|
Moving (Kate Bush Song)
"Moving" is a song written and recorded by English singer-songwriter Kate Bush for her debut album, ''The Kick Inside'' (1978). It was released as a single only in Japan in April 1978 by EMI Music Japan. Written by Bush and produced by Andrew Powell, the song is a tribute to Lindsay Kemp, her mime teacher. "Moving" opens with whale vocalisation, whale song sampled from ''Songs of the Humpback Whale'', an LP record, LP including recordings of whale vocalisations made by Roger Payne, Dr. Roger S. Payne. Bush performed "Moving" at Tokyo Music Festival, on BBC's ''Saturday Night Live, Saturday Nights at the Mill'', on a Dutch TV show set in Efteling park and on her first tour, The Tour of Life (1979). Background Kate Bush signed a contract with EMI Records in her late teens. Between recording demos with Gilmour as producer and releasing her first album she pursued her studies and gained maturity in her writing. After seeing an advertisement for Lindsay Kemp's ''Flowers'' spectacle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
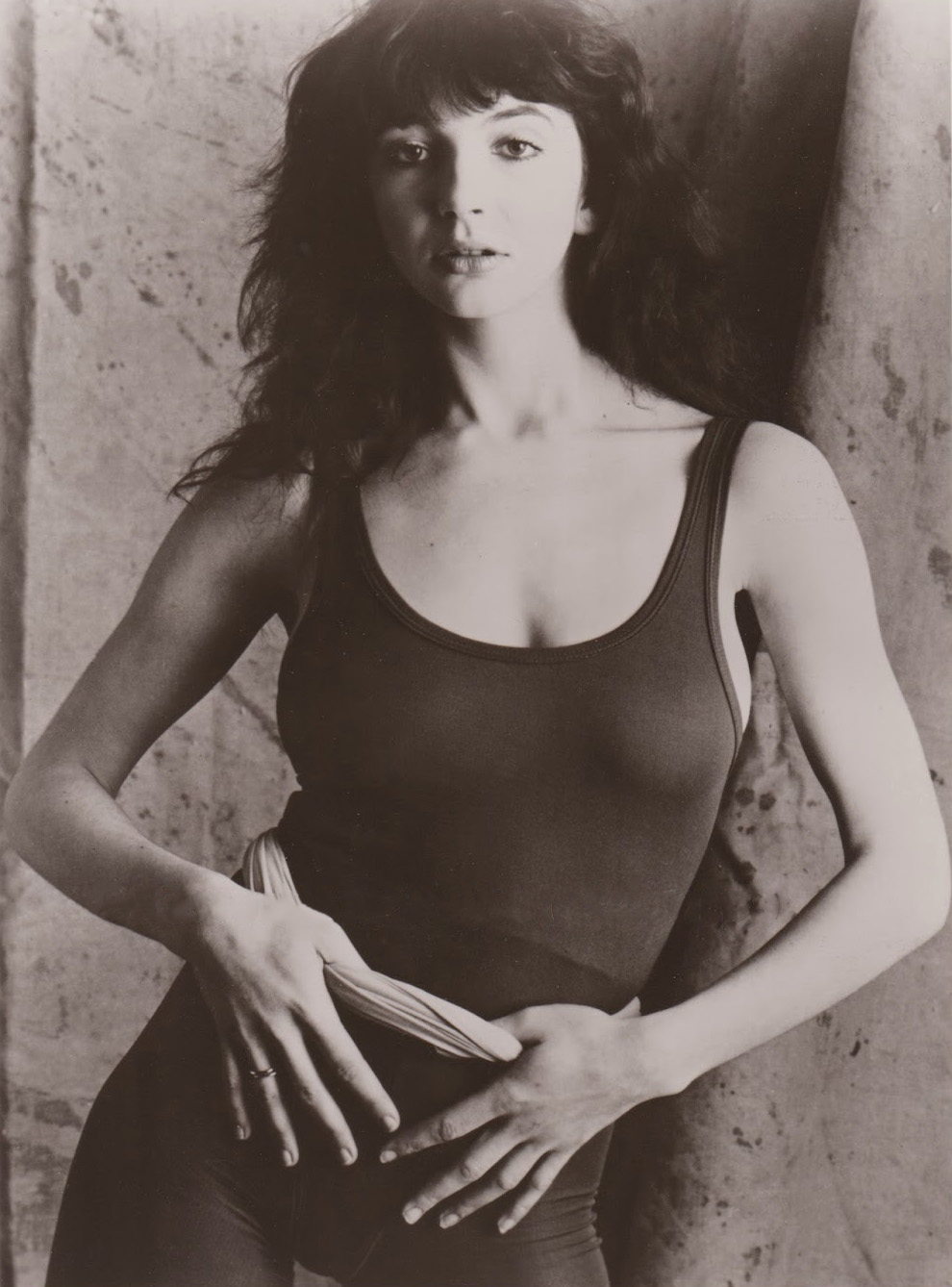
Kate Bush
Catherine Bush (born 30 July 1958) is an English singer, songwriter, record producer, and dancer. Bush began writing songs at age 11. She was signed to EMI Records after David Gilmour of Pink Floyd helped produce a demo tape. In 1978, at the age of 19, she topped the UK singles chart for four weeks with her debut single "Wuthering Heights (song), Wuthering Heights", becoming the first female artist to achieve a UK number one with a fully self-written song. Her debut studio album, ''The Kick Inside'' (1978), peaked at number three on the UK Albums Chart. Bush was the first British solo female artist to top the UK Albums Chart and the first female artist to enter it at number one. Bush has released 25 UK top 40 singles, including the top-10 hits "The Man with the Child in His Eyes" (1978), "Babooshka (song), Babooshka" (1980), "Running Up That Hill" (1985), "Don't Give Up (Peter Gabriel and Kate Bush song), Don't Give Up" (a 1986 duet with Peter Gabriel), and "King of the Moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lindsey Kemp Allan Warren
Lindsey may refer to : Places Canada * Lindsey Lake, Nova Scotia England * Parts of Lindsey, one of the historic Parts of Lincolnshire and an administrative county from 1889 to 1974 ** East Lindsey, an administrative district in Lincolnshire, and a parliamentary constituency between 1983 and 1997 ** West Lindsey, an administrative district in Lincolnshire ** Kingdom of Lindsey, an early medieval kingdom in the area of modern Lincolnshire ** Archdeaconry of Lindsey, created in 1933 and absorbed into the Archdeaconry of Stow & Lindsey in 1994 * Lindsey, Suffolk * Norton Lindsey, Warwickshire United States * Lindsey, Ohio * Lindsey, Wisconsin * Lake Lindsey, Florida * Mount Lindsey, Colorado People * Lindsey (name) * Earl of Lindsey * Robert Bertie, 1st Duke of Ancaster and Kesteven, 1st Marquess of Lindsey Other uses * , a United States Navy destroyer-minelayer in commission from 1944 to 1946 See also * * Lindsay (other) * Linsay * Linsey (other) * Lyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
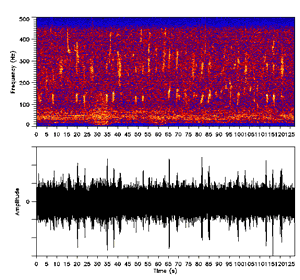
Whale Vocalization
Whales use a variety of sounds for animal communication, communication and sensation. The mechanisms used to produce sound vary from one family of cetaceans to another. Marine mammals, including whales, dolphins, and porpoises, are much more dependent on sound than land mammals due to the limited effectiveness of other senses in water. Visual perception, Sight is less effective for marine mammals because of the way particulates in the ocean scatter light. Olfaction, Smell is also limited, as molecules diffuse more slowly in water than in air, which makes smelling less effective. However, the speed of sound is roughly four times greater in water than in the atmosphere at sea level. As sea mammals are so dependent on hearing to communicate and feed, environmentalists and cetology, cetologists are concerned that they are being harmed by the increased ambient noise in the world's oceans caused by ships, sonar and marine Reflection seismology, seismic surveys. The word "song" is use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Signature
A time signature (also known as meter signature, metre signature, and measure signature) is an indication in music notation that specifies how many note values of a particular type fit into each measure ( bar). The time signature indicates the meter of a musical movement at the bar level. In a music score the time signature appears as two stacked numerals, such as (spoken as ''four–four time''), or a time symbol, such as (spoken as ''common time''). It immediately follows the key signature (or if there is no key signature, the clef symbol). A mid-score time signature, usually immediately following a barline, indicates a change of meter. Most time signatures are either simple (the note values are grouped in pairs, like , , and ), or compound (grouped in threes, like , , and ). Less common signatures indicate complex, mixed, additive, and irrational meters. Time signature notation Most time signatures consist of two numerals, one stacked above the other: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key (music)
In music theory, the key of a piece is the group of pitches, or scale, that forms the basis of a musical composition in Western classical music, jazz music, art music, and pop music. A particular key features a '' tonic (main) note'' and its corresponding '' chords'', also called a ''tonic'' or ''tonic chord'', which provides a subjective sense of arrival and rest. The tonic also has a unique relationship to the other pitches of the same key, their corresponding chords, and pitches and chords outside the key. Notes and chords other than the tonic in a piece create varying degrees of tension, resolved when the tonic note or chord returns. The key may be in the major mode, minor mode, or one of several other modes. Musicians assume major when this is not specified; for example, "this piece is in C" implies that the key of the piece is C major. Popular songs and classical music from the common practice period are usually in a single key; longer pieces in the classical repe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrain
A refrain (from Vulgar Latin ''refringere'', "to repeat", and later from Old French ''refraindre'') is the Line (poetry)">line or lines that are repeated in poetry or in music">poetry.html" ;"title="Line (poetry)">line or lines that are repeated in poetry">Line (poetry)">line or lines that are repeated in poetry or in music—the "chorus" of a song. Poetry, Poetic fixed forms that feature refrains include the villanelle, the virelay, and the sestina. In popular music, the refrain or chorus may contrast with the Verse (popular music), verse melodically, rhythmically, and harmonically; it may assume a higher level of dynamics and activity, often with added instrumentation. Chorus form, or strophic form, is a sectional and/or additive way of structuring a piece of music based on the repetition of one formal section or block played repeatedly. Usage in history Although repeats of refrains may use different words, refrains are made recognizable by reusing the same melody (whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Structure (popular Music)
Song structure is the arrangement of a song, and is a part of the songwriting process. It is typically sectional, which uses repeating forms in songs. Common piece-level musical forms for vocal music include bar form, 32-bar form, verse–chorus form, ternary form, strophic form, and the 12-bar blues. Popular music songs traditionally use the same music for each verse or stanza of lyrics (as opposed to songs that are "through-composed"—an approach used in classical music art songs). Pop and traditional forms can be used even with songs that have structural differences in melodies. The most common format in modern popular music is introduction (intro), verse, pre-chorus, chorus, verse, pre-chorus, chorus, bridge, and chorus, with an optional outro. In rock music styles, notably heavy metal music, there is usually one or more guitar solos in the song, often found after the middle chorus part. In pop music, there may be a guitar solo, or a solo performed with another instrument such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord Progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural, or simply changes) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from the common practice era of Classical music to the 21st century. Chord progressions are the foundation of popular music styles (e.g., pop music, rock music), traditional music, as well as genres such as blues and jazz. In these genres, chord progressions are the defining feature on which melody and rhythm are built. In tonal music, chord progressions have the function of either establishing or otherwise contradicting a tonality, the technical name for what is commonly understood as the " key" of a song or piece. Chord progressions, such as the extremely common chord progression I-V-vi-IV, are usually expressed by Roman numerals in Classical music theory. In many styles of popular and traditional music, chord progressions are expressed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coda (music)
In music, a coda (; ; plural ) is a passage (music), passage that brings a piece (or a movement (music), movement) to an end. It may be as simple as a few bar (music), measures, or as complex as an entire section (music), section. In classical music The presence of a coda as a structural element in a movement is especially clear in works written in particular musical forms. Codas were commonly used in both sonata form and Variation (music), variation movements during the Classical era. In a sonata form movement, the recapitulation (music), recapitulation section will, in general, follow the exposition (music), exposition in its thematic content, while adhering to the home key (music), key. The recapitulation often ends with a passage that sounds like a termination, paralleling the music that ended the exposition; thus, any music coming after this termination will be perceived as extra material, i.e., as a coda. In works in variation form, the coda occurs following the last va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-side And B-side
The A-side and B-side are the two sides of vinyl records and cassettes, and the terms have often been printed on the labels of two-sided music recordings. The A-side of a single usually features a recording that its artist, producer, or record company intends to be the initial focus of promotional efforts and radio airplay, with the aim of it becoming a hit record. The B-side (or "flip-side") is a secondary recording that typically receives less attention, although some B-sides have been as successful as, or more so than, their A-sides. Use of this language has largely declined in the 21st century as the music industry has transitioned away from analog recordings towards digital formats without physical sides, such as downloads and streaming. Nevertheless, some artists and labels continue to employ the terms ''A-side'' and ''B-side'' metaphorically to describe the type of content a particular release features, with ''B-side'' sometimes representing a "bonus" track or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sounds (magazine)
''Sounds'' was a UK weekly pop/rock music newspaper, published from 10 October 1970 to 6 April 1991. It was known for giving away posters in the centre of the paper (initially black and white, then colour from late 1971) and later for covering heavy metal (especially the new wave of British heavy metal (NWOBHM)) and punk and Oi! music in its late 1970s–early 1980s heyday. History ''Sounds'' was produced by Spotlight Publications (part of Morgan Grampian), which was set up by John Thompson and Jo Saul with Jack Hutton and Peter Wilkinson, who left ''Melody Maker'' to start their own company. ''Sounds'' was their first project, a weekly paper devoted to progressive rock and described by Hutton, to those he was attempting to recruit from his former publication, as "a leftwing ''Melody Maker''". ''Sounds'' was intended to be a weekly rival to titles such as ''Melody Maker'' and ''New Musical Express'' (''NME''). ''Sounds'' was one of the first music papers to cover punk. Mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Van Laast
Anthony Van Laast is a British choreographer born 31 May 1951 in Sussex, UK."Anthony Van Laast – Holiday on Ice Mystery artistic director" ''Worthing Herald'', 14 November 2008 He has worked mainly for the stage, concerts, television and film. His works have appeared in the West End and on Broadway. Career Van Laast received dance training at the London School o ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |