|
Monument To General Manfredo Fanti, Florence
The Monument to General Manfredo Fanti commemorates General Manfredo Fanti (1806-1865), a soldier and leader in battles for Italian independence and unification. The statue, erected in 1873, is located in the Piazza San Marco in central Florence, region of Tuscany, Italy. After his death, the city commissioned a statue from Pio Fedi, a sculptor in Florence. The statue was erected in the piazza, which stands before the headquarters of the Royal Military Command, on the corner of via Arazzieri. The general in his cape and sword, nearly steps off the pedestal. The plinth has two marble bas-reliefs, one of the arms of war, the other an episode in the Battle of San Martino. At the four corners are four figures symbolize politics, strategy, tactics, and fortifications. Florentines have contrasted this statue with Fedi's other masterpiece: the ''Rape of Polyxena'' (1865) in the Loggia dei Lanzi file:Firenze, loggia dei lanzi (2020) 01.jpg, 300px, The Loggia dei Lanzi, also called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pio Fedi, Monumento Al Generale Manfredo Fanti, Firenze 1873, 01 or П. O., Greek-Australian poet born 1951
{{Disambiguation, geo ...
Pio or PIO may refer to: Places * Pio Lake, Italy * Pio Island, Solomon Islands * Pio Point, Bird Island, south Atlantic Ocean People * Pio (given name) * Pio (surname) * Pio (footballer, born 1986), Brazilian footballer * Pio (footballer, born 1988), Brazilian footballer PIO * Programmed input–output, a method of computer data transmission * Public information officer of a government department * Person of Indian Origin, a person of Indian descent * Pilot-induced oscillation, an undesirable phenomenon in aircraft control Other uses * Pio, prefix of 250 octets, a unit of information in computer science See also * Pi O П. O. (or Pi O, born 1951) is a Greek-Australian, working class, anarchist poet. Biography Born in Katerini, Greece, П. O. came to Australia with his family around 1954. After time in Bonegilla Migrant Reception and Training Centre, the fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manfredo Fanti
Manfredo Fanti (23 February 1806 – 5 April 1865) was an Italian general; he is known as the founder of the Royal Italian Army. Biography Manfredo Fanti was born at Carpi (Emilia-Romagna) and educated at the military college of Modena. In 1831 he was implicated in the revolutionary movement organized by Ciro Menotti, and was condemned to death and hanged in effigy, but escaped to France, where he was given an appointment in the French corps of engineers. In 1833 he took part in Mazzini's abortive attempt to invade Savoy, and in 1835 he went to Spain to serve in Queen Christina's army against the Carlists. There he remained for thirteen years, distinguishing himself in battle and rising to a high staff appointment. But on the outbreak of the war between Piedmont and Austria in 1848 he hurried back to Italy, and although at first his services were rejected both by the Piedmontese government and the Lombard provisional government, he was afterwards given the command of a Lomba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Unification
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of Sardinia, resulting in the creation of the Kingdom of Italy. Inspired by the rebellions in the 1820s and 1830s against the outcome of the Congress of Vienna, the unification process was precipitated by the Revolutions of 1848, and reached completion in 1870 after the capture of Rome and its designation as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy. Individuals who played a major part in the struggle for unification and liberation from foreign domination included King Victor Emmanuel II of Italy; politician, economist and statesman Camillo Benso, Count of Cavour; general Giuseppe Garibaldi; and journalist and politician Giuseppe Mazzini. Borrowing from the old Latin title '' Pater Patriae'' of the Roman emperors, the Italians gave to King Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piazza San Marco, Florence
Piazza San Marco is a city square in Florence, Italy. In the center of the piazza is the Monument to Generale Manfredo Fanti. Buildings around the square *Museo Nazionale di San Marco * Basilica di San Marco (Florence) *Accademia di Belle Arti di Firenze The Accademia di Belle Arti di Firenze () is an instructional art academy in Florence, in Tuscany, in central Italy. It was founded by Cosimo I de' Medici in 1563, under the influence of Giorgio Vasari. Michelangelo, Benvenuto Cellini and ... * Palazzina della Livia * Bernardo Fallani Marco Odonyms referring to religion {{Italy-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025. Florence was a centre of Middle Ages, medieval European trade and finance and one of the wealthiest cities of that era. It is considered by many academics to have been the birthplace of the Renaissance, becoming a major artistic, cultural, commercial, political, economic and financial center. During this time, Florence rose to a position of enormous influence in Italy, Europe, and beyond. Its turbulent political history includes periods of rule by the powerful House of Medici, Medici family and numerous religious and republican revolutions. From 1865 to 1871 the city served as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy. The Florentine dialect forms the base of Italian language, standard Italian and it became the language of culture throughout Italy due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of 3,660,834 inhabitants as of 2025. The capital city is Florence. Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its influence on high culture. It is regarded as the birthplace of the Italian Renaissance and of the foundations of the Italian language. The prestige established by the Tuscan dialect's use in literature by Dante Alighieri, Petrarch, Giovanni Boccaccio, Niccolò Machiavelli and Francesco Guicciardini led to its subsequent elaboration as the language of culture throughout Italy. It has been home to many figures influential in the history of art and science, and contains well-known museums such as the Uffizi and the Palazzo Pitti. Tuscany is also known for its wines, including Chianti, Vino Nobile di Montepulciano, Morellino di Scansano, Brunello di Montalcino and white Vernaccia di San Gimignano. Having a strong linguistic and cultural identity, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pio Fedi
Pio Fedi (31 May 1816, Viterbo - 1 June 1892, Florence) was an Italian sculptor who worked chiefly in the Romantic style. Biography He was born to Leopoldo Fedi, a small landowner, and his wife, Camilla née Franchini. Due to economic difficulties, they left Viterbo when he still quite young; living in Arezzo and Florence. There, he worked for a goldsmith. This led to lessons in engraving from Raffaello Sanzio Morghen and Giovita Garavaglia. From 1838 to 1840, he lived in Vienna with his father and continued his studies at the Academy of Fine Arts, but he was forced to abandon that potential career due to eye problems caused by the acid fumes. In addition, he designed the Monument to General Manfredo Fanti, molded in bronze by , which stands in the Piazza San Marco. His memorial to the poet Giovanni Battista Niccolini is in the church of Santa Croce. The statue, an allegory of the ''Freedom of Poetry'', may have inspired Bartholdi's depiction of the Statue of Liberty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
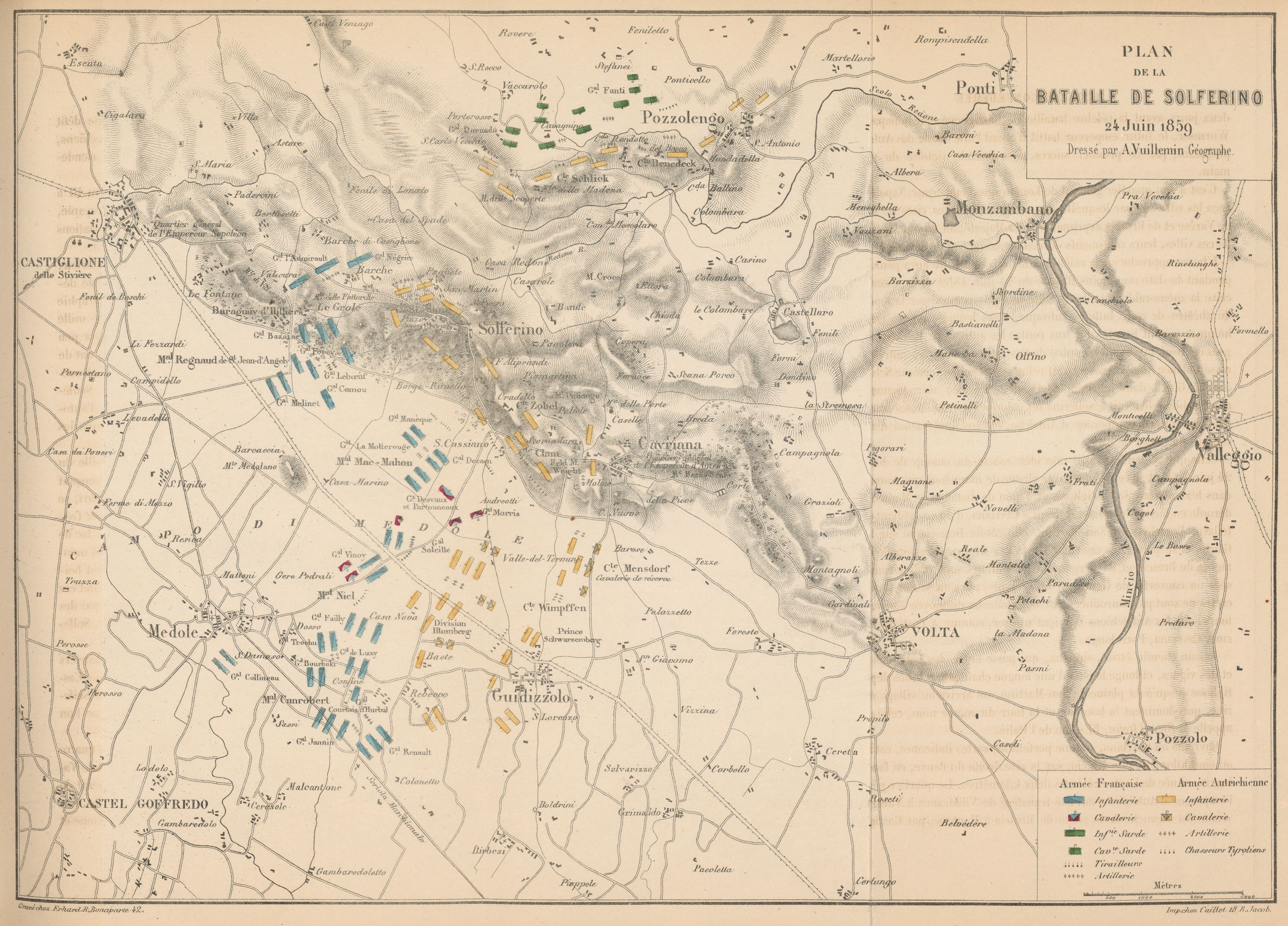
Battle Of San Martino
The Battle of Solferino (referred to in Italy as the Battle of Solferino and San Martino) on 24 June 1859 resulted in the victory of the allied French army under Napoleon III and the Piedmont-Sardinian army under Victor Emmanuel II (together known as the Franco-Sardinian alliance) against the Austrian army under Emperor Franz Joseph I. It was the last major battle in world history where all the armies were under the personal command of their monarchs. Perhaps 300,000 soldiers fought in the important battle, the largest since the Battle of Leipzig in 1813. There were about 130,000 Austrian troops and a combined total of 140,000 French and allied Piedmontese troops. After the battle, the Austrian emperor refrained from further direct command of the army. The battle led the Swiss Jean-Henri Dunant to write his book ''A Memory of Solferino''. Although he did not witness the battle (his statement is contained in an "unpublished page" included in the 1939 English edition published by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loggia Dei Lanzi
file:Firenze, loggia dei lanzi (2020) 01.jpg, 300px, The Loggia dei Lanzi, also called the Loggia della Signoria, is a building on the south corner of the Piazza della Signoria in Florence, Italy, adjoining the Uffizi, Uffizi Gallery (leading to the Arno), and diagonally the Palazzo della Signoria, the political center of the city. It consists of wide arches open to the street. The arches rest on clustered pilasters with Corinthian capitals. The wide arches appealed so much to the Florentines that Michelangelo proposed that they should be continued all around the Piazza della Signoria. History Sometimes erroneously referred to as ''Loggia dell' Andrea Orcagna, Orcagna'' because it was once thought to be designed by that artist, it was built between 1376 and 1382 by Benci di Cione and Simone di Francesco Talenti, possibly following a design by Jacopo di Sione, to house the assemblies of the people and hold public ceremonies, such as the swearing into office of the Gonfaloniers an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpi, Italy
Carpi (; ) is an Italian town and ''comune'' of about 71,000 inhabitants in the province of Modena, Emilia-Romagna. It is a busy centre for industrial and craft activities and for cultural and commercial exchanges. History The name ''Carpi'' is derived from ''Carpinus betulus, carpinus'' 'hornbeam', a tree particularly widespread in medieval times in the Po River, Po Valley region. In prehistoric times it was a settlement of the Villanovan Culture. The foundation by the Lombards, Lombard king Aistulf of Santa Maria in Castello, Carpi, St. Mary's Church in the castle (''Castrum Carpi'') in 752 was the first step in the current settlement of the city. From 1319 to 1525, it was ruled by the Pio di Savoia, Pio family, after whom it was acquired by the House of Este, Este, as part of the Duchy of Modena. The city received a Silver Medal for Military Valour in recognition of its participation in the resistance against the Wehrmacht, German occupation during World War II. The town has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monuments And Memorials In Florence
A monument is a type of structure that was explicitly created to commemorate a person or event, or which has become relevant to a social group as a part of their remembrance of historic times or cultural heritage, due to its artistic, historical, political, technical or architectural importance. Examples of monuments include statues, (war) memorials, historical buildings, archaeological sites, and cultural assets. If there is a public interest in its preservation, a monument can for example be listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The '' Palgrave Encyclopedia of Cultural Heritage and Conflict'' gives the next definition of monument:Monuments result from social practices of construction or conservation of material artifacts through which the ideology of their promoters is manifested. The concept of the modern monument emerged with the development of capital and the nation-state in the fifteenth century when the ruling classes began to build and conserve what were termed monument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Sculptures In Florence
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloids (such as arsenic or silicon). These additions produce a range of alloys some of which are harder than copper alone or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period during which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age, which started about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |