|
Molybdenum Oxotransferase
The enzyme super-family of molybdenum oxotransferases all contain molybdenum, and promote oxygen atom transfer reactions.* Stephen J. Lippard, Jeremy M. Berg, ''Principles of Bioinorganic Chemistry'', University Science Books, 1994, , pg 31/ref> Enzymes in this family include DMSO reductase, xanthine oxidase, nitrite reductase Nitrite reductase refers to any of several classes of enzymes that catalyze the reduction of nitrite. There are two classes of NIR's. A multi haem enzyme reduces NO2− to a variety of products. Copper containing enzymes carry out a single elect ..., and sulfite oxidase. See also * Bioinorganic chemistry References Metalloproteins Molybdenum compounds {{enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' Chemical specificity, specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, but the element was discovered (in the sense of differentiating it as a new entity from the mineral salts of other metals) in 1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The metal was first isolated in 1781 by Peter Jacob Hjelm. Molybdenum does not occur naturally as a free metal on Earth; it is found only in various oxidation states in minerals. The free element, a silvery metal with a grey cast, has the sixth-highest melting point of any element. It readily forms hard, stable carbides in alloys, and for this reason most of the world production of the element (about 80%) is used in steel alloys, including high-strength alloys and superalloys. Most molybdenum compounds have low so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DMSO Reductase
DMSO reductase is a molybdenum-containing enzyme that catalyzes reduction of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to dimethyl sulfide (DMS). This enzyme serves as the terminal reductase under anaerobic conditions in some bacteria, with DMSO being the terminal electron acceptor. During the course of the reaction, the oxygen atom in DMSO is transferred to molybdenum, and then reduced to water. DMSO reductase (DMSOR) and other members of the DMSO reductase family are unique to bacteria and archaea. Enzymes of this family in anaerobic oxidative phosphorylation and inorganic-donor-based lithotrophic respiration. These enzymes have been engineered to degrade oxoanions. DMSOR catalyzes the transfer of two electrons and one oxygen atom in the reaction: The active site of DMSOR contains molybdenum, which is otherwise rare in biology. Tertiary structure and active site As for other members of DMSO reductase family, the tertiary structure of DMSOR is composed of Mo-surrounding domains I-IV, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
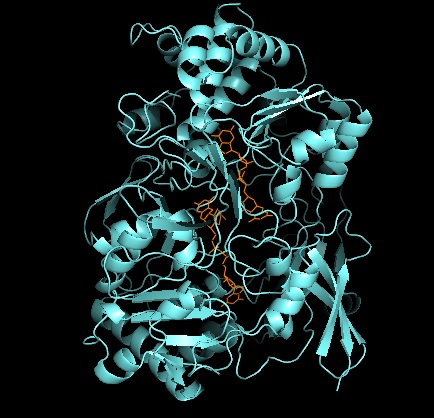
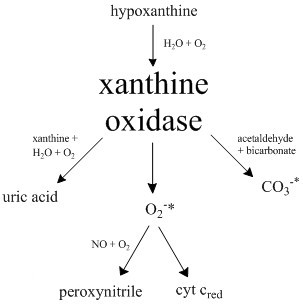
Xanthine Oxidase
Xanthine oxidase (XO, sometimes XAO) is a form of xanthine oxidoreductase, a type of enzyme that generates reactive oxygen species. These enzymes catalyze the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and can further catalyze the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. These enzymes play an important role in the catabolism of purines in some species, including humans. Xanthine oxidase is defined as an ''enzyme activity'' (EC 1.17.3.2). The same protein, which in humans has the HGNC approved gene symbol ''XDH'', can also have xanthine dehydrogenase activity (EC 1.17.1.4). Most of the protein in the liver exists in a form with xanthine dehydrogenase activity, but it can be converted to xanthine oxidase by reversible sulfhydryl oxidation or by irreversible proteolytic modification. Reaction The following chemical reactions are catalyzed by xanthine oxidase: * hypoxanthine + H2O + O2 \rightleftharpoons xanthine + H2O2 * xanthine + H2O + O2 \rightleftharpoons uric acid + H2O2 * Xant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrite Reductase
Nitrite reductase refers to any of several classes of enzymes that catalyze the reduction of nitrite. There are two classes of NIR's. A multi haem enzyme reduces NO2− to a variety of products. Copper containing enzymes carry out a single electron transfer to produce nitric oxide. Iron based There are several types of iron based enzymes. Cytochrome cd1, or ''Pseudomonas'' cytochrome oxidase contains two c and two d type hemes with two polypeptide chains. Different forms of this reductase catalyze the formation of nitric oxide or nitrous oxide. A version of this compound was originally called [Ferrocytochrome c-551:oxidoreductase]. It was initially considered an oxidase. It catalyzes the reduction of NO2− to NO. This tetraheme enzyme has two Protein subunit, subunits, each containing a c-type and a d-type heme. The reduced d hemes bind nitrite and convert it to product. Cytochrome c nitrite reductase (ccNIR) is a multiheme enzyme that converts nitrite to ammonia on each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfite Oxidase
Sulfite oxidase () is an enzyme in the mitochondria of all eukaryotes, with exception of the yeasts. It oxidizes sulfite to sulfate and, via cytochrome c, transfers the electrons produced to the electron transport chain, allowing generation of ATP in oxidative phosphorylation. This is the last step in the metabolism of sulfur-containing compounds and the sulfate is excreted. Sulfite oxidase is a metallo-enzyme that utilizes a molybdopterin cofactor and a heme group (in a case of animals). It is one of the cytochromes ''b''5 and belongs to the enzyme super-family of molybdenum oxotransferases that also includes DMSO reductase, xanthine oxidase, and nitrite reductase. In mammals, the expression levels of sulfite oxidase is high in the liver, kidney, and heart, and very low in spleen, brain, skeletal muscle, and blood. Structure As a homodimer, sulfite oxidase contains two identical subunits with an N-terminal domain and a C-terminal domain. These two domains are connected b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinorganic Chemistry
Bioinorganic chemistry is a field that examines the role of metals in biology Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditar .... Bioinorganic chemistry includes the study of both natural phenomena such as the behavior of metalloproteins as well as artificially introduced metals, including those that are essential element, non-essential, in medicine and toxicology. Many biological processes such as cellular respiration, respiration depend upon molecules that fall within the realm of inorganic chemistry. The discipline also includes the study of inorganic models or mimics that imitate the behaviour of metalloproteins. As a mix of biochemistry and inorganic chemistry, bioinorganic chemistry is important in elucidating the implications of electron-transfer proteins, substrate bindin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metalloproteins
Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large proportion of all proteins are part of this category. For instance, at least 1000 human proteins (out of ~20,000) contain zinc-binding protein domains although there may be up to 3000 human zinc metalloproteins. Abundance It is estimated that approximately half of all proteins contain a metal. In another estimate, about one quarter to one third of all proteins are proposed to require metals to carry out their functions. Thus, metalloproteins have many different functions in cells, such as storage and transport of proteins, enzymes and signal transduction proteins, or infectious diseases. The abundance of metal binding proteins may be inherent to the amino acids that proteins use, as even artificial proteins without evolutionary history will readily bind metals. Most metals in the human body are bound to proteins. For instance, the relatively high concentration of iron in the human body i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |