|
Minsk Offensive
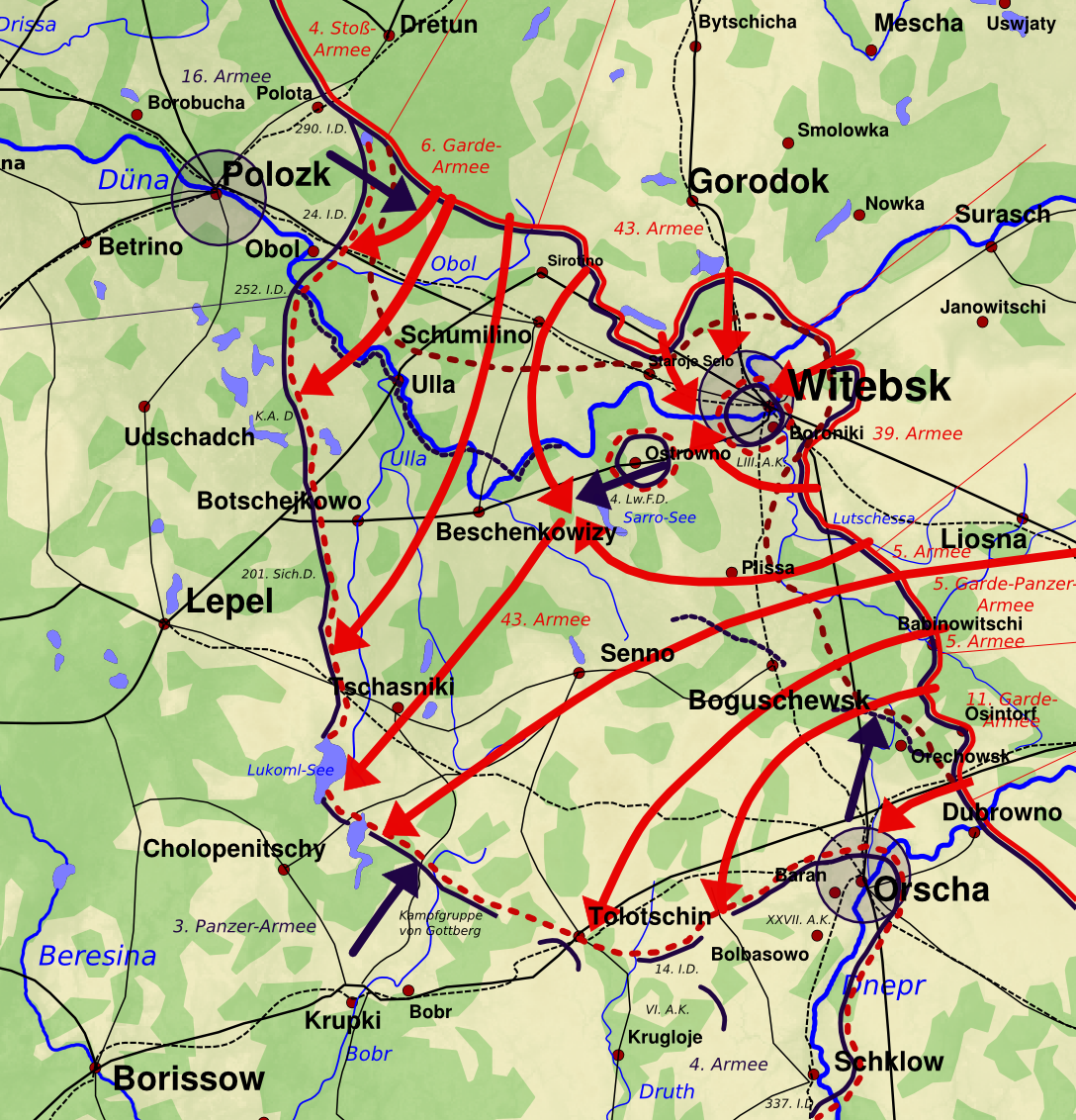
The Minsk offensive () was part of the second phase of the Belorussian strategic offensive of the Red Army in summer 1944, commonly known as Operation Bagration. The Red Army encircled the German 4th Army (Wehrmacht), Fourth Army in the city of Minsk. Hitler ordered the Fourth Army to hold fast, declaring the city to be a fortified place () and defended even if encircled. The Soviet Fifth Guards Tank Army (Soviet Union), 5th Guards Tank Army attacked from the north-east, while the 2nd Guards Tank Corps moved in from the east, and the 65th Army advanced from the south. About 100,000 Axis soldiers from the Fourth and Ninth Armies were encircled, of whom some 40,000 were killed and most of the rest captured. The result was a complete victory for the Red Army, the liberation of Minsk, and the rapid destruction of much of the German Army Group Centre. Role in the conflict The capturing of Minsk played an important role in Operation Bagration and in World War II, WWII itself. With the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Bagration
Operation Bagration () was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation (), a military campaign fought between 22 June and 19 August 1944 in Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Byelorussia in the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II, just over two weeks after the start of Operation Overlord in the west. It was during this operation that Nazi Germany was forced to fight simultaneously on two major fronts for the first time since the war began. The Soviet Union destroyed 28 of the divisions of Army Group Centre and completely shattered the German front line. The overall engagement is the largest defeat in German military history, with around 450,000 German casualties, while setting the stage for the subsequent isolation of 300,000 German soldiers in the Courland Pocket. On 22 June 1944, the Red Army attacked Army Group Centre in Byelorussia, with the objective of encircling and destroying its main component armies. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People's Commissars to oppose the military forces of the new nation's adversaries during the Russian Civil War, especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army. In February 1946, the Red Army (which embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces alongside the Soviet Navy) was renamed the "Soviet Army". Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union it was split between the post-Soviet states, with its bulk becoming the Russian Ground Forces, commonly considered to be the successor of the Soviet Army. The Red Army provided the largest land warfare, ground force in the Allies of World War II, Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its Soviet invasion of Manchuria, invasion of Manchuria assisted the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th Panzer Division (Wehrmacht)
The 5th Panzer Division () was an armoured division of the German Army during World War II, established in 1938. The division fought in Poland, France, the Balkans and in the Soviet Union; first as part of Army Group Centre (1941–44) and then Army Group North. The division surrendered to Soviet and Western Allied forces in April and May 1945. History The 5th Panzer Division was formed in Oppeln, now Opole in Poland, on 15 November 1938 as part of a second wave of new armoured divisions in Germany following the creation of the original three tank divisions in 1935. Alongside the 5th Panzer Division the 4th had been formed in Würzburg five days earlier. The personnel of the division was mainly made up of Silesians and Sudeten Germans, the Sudetenland having been annexed by Germany shortly before.Mitcham, p. 65. The division took part in the invasion of Poland in 1939 but played no major role in it, being part of the southern thrust of the German advance towards Lwów a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavel Rotmistrov
Chief marshal of the armored troops Pavel Alexeyevich Rotmistrov (; 6 July 1901 – 6 April 1982) was a Soviet military commander of armoured troops in the Red Army during and following World War II. He fought from the first days and was present in every major Soviet battle including Battle of Moscow, Battle of Stalingrad and for leading the 5th Guards Tank Army at the Battle of Prokhorovka at the Battle of Kursk. Rotmistrov became the first Marshal of the Soviet armoured troops. Pre-War Rotmistrov joined the Red Army in 1919, and served during the Russian Civil War, during which he was involved in the suppression of the Kronstadt rebellion and in the Polish Soviet War. He commanded a platoon and later rifle company in 31st Rifle Regiment of 11th Rifle Division. In 1928 he entered Frunze Military Academy. From 1937 to 1940 he was an instructor at the Moscow Higher Military Academy. In May 1941 he became Chief of Staff of the 3rd Mechanised Corps. Second World War Rotmistro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th Guards Tank Army
The 5th Guards Tank Army (Russian: 5-я гварде́йская та́нковая а́рмия) was a Soviet Guards armored formation which fought in many notable actions during World War II. The army was formed in February 1943. Until the aftermath of the Vilnius Offensive in July 1944, it was commanded by Pavel Rotmistrov. Its organisation varied throughout its history, but in general included two or more Guards Tank Corps and one or more Guards Mechanised Corps. It was considered an elite formation. Under Red Army doctrine of deep operations, Tank Armies were primarily to be used for large-scale exploitation of major offensives. Once a breach in enemy lines had been made by other units (typically Shock Armies or combined-arms armies), the tank army would be inserted into the gap to drive deep into enemy territory, attacking rear areas and seizing major communications centers to disrupt the enemy reactions. Tank armies were expected to penetrate up to several hundred kilom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molodechno
Maladzyechna, or Molodechno, is a town in Minsk Region, Belarus. It serves as the administrative centre of Maladzyechna District (and formerly of Molodechno Region from 1944 to 1960). Maladzyechna is located northwest of Minsk. In 2006, it had an estimated population of 98,514 inhabitants. As of 2025, it has a population of 88,290. Located on the Usha River, it has been a settlement since 1388 when it was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. It was also home to the Cold War facility Maladzyechna (air base), Maladzyechna air base. History Early history The fortification on the right bank of the was first mentioned in 1388, although it is probable it was erected even before that date. Rectangular earthworks with stone walls 3,5 metres high and 11 metres wide formed the basis of the future castles and military camps formed on that location. The town itself was first mentioned the following year in a document issued by Kaributas, Prince of Severian Novgorod, who on December 16 as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stavka
The ''Stavka'' ( Russian and Ukrainian: Ставка, ) is a name of the high command of the armed forces used formerly in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union and currently in Ukraine. In Imperial Russia ''Stavka'' referred to the administrative staff, and to the General Headquarters in the late 19th-century Imperial Russian armed forces and subsequently in the Soviet Union. In Western literature it is sometimes written in uppercase (''STAVKA''), although it is not an acronym. ''Stavka'' may refer to its members, as well as to the headquarters location (its original meaning from the old Russian word '' ставка'', 'tent'). Stavka of the Supreme Commander during World War I The commander-in-chief of the Russian army at the beginning of World War I was Grand Duke Nicholas Nicholaievitch, a grandson of Tsar Nicholas I. Appointed at the last minute in August 1914, he played no part in formulating the military plans in use at the beginning of the war. Nikolai Yanushke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berezina
The Berezina or Byarezina (, ; ) is a river in Belarus and a right tributary of the Dnieper. The river starts in the Berezinsky Biosphere Reserve. The length of the Berezina is . The width of the river is 15–20 m, the maximum is 60 m. The banks are low (up to 0.5 m), steep in some areas (up to 1.5 m high), sandy, and the floodplain is swampy. The Berezina usually freezes over in the first half of December. Its main tributaries are Bobr, Klyava, Ol'sa and from the left and Hayna and Svislach from the right. The Berezinsky Biosphere Reserve by the river is on the UNESCO list of biosphere reserves. Peat bogs cover 430 km2 and thus occupy a large part of the reserve. These open peat zones have remained virtually untouched and are among Europe's largest bogs. Settlements Cities and towns on the Berezina from north to south include: * Dokshytsy * Svislach * Barysaw * Babruysk * Svyetlahorsk Historical significance The Berezina has been the site of several battles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th Army (German Empire)
The 4th Army () was an army level command of the German Army in World War I. It was formed on mobilisation in August 1914 from the VI Army Inspection. The army was disbanded in 1919 during demobilization after the war. History At the outset of war, the 4th Army, with the 5th Army, formed the center of the German armies on the Western Front, moving through Luxembourg and Belgium in support of the great wheel of the right wing that was to pin down and defeat the French armies. The 4th Army defeated Belgian forces on the frontier, drove the French out of the Ardennes and then encountered the British Expeditionary Force in the "Race to the Sea" at the First Battle of Ypres. The 4th Army faced the British in Flanders for the rest of the war, notably defending in the Battle of Passchendaele (1917), attacking in the 1918 German spring offensive and finally being pushed back in the Hundred Days Offensive from August 1918. At the end of the war it was serving as part of '' Heeresg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |