|
Mount Yasur
Mount Yasur is a volcano on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, high above sea level, on the coast near Sulphur Bay, northeast of the taller Mount Tukosmera, which was active in the Pleistocene. It has a largely unvegetated pyroclastic cone with a nearly circular summit crater 400 m in diameter. It is a stratovolcano, caused by the eastward-moving Indo-Australian Plate being subducted under the westward-moving Pacific Plate. It has been erupting nearly continuously for several hundred years, although it can usually be approached safely. Its eruptions, which often occur several times an hour, are classified as Strombolian or Vulcanian. A large lava plain creeps across the valley at the base. The glow of the volcano was apparently what attracted Captain James Cook on the first European journey to the island in 1774. Today, the mountain is a sacred area for the John Frum cargo cult. Members of the cult revere John Frum, a deified messenger who foretold the bringing of wealth to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanna (island)
Tanna (sometimes misspelled ''Tana'') is an island in southern Vanuatu. Tanna is the most populous island of Tafea Province, and the third most populous in the country (after Efate and Espiritu Santo). It is home to five indigenous languages, which also rank among the most widely spoken in the whole archipelago, ranging from 3,500 to 11,500 speakers. Tanna has been featured in numerous documentaries and TV shows around the world. This is partly due to Mount Yasur, an active volcano and a major tourist attraction. It is also of interest for its vibrant Melanesian culture, through dances and festivals. The island has attracted the attention of many anthropologists for its cargo cults. Name The name ''Tanna'', first cited by James Cook, is derived from the word ''tana'' in the Kwamera language, meaning 'earth'. Etymologically, ''Tanna'' goes back to Proto-Oceanic *''tanoq'', from Proto-Malayo-Polynesian * ''taneq'', with the same meaning. Geography Tanna is long and wide, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Of America
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five major island territories and various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's third-largest land area and third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three largest metropolitan areas are New York, Los Angeles, and Chicago, and its three most populous states are California, Texas, and Florida. Paleo-Indians migrated from North Asia to North America over 12,000 years ago, and formed various civilizations. Spanish colonization led to the establishment in 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VEI-4 Volcanoes
The volcanic explosivity index (VEI) is a scale used to measure the size of explosive volcanic eruptions. It was devised by Christopher G. Newhall of the United States Geological Survey and Stephen Self in 1982. Volume of products, eruption cloud height, and qualitative observations (using terms ranging from "gentle" to "mega-colossal") are used to determine the explosivity value. The scale is open-ended with the largest eruptions in history given a magnitude of 8. A value of 0 is given for non-explosive eruptions, defined as less than of tephra ejected; and 8 representing a supervolcanic eruption that can eject (240 cubic miles) of tephra and have a cloud column height of over . The scale is logarithmic, with each interval on the scale representing a tenfold increase in observed ejecta criteria, with the exception of between VEI-0, VEI-1 and VEI-2. Classification With indices running from 0 to 8, the VEI associated with an eruption is dependent on how much volcanic materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articles Containing Video Clips
Article often refers to: * Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness * Article (publishing) An article or piece is a written work published in a Publishing, print or electronic media, electronic medium, for the propagation of news, research results, academic analysis or debate. News A news article discusses current or recent news of e ..., a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication Article(s) may also refer to: Government and law * Elements of treaties of the European Union * Articles of association, the regulations governing a company, used in India, the UK and other countries; called articles of incorporation in the US * Articles of clerkship, the contract accepted to become an articled clerk * Articles of Confederation, the predecessor to the current United States Constitution * Article of impeachment, a formal document and charge used for impeachment in the United States * Article of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
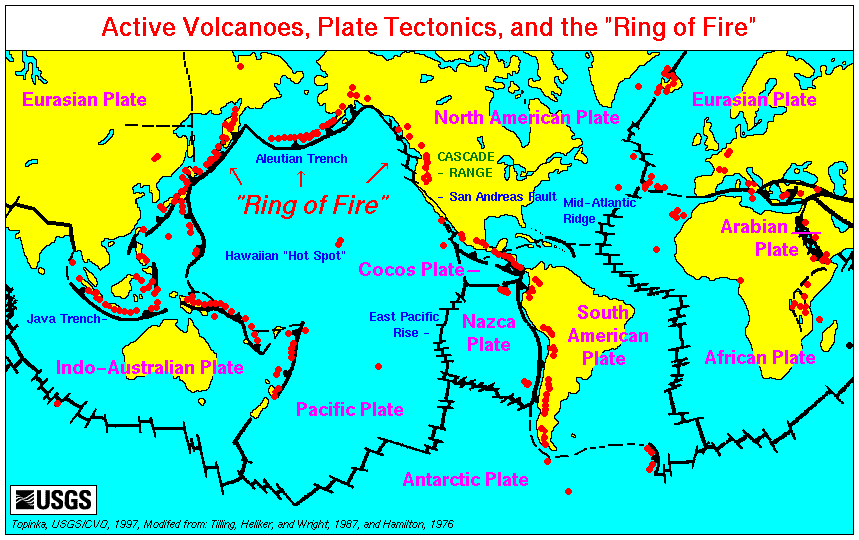
Volcanoes Of Vanuatu
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macdonald%20Mid-Ocean%20Ridge%20Tectonics.pdf Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene Stratovolcanoes
The Holocene () is the current geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene is an interglacial period within the ongoing glacial cycles of the Quaternary, and is equivalent to Marine Isotope Stage 1. The Holocene correlates with the last maximum axial tilt towards the Sun of the Earth's obliquity. The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth, and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global significance for the future evolution of living species, including approximately synchronous lithospheric evidence, or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Vanuatu
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Volcanoes
An active volcano is a volcano that is currently erupting, or has the potential to erupt in the future. Conventionally it is applied to any that have erupted during the Holocene (the current geologic epoch that began approximately 11,700 years ago). A volcano that is not currently erupting but could erupt in the future is known as a dormant volcano. Volcanoes that will not erupt again are known as extinct volcanoes. Overview There are 1,350 potentially active volcanoes around the world, 500 of which have erupted in historical time. Many active volcanoes are located along the Pacific Rim, also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire. An estimated 500 million people live near active volcanoes. ''Historical time'' (or recorded history) is another timeframe for ''active''. The span of recorded history differs from region to region. In China and the Mediterranean, it reaches back nearly 3,000 years, but in the Pacific Northwest of the United States and Canada, it reaches back less tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Guardian Media Group, owned by the Scott Trust Limited. The trust was created in 1936 to "secure the financial and editorial independence of ''The Guardian'' in perpetuity and to safeguard the journalistic freedom and liberal values of ''The Guardian'' free from commercial or political interference". The trust was converted into a limited company in 2008, with a constitution written so as to maintain for ''The Guardian'' the same protections as were built into the structure of the Scott Trust by its creators. Profits are reinvested in its journalism rather than distributed to owners or shareholders. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. The editor-in-chief Katharine Viner succeeded Alan Rusbridger in 2015. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Volcano
An active volcano is a volcano that is currently erupting, or has the potential to erupt in the future. Conventionally it is applied to any that have erupted during the Holocene (the current geologic epoch that began approximately 11,700 years ago). A volcano that is not currently erupting but could erupt in the future is known as a dormant volcano. Volcanoes that will not erupt again are known as extinct volcanoes. Overview There are 1,350 potentially active volcanoes around the world, 500 of which have erupted in historical time. Many active volcanoes are located along the Pacific Rim, also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire. An estimated 500 million people live near active volcanoes. ''Historical time'' (or recorded history) is another timeframe for ''active''. The span of recorded history differs from region to region. In China and the Mediterranean, it reaches back nearly 3,000 years, but in the Pacific Northwest of the United States and Canada, it reaches back less tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Geological Sciences
The International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) is an international non-governmental organization devoted to global cooperation in the field of geology. As of 2023, it represents more than 1 million geoscientists around the world. About Founded in 1961, the IUGS was established to maintain collaboration between the International Geological Congresses, which have taken place every four years since 1875. It is a Scientific Union member of the International Science Council (ISC), formerly the International Council for Science (ICSU), which it recognizes as the co-ordinating body for the international organization of science. Currently, geologists from 121 countries (and regions) are represented in the IUGS. A broad range of scientific topics is covered by its commission, task groups, joint programmes and affiliated organizations. IUGS promotes and encourages the study of geological problems, especially those of worldwide significance, and supports and facilitates international ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |