|
Ministry Of Public Works (imperial China)
The Ministry of Works or was one of the Six Ministries under the Department of State Affairs in imperial China. The Ministry of Works is also commonly translated into English as the or History The ministry was established during the Sui dynasty as one of the six functional divisions of the Department of State Affairs. It was also part of the same department during the Five Dynasties period and the Song dynasty. After the merger of the " three departments" (''Zhongshu Sheng'', '' Menxia Sheng'' and '' Shangshu Sheng''), it was reassigned to the ''Zhongshu Sheng'' (Secretariat) in the Yuan Empire and later the Ming Empire. In 1380, the office of Secretariat was abolished and the ministries, including the Ministry of Works, became independent and continued to report directly to the emperor. Under the Ming and Qing, it lost some influence in favor of agencies run by palace eunuchs, provincial coordinators, and governors. It was usually considered the weakest of the six minis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
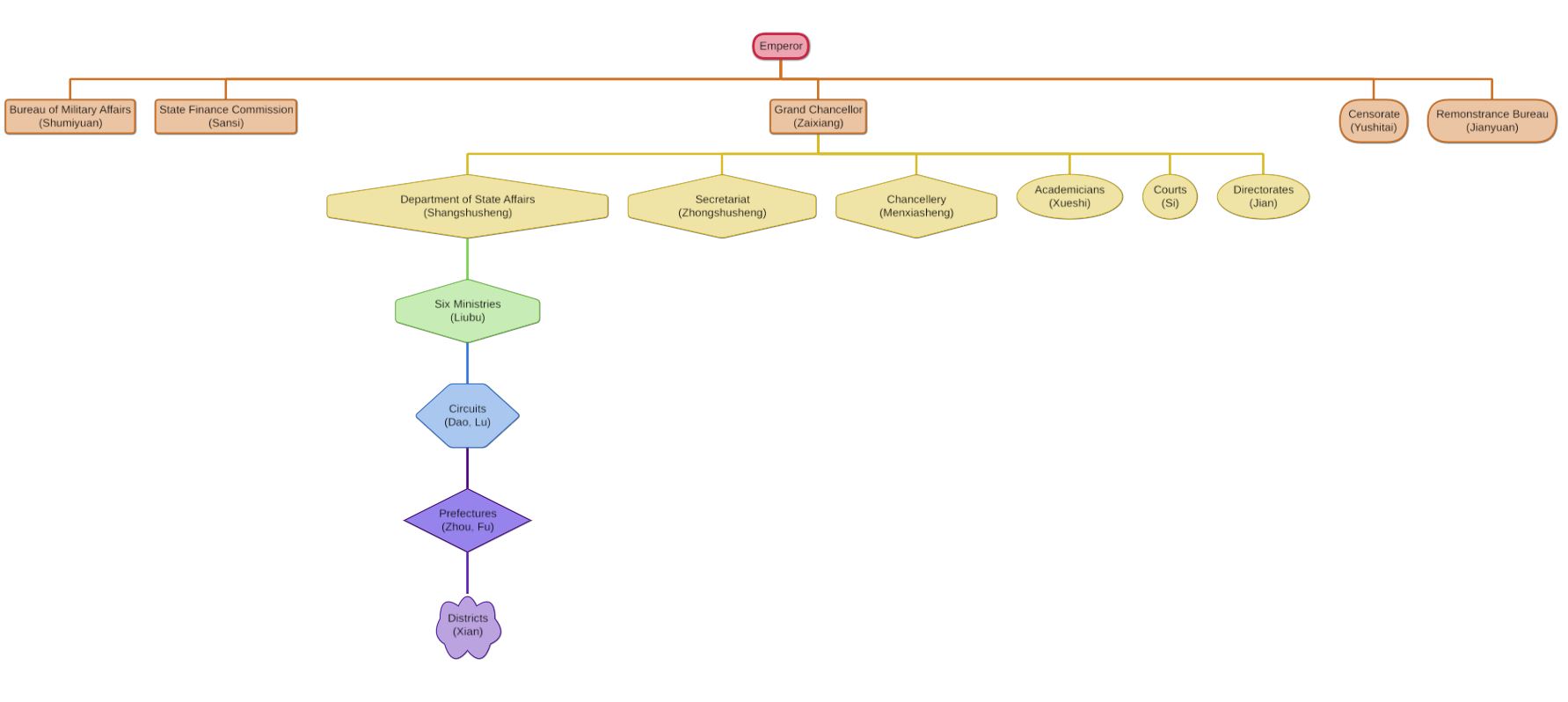
Three Departments And Six Ministries
The Three Departments and Six Ministries () system was the primary administrative structure in imperial China from the Sui dynasty (581–618) to the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368). It was also used by Balhae (698–926) and Goryeo (918–1392) and various other kingdoms in Manchuria, Korea and Vietnam. The Three Departments were three top-level administrative structures in imperial China. They were the Central Secretariat, responsible for drafting policy, the Chancellery, responsible for reviewing policy and advising the emperor, and the Department of State Affairs, responsible for implementing policy. The former two were loosely joined as the Secretariat-Chancellery during the late Tang dynasty, Song dynasty and in the Korean kingdom of Goryeo. The Six Ministries (also translated as Six Boards) were direct administrative organs of the state under the authority of the Department of State Affairs. They were the Ministries of Personnel, Rites, War, Justice, Works, and Revenue. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of The Song Dynasty
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The main types of modern political systems recognized are democracies, totalitarian regimes, and, sitting between these two, authoritarian regimes with a variety of hybrid regimes. Modern classification systems also include monarchies as a standalone entity or as a hybrid system of the main three. Historically prevalent forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of The Ming Dynasty
The government of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) was modeled after the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. Over time, the government system changed and adapted to circumstances. The Ming government was traditionally divided into three branches—civil, military and surveillance, with the imperial household and its eunuchs holding a distinct position. In the beginning, the central civil authorities were led by the Central Secretariat, which oversaw six ministries and other less significant institutions. The Chief Military Commission served as the high command of the army, while the Censorate held the highest control authority. The empire was divided into two metropolitan areas and thirteen provinces, each of which was managed by a Branch Secretariat. The lower levels of administration included prefectures and subprefectures, with the lowest level being the counties. During the Ming dynasty, there were approximately 1,400 counties in China. In 1376, the Branch Secretariats were abolished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Six Ministries
The Three Departments and Six Ministries () system was the primary administrative structure in History of China#Imperial China, imperial China from the Sui dynasty (581–618) to the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368). It was also used by Balhae (698–926) and Goryeo (918–1392) and various other kingdoms in Manchuria, Korea and Vietnam. The Three Departments were three top-level administrative structures in imperial China. They were the Zhongshu Sheng, Central Secretariat, responsible for drafting policy, the Menxia Sheng, Chancellery, responsible for reviewing policy and advising the emperor, and the Department of State Affairs, responsible for implementing policy. The former two were loosely joined as the Secretariat-Chancellery during the late Tang dynasty, Song dynasty and in the Korean kingdom of Goryeo. The Six Ministries (also translated as Six Boards) were direct administrative organs of the state under the authority of the Department of State Affairs. They were the Ministrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Imperial China
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The main types of modern political systems recognized are democracies, totalitarian regimes, and, sitting between these two, authoritarian regimes with a variety of hybrid regimes. Modern classification systems also include monarchies as a standalone entity or as a hybrid system of the main three. Historically prevalent forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Natural Resources (China)
The Ministry of Natural Resources is an executive-department of the State Council of the People's Republic of China which is responsible for natural resources in the country. It is the 14th-ranking department of the State Council. It was formed on 19 March 2018, taking on the responsibilities of the now-defunct Ministry of Land and Resources, State Bureau of Surveying and Mapping and State Oceanic Administration, with additional responsibilities coming from other departments and ministries. History On March 19, 2018, the simultaneous creation of the Ministry of Natural Resources and dissolution of the Ministry of Land and Resources, State Oceanic Administration, and State Bureau of Surveying and Mapping was announced as part of the deepening the reform of the Party and state institutions. That same day, Lu Hao was elected Minister of Natural Resources. In 2019, the Ministry held its first international forum on nature protection. On August 26, 2019, President Xi Jinping s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Labor (Taiwan)
The Ministry of Labor (MOL; ) is a ministry of the Taiwanese Executive Yuan administering policies relating to employees and labor. The MOL works with various international organizations and engages in bilateral exchanges to elevate the welfare of laborers in Taiwan, administering programs such as Labor Insurance. History In 1947, before the implementation of Constitution of the Republic of China, the Nationalist government planned to establish the Ministry of Labor under the Executive Yuan. On 18 May 1948, the Ministry of Society () was founded by the Executive Yuan, and labor affairs were downgraded to an agency under the Ministry of Society. On 21 March 1949, the Ministry of Society was abolished, and labor affairs were then administered by the a newly founded Division of Labor under the Ministry of the Interior (Taiwan), Ministry of the Interior. On 1 August 1987, the Council of Labor Affairs () was established as an independent agency under the Executive Yuan. The council wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Human Resources And Social Security
The Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security (MOHRSS) is a ministry under the State Council of China which is responsible for national labor policies, standards, regulations and managing the national social security. This includes labor force management, labor relationship readjustment, social insurance management and legal construction of labor. The State Bureau of Civil Servants reports to the new ministry. Responsibilities The Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security (MOHRSS) formulates development plans for human resources and social security policies, promotes employment, creates income policies for personnel in institutions, and develops a multi-level social security system for urban areas and rural areas. The MOHRSS has responsibility for managing the employment market in mainland China. The ministry also oversees the China Overseas Talent Network, part of the Thousand Talents Plan, and has internal bureaus focused on technology transfer. History In Octo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Chinese Measures
A tradition is a system of beliefs or behaviors (folk custom) passed down within a group of people or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examples include holidays or impractical but socially meaningful clothes (like lawyers' wigs or military officers' spurs), but the idea has also been applied to social norms and behaviors such as greetings, etc. Traditions can persist and evolve for thousands of years— the word ''tradition'' itself derives from the Latin word ''tradere'' literally meaning to transmit, to hand over, to give for safekeeping. While it is reportedly assumed that traditions have an ancient history, many traditions have been invented on purpose, whether it be political or cultural, over short periods of time. Various academic disciplines also use the word in a variety of ways. The phrase "according to tradition" or "by tradition" usually means that what follows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Personnel (imperial China)
The Ministry of Personnel was one of the Three Departments and Six Ministries, Six Ministries under the Department of State Affairs in history of China, imperial China, Korea, and Vietnam. Functions Under the Ming government, Ming, the Ministry of Personnel was in charge of civil appointments, merit ratings, promotions, and demotions of officials, as well as granting of Chinese nobility, honorific titles. Military appointments, promotions, and demotions fell under the purview of the Ministry of War (imperial China), Ministry of War. See also * Imperial examination * Scholar-bureaucrat or mandarin * Examination Yuan References Citations Sources * Government of Imperial China Six Ministries Government of the Ming dynasty Government of the Tang dynasty Government of the Song dynasty Government of the Yuan dynasty Government of the Qing dynasty Government of the Sui dynasty {{China-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |