|
Moral Psychology
Moral psychology is the study of human thought and behavior in ethical contexts. Historically, the term "moral psychology" was used relatively narrowly to refer to the study of moral development. This field of study is interdisciplinary between the application of philosophy and psychology. Moral psychology eventually came to refer more broadly to various topics at the intersection of ethics, psychology, and philosophy of mind. Some of the main topics of the field are moral judgment, moral reasoning, moral satisficing, moral sensitivity, moral responsibility, moral motivation, moral identity, moral action, moral development, moral diversity, moral character (especially as related to virtue ethics), altruism, psychological egoism, moral luck, moral forecasting, moral emotion, affective forecasting, and moral disagreement. Today, moral psychology is a thriving area of research spanning many disciplines, with major bodies of research on the biological, cognitive/computational and cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moral Development
Moral development focuses on the emergence, change, and understanding of morality from infancy through adulthood. The theory states that morality develops across the lifespan in a variety of ways. Morality is influenced by an individual's experiences, behavior, and when they are faced with moral issues through different periods of physical and cognitive development. Morality concerns an individual's reforming sense of what is right and wrong; it is for this reason that young children have different moral judgment and character than that of a grown adult. Morality in itself is often a synonym for "rightness" or "goodness." It also refers to a specific code of conduct that is derived from one's culture, religion, or personal philosophy that guides one's actions, behaviors, and thoughts. Some of the earliest known moral development theories came from philosophers like Confucius, Aristotle and Rousseau, who took a more humanist perspective and focused on the development of a sens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kohlberg's Stages Of Moral Development
Lawrence Kohlberg's stages of moral development constitute an adaptation of a psychological theory originally conceived by the Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget. Kohlberg began work on this topic as a psychology graduate student at the University of Chicago in 1958 and expanded upon the theory throughout his life. The theory holds that moral reasoning, a necessary (but not sufficient) condition for ethical behavior, has six developmental stages, each more adequate at responding to moral dilemmas than its predecessor. Kohlberg followed the development of moral judgment far beyond the ages studied earlier by Piaget, who also claimed that logic and morality develop through constructive stages. Expanding on Piaget's work, Kohlberg determined that the process of moral development was principally concerned with justice and that it continued throughout the individual's life, a notion that led to dialogue on the philosophical implications of such research. The six stages of moral develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with selective breeding, artificial selection, which is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Genetic diversity, Variation of traits, both Genotype, genotypic and phenotypic, exists within all populations of organisms. However, some traits are more likely to facilitate survival and reproductive success. Thus, these traits are passed the next generation. These traits can also become more Allele frequency, common within a population if the environment that favours these traits remains fixed. If new traits become more favoured due to changes in a specific Ecological niche, niche, microevolution occurs. If new traits become more favoured due to changes in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Selection
Group selection is a proposed mechanism of evolution in which natural selection acts at the level of the group, instead of at the level of the individual or gene. Early authors such as V. C. Wynne-Edwards and Konrad Lorenz argued that the behavior of animals could affect their survival and reproduction as groups, speaking for instance of actions for the good of the species. In the 1930s, Ronald Fisher and J. B. S. Haldane proposed the concept of kin selection, a form of biological altruism from the gene-centered view of evolution, arguing that animals should sacrifice for their relatives, and thereby implying that they should not sacrifice for non-relatives. From the mid-1960s, evolutionary biologists such as John Maynard Smith, W. D. Hamilton, George C. Williams, and Richard Dawkins argued that natural selection acted primarily at the level of the gene. They argued on the basis of mathematical models that individuals would not altruistically sacrifice fitness for the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Sloan Wilson
David Sloan Wilson (born 1949) is an American evolutionary biologist and a Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Biological Sciences and Anthropology at Binghamton University. He is a son of author Sloan Wilson, a co-founder of Evolution Institute and a co-founder of Prosocial World. He has studied social evolution in Binghamton. Early life and academic career David Sloan Wilson is the son of the writer Sloan Wilson. He graduated with a B.A. with high honors in 1971 from the University of Rochester. He completed his Ph.D. in 1975 at Michigan State University. Wilson then worked as a research fellow in the Biological Laboratories at Harvard University from 1974 to 1975. He held a dual position as research associate in zoology at the University of the Witwatersrand and the University of Washington from 1975 to 1976. After this he was a senior research officer at the South African National Research Institute for the Mathematical Sciences from 1976 to 1977. Wilson moved back to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliott Sober
Elliott R. Sober (born 6 June 1948) is an American philosopher. He is noted for his work in philosophy of biology and general philosophy of science. Sober is Hans Reichenbach Professor and William F. Vilas Research Professor Emeritus in the Department of Philosophy at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. Education and career Sober earned his Ph.D. in philosophy from Harvard University under the supervision of Hilary Putnam, after doing graduate work at Cambridge University under the supervision of Mary Hesse. His work has also been strongly influenced by the biologist Richard Lewontin, and he has collaborated with David Sloan Wilson, Steven Orzack and Mike Steel, also biologists. Sober joined the Wisconsin faculty in 1974, and retired in 2023. He was also a tenured professor of philosophy at Stanford University in 2003-04, before returning to Wisconsin. He will be a visiting professor at Stanford for 2023-2026. Sober has served as the president of both the Central Divis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Psychology
The ''Annual Review of Psychology'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes review articles about psychology. First published in 1950, its longest-serving editors have been Mark Rosenzweig (1969–1994) and Susan Fiske (2000–present). As of 2023, ''Annual Review of Psychology'' is being published as open access, under the Subscribe to Open model. As of 2024, '' Journal Citation Reports'' gives the journal a 2023 impact factor of 23.6, ranking it first of 92 journal titles in the category "Psychology (Science)" and first of 218 titles in the category "Psychology, Multidisciplinary (Social Science)". History In 1947, the board of directors of the publishing company Annual Reviews asked a number of psychologists if it would be useful to have a journal that published an annual volume of review articles that summarized recent developments in the field. Responses were very positive, so in September 1947 they announced that the first volume of the ''Annual Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation. The scientific theory of evolution by natural selection was conceived independently by two British naturalists, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, in the mid-19th century as an explanation for why organisms are adapted to their physical and biological environments. The theory was first set out in detail in Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species''. Evolution by natural selection is established by observable facts about living organisms: (1) more offspring are often produced than can possibly survive; (2) phenotypic variatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
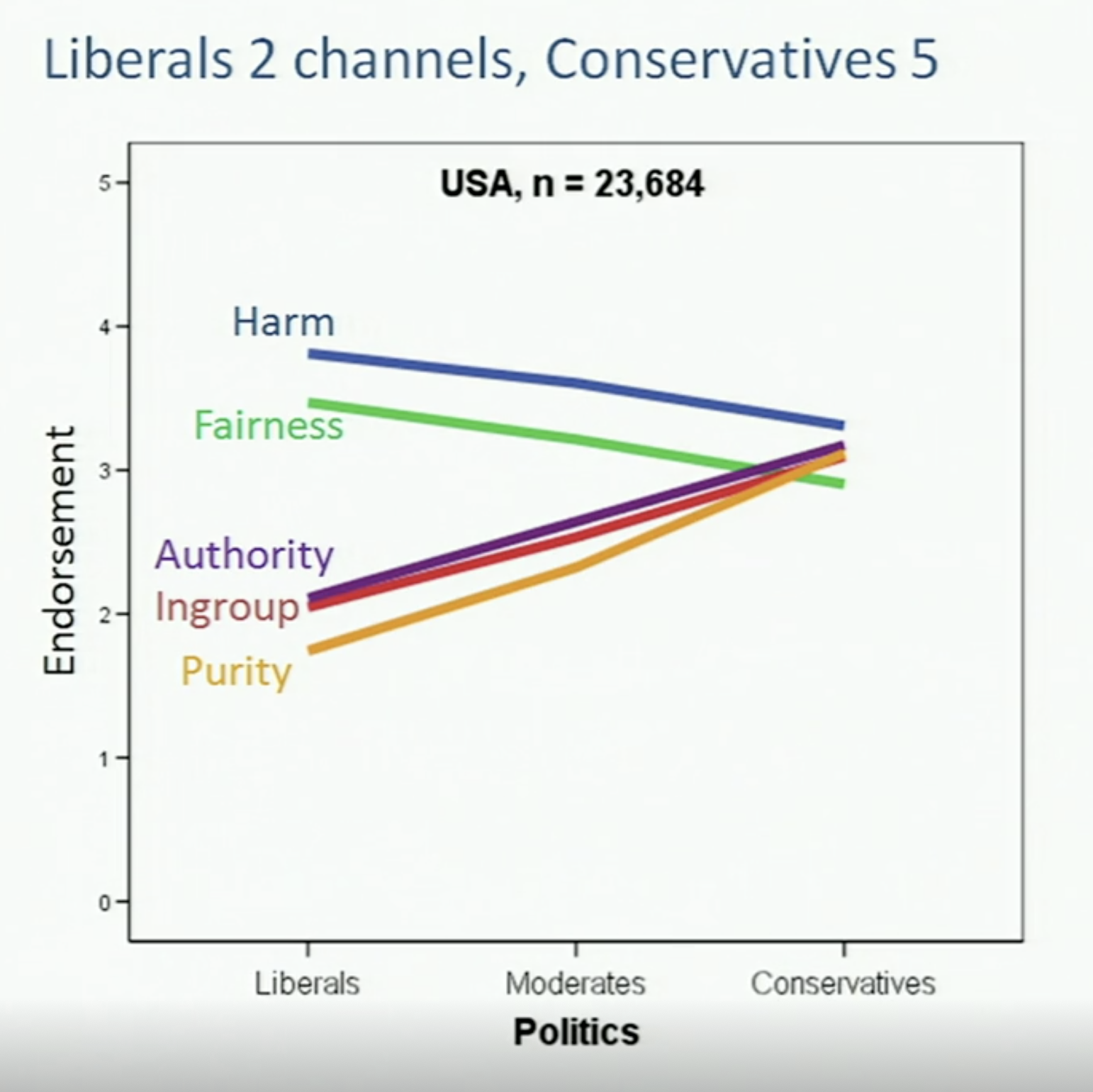
Moral Foundations Theory
Moral foundations theory is a social psychological theory intended to explain the origins of and variation in human moral reasoning on the basis of innate, modular foundations. It was first proposed by the psychologists Jonathan Haidt, Craig Joseph, and Jesse Graham, building on the work of cultural anthropologist Richard Shweder. More recently, Mohammad Atari, Jesse Graham, and Jonathan Haidt have revised some aspects of the theory and developed new measurement tools. The theory has been developed by a diverse group of collaborators and popularized in Haidt's book '' The Righteous Mind''. The theory proposes that morality is "more than one thing", first arguing for five foundations, and later expanding for six foundations (adding Liberty/Oppression): * Care/harm * Fairness/cheating * Loyalty/betrayal * Authority/subversion * Sanctity/degradation * Liberty/oppression. Its authors remain open to the addition, subtraction, or modification of the set of foundations. Although the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defining Issues Test
The Defining Issues Test is a component model of moral development devised by James Rest in 1974. The University of Minnesota formally established the Center for the Study of Ethical Development as a vehicle for research around this test in 1982. The Center relocated to larger premises within the University of Alabama and is now located in Capital Hall. Because it is not possible to score DIT-1 and DIT-2 personally, the Center of Ethical Development at the University of Alabama offers scoring to scholars and researchers worldwide. The Defining Issues Test is a proprietary self-report measure which uses a Likert-type scale to give quantitative ratings and rankings to issues surrounding five different moral dilemmas, or stories. Specifically, respondents rate 12 issues in terms of their importance to the corresponding dilemma and then rank the four most important issues. The issue statements that respondents respond to are not fully developed stances which fall on one side or ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trolley Problem
The trolley problem is a series of thought experiments in ethics, psychology, and artificial intelligence involving stylized ethical dilemmas of whether to sacrifice one person to save a larger number. The series usually begins with a Scenario (vehicular automation), scenario in which a runaway train, runaway tram, trolley or train is on course to collide with and kill a number of people (traditionally five) down the railway track, track, but a driver or bystander can intervene and divert the vehicle to kill just one person on a different track. Then other variations of the runaway vehicle, and analogous life-and-death dilemmas (medical, judicial, etc.) are posed, each containing the option to either do nothing, in which case several people will be killed, or intervene and sacrifice one initially "safe" person to save the others. Opinions on the ethics of each scenario turn out to be sensitive to details of the story that may seem immaterial to the abstract dilemma. The questi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |