|
Moby Dick (2010 Film)
''Moby Dick'' (alternatively titled ''2010: Moby Dick'' or ''Moby Dick: 2010'') is a 2010 American thriller film that is an adaptation of Herman Melville's 1851 novel ''Moby-Dick''. The film is an Asylum production, and stars Barry Bostwick as Captain Ahab. It also stars Renee O'Connor, Michael B. Teh, and Adam Grimes and is directed by Trey Stokes. Plot On November 20, 1969, 50 miles off Soviet waters, the USS ''Acushnet'' dives under the ice. A young Ahab listens to sonar for enemy submarines when suddenly he detects an unknown target. When the captain listens, he hears nothing, but Ahab insists on a presence in the emptiness. The target dives into a trench, but the captain abandons his search in favor of photographing the target. The target attacks the submarine and brings the vessel up to the icy surface, revealing to be an enormous white whale. Ahab survives, but loses his left leg to the beast when it hauls the other half of the submarine back underwater. In the present day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trey Stokes
Trey Stokes (born 1960 in Nashville, Tennessee) is an American filmmaker and puppeteer, best known for his ''Star Wars'' parody series '' Pink Five'', and his puppeteering work on various movie, TV, and motion-ride projects. Early career Stokes majored in Cinema Production at the University of Southern California. After working as a puppeteer for several years, he was hired as the head puppeteer on the 1988 remake of ''The Blob''. This led to many other film puppeteering jobs, including ''Species'', '' RoboCop 2'', and eventually head puppeteer on ''The Abyss''. In 1990, he programmed the motion simulator for ''The Funtastic World of Hanna-Barbera'' at Universal Studios Florida. In 1995, Stokes was hired as the animation department supervisor for Tippett Studio, and worked on the films ''Starship Troopers'' and '' My Favorite Martian (film)''. Stokes gained some notoriety for helping debunk Fox Network's ''Alien Autopsy: Fact or Fiction?'' as a hoax with his articleHow to Buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Science Monitor
''The Christian Science Monitor'' (''CSM''), commonly known as ''The Monitor'', is a nonprofit news organization that publishes daily articles both in electronic format and a weekly print edition. It was founded in 1908 as a daily newspaper by Mary Baker Eddy, founder of the new religious movement Christian Science, Church of Christ, Scientist. Since its founding, the newspaper has been based in Boston. Over its existence, seven ''Monitor'' journalists have been awarded the Pulitzer Prize, including Edmund Stevens (1950), John Hughes (1968), Howard James (1968), Robert Cahn (1969), Richard Strout (1978), David S. Rohde (1996), and Clay Bennett (2002)."Pulitzer Prizes" at ''The Christian Science Monitor'' official website History 20th century [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Bales By Gage Skidmore
Paul may refer to: People * Paul (given name), a given name, including a list of people * Paul (surname), a list of people * Paul the Apostle, an apostle who wrote many of the books of the New Testament * Ray Hildebrand, half of the singing duo Paul & Paula * Paul Stookey, one-third of the folk music trio Peter, Paul and Mary * Billy Paul, stage name of American soul singer Paul Williams (1934–2016) * Vinnie Paul, drummer for American Metal band Pantera * Paul Avril, pseudonym of Édouard-Henri Avril (1849–1928), French painter and commercial artist * Paul, pen name under which Walter Scott wrote ''Paul's letters to his Kinsfolk'' in 1816 * Jean Paul, pen name of Johann Paul Friedrich Richter (1763–1825), German Romantic writer Places *Paul, Cornwall, a village in the civil parish of Penzance, United Kingdom *Paul (civil parish), Cornwall, United Kingdom *Paul, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community *Paul, Idaho, United States, a city *Paul, Nebraska, United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulkington (character Moby-Dick)
Bulkington is a character in Herman Melville's 1851 novel ''Moby-Dick''. Bulkington is referred to only by his last name and appears only twice, briefly in Chapter 3, "The Spouter Inn", and then in Chapter 23, "The Lee Shore", a short chapter of several hundred words devoted entirely to him. Critics and scholars, however, have paid attention to his role. Some see Bulkington as representing a historical or contemporary figure, or take his early appearance and then disappearance to bolster the theory that Melville composed the novel in several stages and Bulkington became unnecessary when Melville expanded his conception. The Bulkington Pass is on the south side of the Flask Glacier and west of Bildad Peak, a series of features that the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-names Committee named after characters from ''Moby-Dick''.U.S. Geological SurveAntarctica Detail/ref> Appearances In Chapter 3, "The Spouter Inn", the crew of the ship USS ''Grampus'' celebrate their return from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queequeg
Queequeg is a character in the 1851 novel ''Moby-Dick'' by American author Herman Melville. The story outlines his royal, Polynesian descent, as well as his desire to "visit Christendom" that led him to leave his homeland. Queequeg is visually distinguished by his striking facial tattoos and tan skin. Ishmael encounters Queequeg in Chapter Three and they become unlikely friends. Once aboard the whaling ship the ''Pequod'', Queequeg becomes the harpooner for the mate Starbuck. Familial and cultural history Queequeg is native to the fictional island of Kokovoko (also known as Rokovoko), an "island far away to the West and South", or more specifically in the South Pacific Ocean. He was the son of High Chief, King as well various other well-respected individuals of his community. Queequeg's culture is referenced to be cannibalistic. The narration of the book makes it clear that cannibalism was not universally accepted at this time. In the novel, Queequeg is described as having ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishmael (Moby-Dick)
Ishmael is a character in Herman Melville's ''Moby-Dick'' (1851), which opens with the line "Call me Ishmael." He is the first-person narrator of much of the book. Because Ishmael plays a minor role in the plot, early critics of ''Moby-Dick'' assumed that Captain Ahab was the protagonist. Many either confused Ishmael with Melville or overlooked the role he played. Later critics distinguished Ishmael from Melville, and some saw his mystic and speculative consciousness as the novel's central force rather than Captain Ahab's monomaniacal force of will. The Biblical name Ishmael has come to symbolize orphans, exiles, and social outcasts. By contrast with his eponym from the Book of Genesis, who is banished into the desert, Melville's Ishmael wanders upon the sea. Each Ishmael, however, experiences a miraculous rescue; in the Bible from thirst, in the novel from drowning. Characteristics Both Ahab and Ishmael are fascinated by the whale, but whereas Ahab perceives him exclusivel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical parts of the oceans and seas where corals can develop. Most of the approximately 440 atolls in the world are in the Pacific Ocean. Two different, well-cited models, the subsidence model and the antecedent karst model, have been used to explain the development of atolls.Droxler, A.W. and Jorry, S.J., 2021. "The Origin of Modern Atolls: Challenging Darwin's Deeply Ingrained Theory". ''Annual Review of Marine Science'', 13, pp. 537–573. According to Charles Darwin's subsidence model, the formation of an atoll is explained by the sinking of a volcanic island around which a coral fringing reef has formed. Over geologic time, the volcanic island becomes extinct and eroded as it subsides completely beneath the surface of the ocean. As the volcanic island subsides, the coral fringing reef becomes a ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
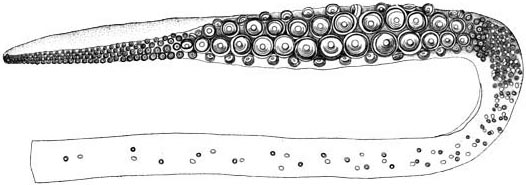
Giant Squid
The giant squid (''Architeuthis dux'') is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida (though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also ... in the family (biology), family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of deep-sea gigantism, abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum body size at around for females, with males slightly shorter, from the cephalopod fin, posterior fins to the tip of its long cephalopod limb, arms. This makes it longer than the colossal squid at an estimated , but substantially lighter, as it is less robust and its arms make up much of the length. The Mantle (mollusc), mantle of the giant squid is about long (longer for females, shorter for males), and the feeding tentacles of the giant squid, concealed in life, are . Clai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). Yields in the low kilotons can devastate cities. A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than 1.2 megatons of TNT (5.0 PJ). Apart from the blast, effects of nuclear weapons include firestorms, extreme heat and ionizing radiation, radioactive nuclear fallout, an electromagnetic pulse, and a radar blackout. The first nuclear weapons were developed by the Allied Manhattan Project during World War II. Their production continues to require a large scientific and industrial complex, pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. "Sonar" can refer to one of two types of technology: ''passive'' sonar means listening for the sound made by vessels; ''active'' sonar means emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and sodar (an upward-looking in-air sonar) is used for atmospheric investigations. The term ''sonar'' is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low (infrasonic) to extrem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
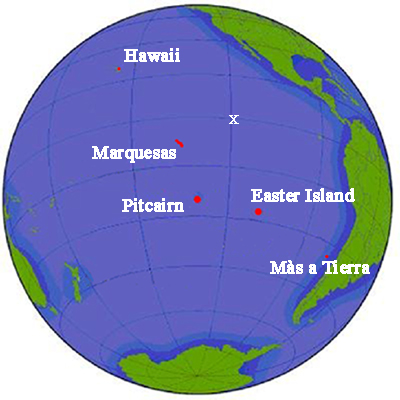
Essex (1799 Whaleship)
''Essex'' was an American whaling ship from Nantucket, Massachusetts, which was launched in 1799. On November 20, 1820, while at sea in the southern Pacific Ocean under the command of Captain George Pollard Jr., the ship was attacked and sunk by a sperm whale. About from the coast of South America, the 20-man crew was forced to make for land in three whaleboats with what food and water they could salvage from the wreck. After a month at sea the crew landed on the uninhabited Henderson Island. Three men elected to stay on the island, from which they were rescued in April 1821, while the remaining seventeen set off again for the coast of South America. The men suffered severe dehydration, starvation and exposure on the open ocean, and the survivors eventually resorted to cannibalism. By the time they were rescued in February 1821, three months after the sinking of ''Essex'', only five of the seventeen were alive. First mate Owen Chase and cabin boy Thomas Nickerson later wrote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |