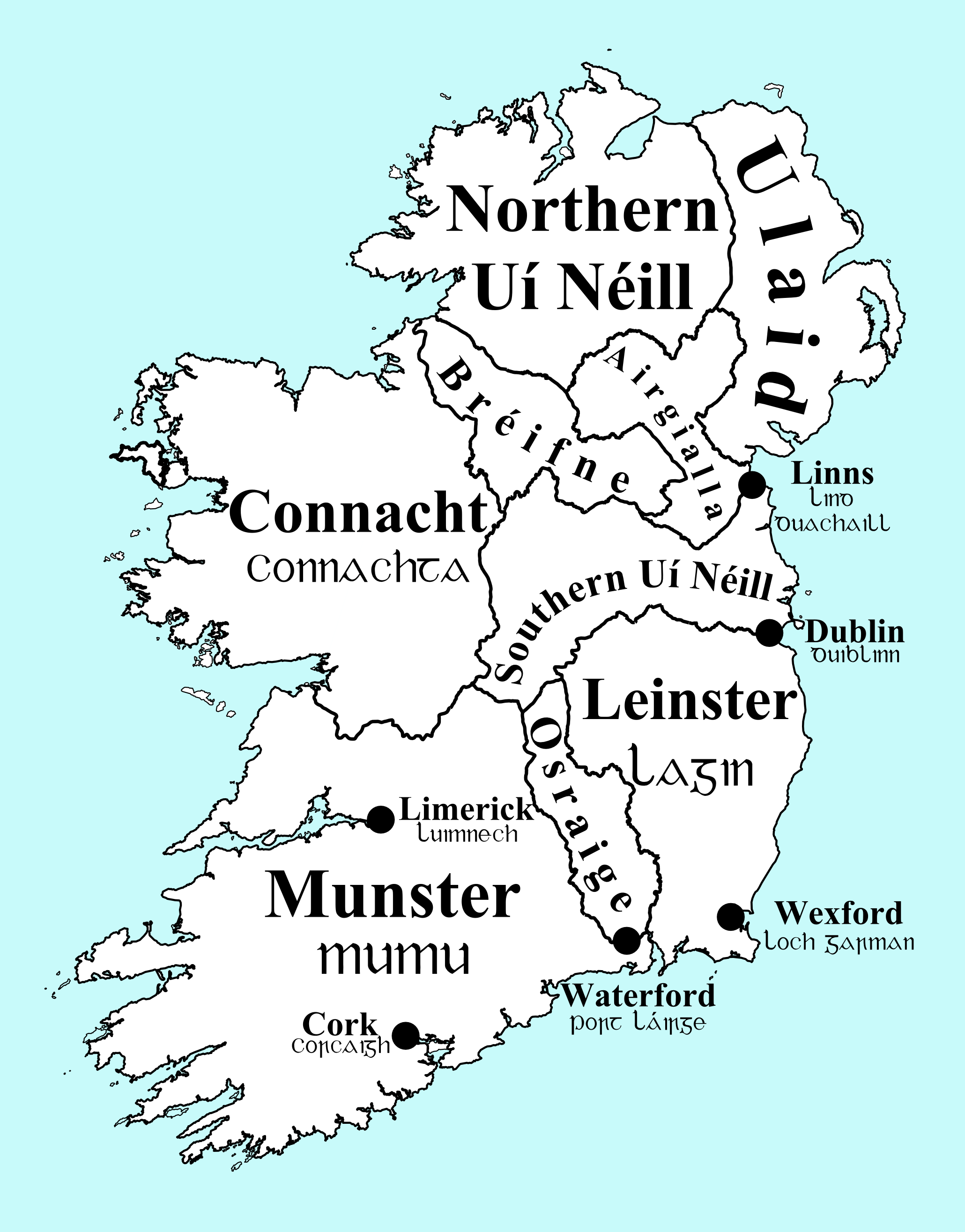
Southern Uí Néill
The Southern Uí Néill ( ga, Uí Néill an Deiscirt, IPA: �iːˈnʲeːl̪ʲˈanˠˈdʲɛʃcəɾˠtʲ were that branch of the Uí Néill dynasty that invaded and settled in the Kingdom of Mide and its associated kingdoms. In the initial decades two sons of Niall Noigiallach, Lóegaire and Coirpre and their immediate descendants led the dynasty. However, after the murder of Túathal Máelgarb in about 549, it was left to another branch of the family descended from another of Niall's sons – Conall Cremthainne – to continue Uí Néill expansion and consolidate their position. No descendants of either Lugaid mac Lóegairi or Túathal Máelgarb are recorded, and it is not unlikely that they were either erased from the genealogical record, or indeed literally erased from history. Just as their kinsmen the Northern Uí Néill split into two main branches, so too did the Southern Uí Néill, both being descended from sons of Diarmait mac Cerbaill, Colmán Már and Áed Sláine. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steward (office)
A steward is an official who is appointed by the legal ruling monarch to represent them in a country and who may have a mandate to govern it in their name; in the latter case, it is synonymous with the position of regent, vicegerent, viceroy, king's lieutenant (for Romance languages), governor, or deputy (the Roman ''rector'', ''praefectus'', or ''vicarius''). Etymology From Old English ''stíweard, stiȝweard'', from ''stiȝ'' "hall, household" + ''weard'' "warden, keeper"; corresponding to Dutch: ''stadhouder'', German ''Statthalter'' "place holder", a Germanic parallel to French ''lieutenant''. The Old English term ''stíweard'' is attested from the 11th century. Its first element is most probably ''stiȝ-'' "house, hall" (attested only in composition; its cognate ''stiȝu'' is the ancestor of Modern English ''sty''). Old French and Old Norse ''stívarðr'' are adopted from the Old English. The German and Dutch term (Middle High German ''stat-halter'') is a parallel but indep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muiredach (other)
Muiredach (Old Irish), Muireadhach or Muireach, anglicized variously to Murdoch (other), Murdoch, Murtagh, Murray (surname), Murray, Murdac, Mordacq and other forms, is a Goidelic languages, Goidelic name (meaning "chieftain") popular in Scotland and Ireland in the Middle Ages: * Muiredach Bolgrach, mythological Irish king * Muiredach Tirech, legendary high-king of Ireland * Muiredach mac Eógain (died 489), legendary early king of Ailech * Muiredach Muinderg (died 489), legendary king of the Ulaid * Muiredach of Killala, reputed early Irish saint * Muiredach Muillethan (died 702), king of Connaught * Muiredach mac Ainbcellaig (died c. 770), king of Dál Riata * Muiredach mac Murchado (died 760), king of Leinster * Muiredach mac Brain (died 818) (8th-century–818), king of Leinster * Muiredach mac Ruadrach (8th-century–829), king of Leinster * Muiredach mac Eochada (died 839), king of the Ulaid * Muiredach mac Brain (died 885), king of Munster * Muiredach mac Eochocáin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Buithe
ST, St, or St. may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Stanza, in poetry * Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band * Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise * Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy and theology by St. Thomas Aquinas * St or St., abbreviation of "State", especially in the name of a college or university Businesses and organizations Transportation * Germania (airline) (IATA airline designator ST) * Maharashtra State Road Transport Corporation, abbreviated as State Transport * Sound Transit, Central Puget Sound Regional Transit Authority, Washington state, US * Springfield Terminal Railway (Vermont) (railroad reporting mark ST) * Suffolk County Transit, or Suffolk Transit, the bus system serving Suffolk County, New York Other businesses and organizations * Statstjänstemannaförbundet, or Swedish Union of Civil Servants, a trade union * The Secret Team, an alleged covert alliance between the CIA and American industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaeilge
Irish (an Caighdeán Oifigiúil, Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic languages, Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous language, indigenous to the Ireland, island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English (language), English gradually became Linguistic imperialism, dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as County Cork, Cork, County Donegal, Donegal, County Galway, Galway, and County Kerry, Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties County Mayo, Mayo, County Meath, Meath, and County Waterford, Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second language, second-language speakers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)
