|
Miscibility Gap
A miscibility gap is a region in a phase diagram for a mixture In chemistry, a mixture is a material made up of two or more different chemical substances which can be separated by physical method. It is an impure substance made up of 2 or more elements or compounds mechanically mixed together in any proporti ... of components where the mixture exists as two or more phases – any region of composition of mixtures where the constituents are not completely miscible. The IUPAC Gold Book defines ''miscibility gap'' as "Area within the coexistence curve of an isobaric phase diagram (temperature vs composition) or an isothermal phase diagram (pressure vs composition)." A miscibility gap between isostructural phases may be described as the '' solvus'', a term also used to describe the boundary on a phase diagram between a miscibility gap and other phases. Thermodynamically, miscibility gaps indicate a maximum (''e.g.'' of Gibbs energy) in the composition range. The miscibility ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligoclase
Oligoclase is a rock-forming mineral belonging to the plagioclase feldspars. In chemical composition and in its crystallographic and physical characters it is intermediate between albite ( Na Al Si3 O8) and anorthite ( CaAl2Si2O8). The albite:anorthite molar ratio of oligoclase ranges from 90:10 to 70:30. Oligoclase is a high sodium feldspar crystallizing in the triclinic system. The Mohs hardness is 6 to 6.5 and the specific gravity is 2.64 to 2.66. The refractive indices are: nα = 1.533–1.543, nβ = 1.537–1.548, and nγ = 1.542–1.552. In color it is usually white, with shades of grey, green, or red. Oligoclase is a common mineral in the more silica-rich varieties of igneous rock and in many metamorphic rocks. Name and discovery The name oligoclase was given by August Breithaupt in 1826 from the , little, and , to break, because the mineral was thought to have a less perfect cleavage than albite. It had previously been recognized as a distinct species by J. J. Berzel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materials Science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of researching and discovering materials. Materials engineering is an engineering field of finding uses for materials in other fields and industries. The intellectual origins of materials science stem from the Age of Enlightenment, when researchers began to use analytical thinking from chemistry, physics, and engineering to understand ancient, phenomenological observations in metallurgy and mineralogy. Materials science still incorporates elements of physics, chemistry, and engineering. As such, the field was long considered by academic institutions as a sub-field of these related fields. Beginning in the 1940s, materials science began to be more widely recognized as a specific and distinct field of science and engineering, and major technical universities around the world created dedicated schools for its study. Materials scientists emphasize understanding how the history of a material (''processing'') influences its struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incongruent Melting
Incongruent melting occurs when a solid substance being partially melted does not melt uniformly, so that the chemical composition of neither the resulting liquid nor the resulting solid is the same as that of the original solid. For example, melting of orthoclase (KAlSi3O8) produces leucite (KAlSi2O6) in addition to a melt. The melt produced is richer in silica (SiO2). The proportions of leucite and melt formed can be recombined to yield the bulk composition of the starting feldspar. Another mineral that can melt incongruently is enstatite (Mg2Si2O6), which produces forsterite Forsterite (Mg2SiO4; commonly abbreviated as Fo; also known as white olivine) is the magnesium-rich Endmember, end-member of the olivine solid solution series. It is Isomorphism (crystallography), isomorphous with the iron-rich end-member, fayalit ... (Mg2SiO4) in addition to a melt richer in SiO2 when melting at low pressure. Enstatite melts congruently at higher pressures between 2.5 and 5.5 kilobars. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogeneous mixture of two compounds in solid state and having a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word "solution" is used to describe the intimate mixing of components at the atomic level and distinguishes these homogeneous materials from physical mixtures of components. Two terms are mainly associated with solid solutions – ''solvents'' and ''solutes,'' depending on the relative abundance of the atomic species. In general if two compounds are isostructural then a solid solution will exist between the end members (also known as parents). For example sodium chloride and potassium chloride have the same cubic crystal structure so it is possible to make a pure compound with any ratio of sodium to potassium (Na1-xKx)Cl by dissolving that ratio of NaCl and KCl in water and then evaporating the solution. A member of this family is sold under the bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miscibility
Miscibility () is the property of two substances to mix in all proportions (that is, to fully dissolve in each other at any concentration), forming a homogeneous mixture (a solution). Such substances are said to be miscible (etymologically equivalent to the common term " mixable"). The term is most often applied to liquids but also applies to solids and gases. An example in liquids is the miscibility of water and ethanol as they mix in all proportions. By contrast, substances are said to be immiscible if the mixture does not form a solution for certain proportions. For one example, oil is not soluble in water, so these two solvents are immiscible. As another example, butanone (methyl ethyl ketone) is immiscible in water: it is soluble in water up to about 275 grams per liter, but will separate into two phases beyond that. Organic compounds In organic compounds, the weight percent of hydrocarbon chain often determines the compound's miscibility with water. For examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinodal Decomposition
Spinodal decomposition is a mechanism by which a single thermodynamic Phase (matter), phase spontaneously separates into two phases (without nucleation). Decomposition occurs when there is no Thermodynamics, thermodynamic barrier to phase separation. As a result, phase separation via decomposition does not require the nucleation events resulting from thermodynamic fluctuations, which normally trigger phase separation. Spinodal decomposition is observed when mixtures of metals or polymers separate into two co-existing phases, each rich in one species and poor in the other. When the two phases emerge in approximately equal proportion (each occupying about the same volume or area), characteristic intertwined structures are formed that gradually coarsen (see animation). The dynamics of spinodal decomposition is commonly modeled using the Cahn–Hilliard equation. Spinodal decomposition is fundamentally different from nucleation and growth. When there is a nucleation barrier to the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plagioclase
Plagioclase ( ) is a series of Silicate minerals#Tectosilicates, tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more properly known as the plagioclase feldspar series. This was first shown by the German mineralogist Johann F. C. Hessel, Johann Friedrich Christian Hessel (1796–1872) in 1826. The series ranges from albite to anorthite endmembers (with respective compositions NaAlSi3O8 to CaAl2Si2O8), where sodium and calcium atoms can substitute for each other in the mineral's crystallography, crystal lattice structure. Plagioclase in hand samples is often identified by its polysynthetic crystal twinning or "phonograph record, record-groove" effect. Plagioclase is a major constituent mineral in Earth's crust and is consequently an important diagnostic tool in petrology for identifying the composition, origin and evolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
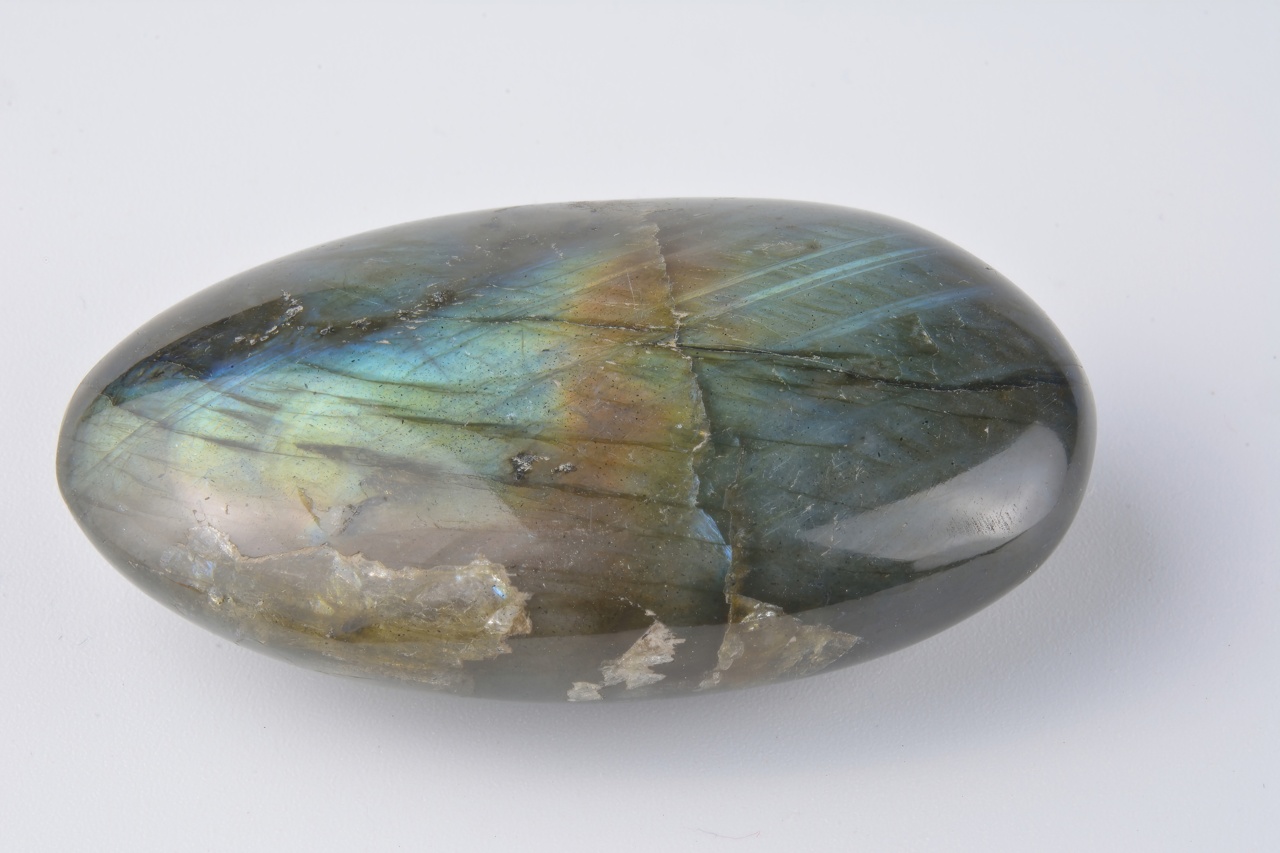
Labradorite
Labradorite (( Ca, Na)( Al, Si)4 O8) is a calcium-enriched feldspar mineral first identified in Labrador, Canada, which can display an iridescent effect ( schiller). Labradorite is an intermediate to calcic member of the plagioclase series. It has an anorthite percentage (%An) of between 50 and 70. The specific gravity ranges from 2.68 to 2.72. The streak is white, like most silicates. The refractive index ranges from 1.559 to 1.573 and twinning is common. As with all plagioclase members, the crystal system is triclinic, and three directions of cleavage are present, two of which are nearly at right angles and are more obvious, being of good to perfect quality (while the third direction is poor). It occurs as clear, white to gray, blocky to lath shaped grains in common mafic igneous rocks such as basalt and gabbro, as well as in anorthosites. Occurrence The geological type area for labradorite is Paul's Island near the town of Nain in Labrador, Canada. It has also been rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixture
In chemistry, a mixture is a material made up of two or more different chemical substances which can be separated by physical method. It is an impure substance made up of 2 or more elements or compounds mechanically mixed together in any proportion. A mixture is the physical combination of two or more substances in which the identities are retained and are mixed in the form of solutions, suspensions or colloids. Mixtures are one product of mechanically blending or mixing chemical substances such as elements and compounds, without chemical bonding or other chemical change, so that each ingredient substance retains its own chemical properties and makeup. Despite the fact that there are no chemical changes to its constituents, the physical properties of a mixture, such as its melting point, may differ from those of the components. Some mixtures can be separated into their components by using physical (mechanical or thermal) means. Azeotropes are one kind of mixture that usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bytownite
Bytownite is a calcium rich member of the plagioclase solid solution series of feldspar minerals with composition between anorthite and labradorite. It is usually defined as having between 70 and 90% An (formula: ). Like others of the series, bytownite forms grey to white triclinic crystals commonly exhibiting the typical plagioclase twinning and associated fine striations. The specific gravity of bytownite varies between 2.74 and 2.75. The refractive indices ranges are nα=1.563 – 1.572, nβ=1.568 – 1.578, and nγ=1.573 – 1.583. Precise determination of these two properties with chemical, X-ray diffraction, or petrographic analysis are required for identification. Occurrence Bytownite is a rock forming mineral occurring in mafic igneous rocks such as gabbros and anorthosites. It also occurs as phenocrysts in mafic volcanic rocks. It is rare in metamorphic rocks. It is typically associated with pyroxenes and olivine. The mineral was first described in 1836 Thomas Thomso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Storage
Thermal energy storage (TES) is the storage of thermal energy for later reuse. Employing widely different technologies, it allows surplus thermal energy to be stored for hours, days, or months. Scale both of storage and use vary from small to large – from individual processes to district, town, or region. Usage examples are the balancing of energy demand between daytime and nighttime, storing summer heat for winter heating, or winter cold for summer cooling (Seasonal thermal energy storage). Storage media include water or ice-slush tanks, masses of native earth or bedrock accessed with heat exchangers by means of boreholes, deep aquifers contained between impermeable strata; shallow, lined pits filled with gravel and water and insulated at the top, as well as eutectic solutions and phase-change materials. Other sources of thermal energy for storage include heat or cold produced with heat pumps from off-peak, lower cost electric power, a practice called peak shaving; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |