|
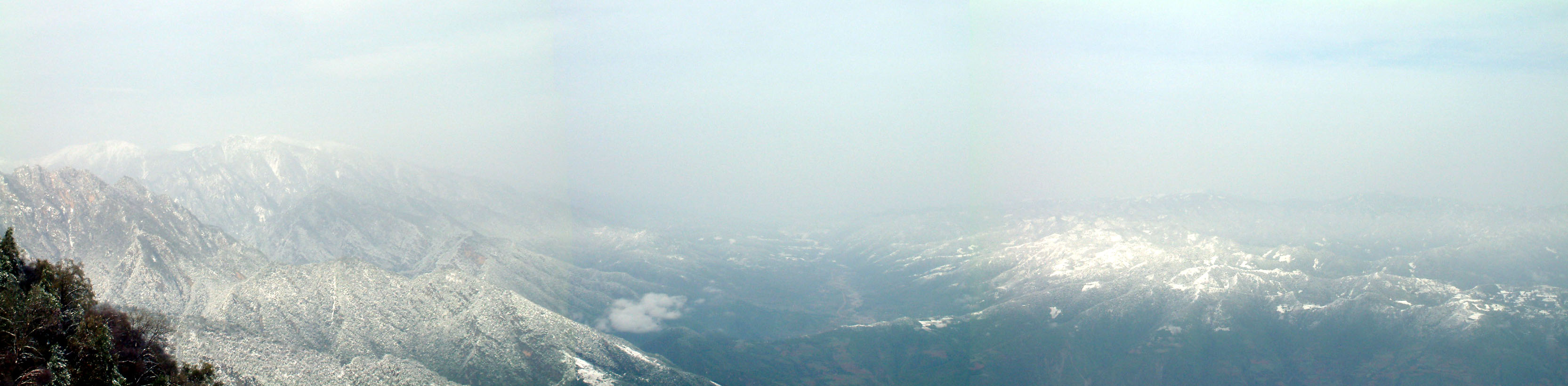
Mount Taibai
Mount Taibai () is a mountain located on the border between Mei, Taibai and Zhouzhi counties in the south west of Shaanxi Province, China. The mount's highest point, Baxian Tower (), rises to a height of and is the tallest in the Qinling Range, as well as the watershed between the Han River and Wei River. Mount Taibai is also the highest mountain in Eastern China. History During the reign of the legendary, morally perfect Three Sovereigns (c. 2852–2070 BC) Mount Taibai was called Mountain of Rich Goods ( pinyin: ''Dun Wu Shān''). During the Xia dynasty (c. 2070–1600 BC) it was known as Mount Taiyi, referring to the brightest star in Chinese astrology with all other stars orbiting around it. In Taoism, Taiyi is a supreme deity and the mountain its physical representation. Furthermore, Taiyi symbolises '' taiji'', a cosmological state of the universe and its affairs on all levels, involving the interaction of Yin and Yang, the Five Phases and finally, all the concrete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra Prominent Peak
An ultra-prominent peak, or ultra for short, is a mountain summit with a topographic prominence of or more; it is also called a P1500. The prominence of a peak is the minimum height of climb to the summit on any route from a higher peak, or from sea level if there is no higher peak. There are approximately 1,500 such peaks on Earth. Some well-known peaks, such as the Matterhorn and Eiger, are not ultras because they are connected to higher mountains by high cols and thus do not achieve enough topographic prominence. The term "ultra" originated with earth scientist Steve Fry, from his studies of the prominence of peaks in Washington (state), Washington in the 1980s. His original term was "ultra major mountain", referring to peaks with at least of prominence. Distribution Currently, over 1,500 ultras have been identified above sea level: 654 in Asia, 357 in North America, 209 in South America, 119 in Europe (including 12 in the Caucasus), 84 in Africa, 54 in Oceania, and 39 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple (Chinese)
Chinese temple architecture refer to a type of structures used as place of worship of Chinese Buddhism, Taoism, Confucianism, or Chinese folk religion, where people revere ethnic Chinese gods and ancestors. They can be classified as: * '' miào'' () or ''diàn'' (), simply means "temple" and mostly enshrines gods of the Chinese pantheon, such as the Dragon King, Tudigong or Matsu; or mythical or historical figures, such as Guandi or Shennong. * '' cí'' (), ''cítáng'' (), ''zōngcí'' () or ''zǔmiào'' (), referring to ancestral temples, mostly enshrining the ancestral gods of a family or clan. * Taoist temples and monasteries: ''guàn'' or '' dàoguàn''; and * Chinese Buddhist temples and monasteries: ''sì'' or ''sìyuàn'' * Temple of Confucius which usually functions as both temple and town school: '' wénmiào'' or '' kŏngmiào''. * Temples of City God (), which worships the patron God of a village, town or a city. * Smaller household shrines or votive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the Mongol Empire, its division. It was established by Kublai (Emperor Shizu or Setsen Khan), the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In Chinese history, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan's enthronement as Khagan in 1206 was described in Chinese language, Chinese as the Han Chinese, Han-style title of Emperor of China, Emperor and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laozi
Laozi (), also romanized as Lao Tzu #Name, among other ways, was a semi-legendary Chinese philosophy, Chinese philosopher and author of the ''Tao Te Ching'' (''Laozi''), one of the foundational texts of Taoism alongside the ''Zhuangzi (book), Zhuangzi''. The name, literally meaning 'Old Master', was likely intended to portray an archaic anonymity that could converse with Confucianism. Modern scholarship generally regards his biographical details as later inventions, and his opus a collaboration. Traditional accounts addend him as , born in the 6th-centuryBC state of Chu during China's Spring and Autumn period (). Serving as the royal archivist for the Zhou dynasty, Zhou court at Wangcheng (Zhou dynasty), Wangcheng (modern Luoyang), he met and impressed Confucius () on one occasion, composing the ''Tao Te Ching'' in a single session before retiring into the western wilderness. A central figure in Chinese culture, Laozi is generally considered the founder of Taoism. He was cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
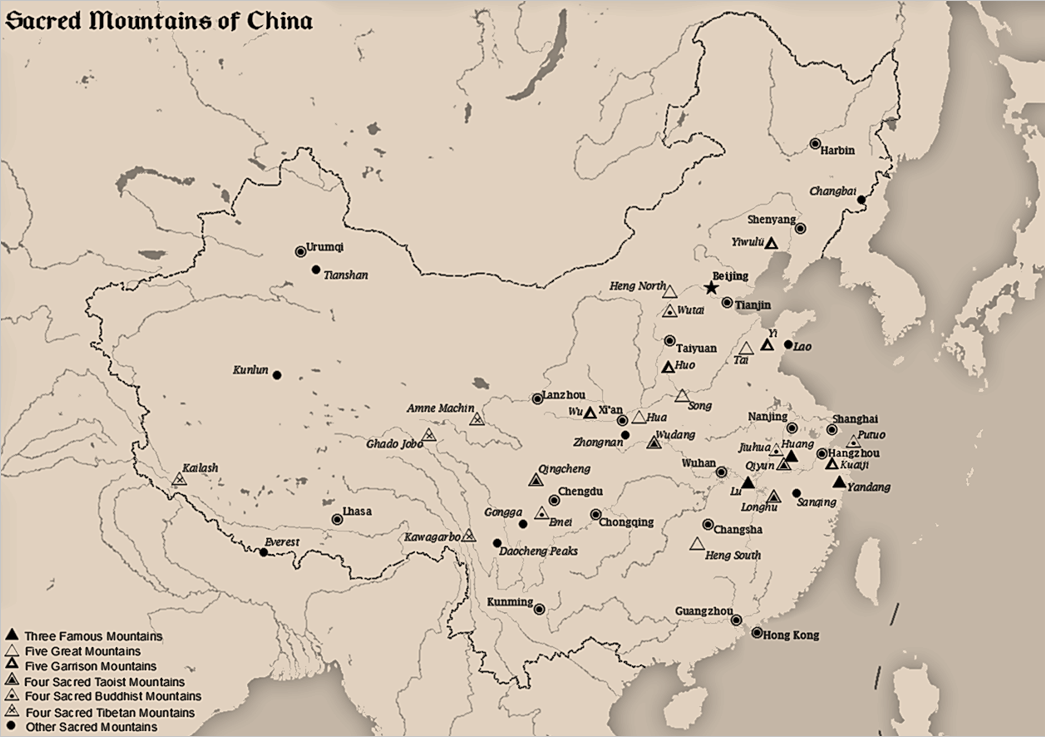
Sacred Mountains Of China
The Sacred Mountains of China are divided into several groups. The ''Five Great Mountains'' () refers to five of the most renowned mountains in Chinese history, which have been the subjects of imperial pilgrimage by emperors throughout ages. They are associated with the supreme God of Heaven and the five main cosmic deities of traditional Chinese religion. The group associated with Buddhism is referred to as the ''Four Sacred Mountains of Buddhism'' (), and the group associated with Taoism is referred to as the ''Four Sacred Mountains of Taoism'' (). The sacred mountains have all been important destinations for pilgrimage, the Chinese term for pilgrimage () being a shortened version of an expression which means "paying respect to a holy mountain" (). The Five Great Mountains The ''Five Great Mountains'' or ''Wuyue'' are arranged according to the five cardinal directions of Chinese geomancy, which includes the center as a direction. The grouping of the five mountains appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yu Youren
Yu Youren (; April 11, 1879 – November 10, 1964) was a Chinese educator, scholar, calligrapher, and politician. Early life He was born on April 11, 1879, in the town of Hedaogang (), Sanyuan County (north of Xi'an), Shaanxi Province, Qing China. His father was Xin Sangong and his mother surnamed Zhao. In 1880, while his father was on business in Sichuan, his mother died and so his aunt brought him to live with her in the village of Yangfu where they lived together for 9 years. After a short stint as a goat herder, he went to a private school at the Mawang Temple in Yangfu and studied under Mr. Diwu. In 1889, he returned with his aunt to Sanyuan and entered the school of Mao Banxiang, under whom he began to study archaic and modern forms of poetry. On occasion, he also had the chance to read a few poems by such Southern Song patriots as Wen Tianxiang and . At the age of 17, he came in first place on entrance examinations and went on to study at the schools like the Dao Aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grotto-heavens
Grotto-heavens () or Dongtian are a type of sacred Taoist site. Grotto-heavens are usually caves, grottoes, mountain hollows, or other underground spaces. In the Tang dynasty, immortals were thought to have lived in certain immortal cave-heaven lands that existed between heaven and earth, shrouded by colorful clouds; wonderful flowers, peach trees and fragrant grass were often said to have grown there. Because every community was supposed to have access to at least one grotto, there were many of them all over China. They were first organized systematically in Tang times by Sima Chengzhen () (647–735, see Zuowanglun) and Du Guangting () (850-933). The most sacred of these sites were divided into two types: The ten greater grotto-heavens and the thirty-six lesser grotto-heavens.Kohn (2000), p. 696. Locations of the ten greater grotto-heavens are as follows: * Mt. Wangwu grotto (Henan) * Mt. Weiyu grotto (Zhejiang) * Mt. Xicheng grotto (Shanxi) * Mt. Xixuan grotto (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li (unit)
''Li'' or ri (, ''lǐ'', or , ''shìlǐ''), also known as the Chinese mile, is a traditional Chinese unit of distance. The ''li'' has varied considerably over time but was usually about one third of an English mile and now has a standardized length of a half-kilometer (). This is then divided into 1,500 chi or "Chinese feet". The character 里 combines the characters for "field" ( 田, ''tián'') and "earth" ( 土, ''tǔ''), since it was considered to be about the length of a single village. As late as the 1940s, a "li" did not represent a fixed measure but could be longer or shorter depending on the ''effort'' required to cover the distance. This traditional unit, in terms of historical usage and distance proportion, can be considered the East Asian counterpart to the Western league unit. However, in English '' league'' commonly means "3 miles." There is also another '' li'' (Traditional: 釐, Simplified: 厘, ''lí'') that indicates a unit of length of a ''chi'', but i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Bai
Li Bai (, 701–762), Literary and colloquial readings, also pronounced Li Bo, courtesy name Taibai (), was a Chinese poet acclaimed as one of the greatest and most important poets of the Tang dynasty and in Chinese history as a whole. He and his friend Du Fu (712–770) were two of the most prominent figures in the flourishing of Chinese poetry under the Tang dynasty, which is often called the "Tang poetry#High Tang, Golden Age of Chinese Poetry". The expression "Three Wonders" denotes Li Bai's poetry, Pei Min's swordplay, and Zhang Xu's calligraphy. Around 1,000 poems attributed to Li are extant. His poems have been collected into the most important Tang dynasty collection, ''Heyue yingling ji'', compiled in 753 by Yin Fan. Thirty-four of Li Bai's poems are included in the anthology ''Three Hundred Tang Poems'', which was first published in the 18th century. Around the same time, translations of his poems began to appear in Europe. In Ezra Pound's famous work ''Cathay (poetry c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinling Range
The Qinling () or Qin Mountains, formerly known as the Nanshan ("Southern Mountains"), are a major east–west mountain range in southern Shaanxi Province, China. The mountains mark the divide between the drainage basins of the Yangtze and Yellow River systems, providing a natural boundary between North and South China and support a huge variety of plant and wildlife, some of which is found nowhere else on earth. To the north is the densely populated Wei River valley, an ancient center of Chinese civilization. To the south is the Han River valley. To the west is the line of mountains along the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. To the east are the lower Funiu and Dabie Mountains, which rise out of the coastal plain. The northern side of the range is prone to hot weather, the rain shadow cast by the physical barrier of the mountains dictating that the land to the north has a semi-arid climate, and is consequently somewhat impoverished in regard to fertility and species d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Central China
South Central China, South-Central China or Central-South China ( zh, c = 中南, p = Zhōngnán, l = Central-South), is a List of regions of China, region of China. It consists of eight provincial administrative regions, namely Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangdong, Guangxi, and Hainan. South Central China sometimes is further classified into regions of South China () and Central China (). Administrative divisions Cities with urban area over one million in population Provincial capitals in bold. See also * Regions of China ** Central China ** South China ** East China ** Northeast China ** Southwest China ** Northwest China Notes References External links {{China topics Regions of China Central China, * South China, * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |