|
Ministry Of Power (India)
The Ministry of Power is an Government of India, Indian government Ministry (government department), ministry. The current cabinet (government), Union Cabinet Minister is Manohar Lal Khattar. The ministry is charged with overseeing Electricity in India, electricity production and infrastructure development, including generation, transmission, and delivery, as well as maintenance projects. The ministry acts as a liaison between the central government and States and territories of India, state electricity operations, as well as with the private sector. The ministry also oversees rural electrification projects. History The Ministry of Power became a ministry on July 2, 1992, during the P. V. Narasimha Rao government. Prior to that time it had been a department (the Department of Power) in the Ministry of Power, Coal and Non-Conventional Energy Sources. That ministry was split into the Ministry of Power, Ministry of Coal, and Ministry of Non-Conventional Energy Sources (renamed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry (government Department)
Ministry or department (also less commonly used secretariat, office, or directorate) are designations used by first-level executive bodies in the machinery of governments that manage a specific sector of public administration." Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона", т. XIX (1896): Мекенен — Мифу-Баня, "Министерства", с. 351—357 :s:ru:ЭСБЕ/Министерства These types of organizations are usually led by a politician who is a member of a cabinet—a body of high-ranking government officials—who may use a title such as minister, secretary, or commissioner, and are typically staffed with members of a non-political civil service, who manage its operations; they may also oversee other government agencies and organizations as part of a political portfolio. Governments may have differing numbers and types of ministries and departments. In some countries, these terms may be used with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Hydropower Corporation
National may refer to: Common uses * Nation or country ** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen Places in the United States * National, Maryland, census-designated place * National, Nevada, ghost town * National, Utah, ghost town * National, West Virginia, unincorporated community Commerce * National (brand), a brand name of electronic goods from Panasonic * National Benzole (or simply known as National), former petrol station chain in the UK, merged with BP * National Book Store, a bookstore and office supplies chain in the Philippines * National Car Rental, an American rental car company * National Energy Systems, a former name of Eco Marine Power * National Entertainment Commission, a former name of the Media Rating Council * National Motor Vehicle Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA 1900–1924 * National Radio Company, Malden, Massachusetts, USA 1914–1991 * National Supermarke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narhar Vishnu Gadgil
Narhar Vishnu Gadgil (10 January 1896 – 12 January 1966) was an Indian freedom fighter and politician from Maharashtra, India. He was also a writer. He wrote in both Marathi and English. His son Vitthalrao Gadgil represented Congress later as minister and ideologue. His grandson Anant Gadgil also went on to become a politician. Gadgil graduated from Fergusson College in Pune in 1918, and obtained a degree in Law in 1920. Activities before India's independence Gadgil was born a member of the Gadgil ''gharana'' of Velneshwar- Wai. In India's pre-independence days, freedom fighters Lokmanya Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Vallabhbhai Patel influenced Gadgil. Spiritual leaders Swami Ramkrishna Paramhans and Swami Vivekanand also made a deep impression on him. He joined the Indian National Congress in 1920, immediately after obtaining his law degree and started his active participation in the national freedom movement. He suffered imprisonment fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhakra Beas Management Board
Bhakra Nangal Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Satluj River in Bhakra Village in Bilaspur district, Himachal Pradesh in northern India. The dam forms the Gobind Sagar reservoir. Nangal Dam is another dam at Nangal in Punjab downstream of Bhakra Dam. However, sometimes both the dams together are called Bhakra-Nangal Dam though they are two separate dams. The dam is located at a gorge near the (now submerged) upstream Bhakra village in Bilaspur district of Himachal Pradesh and is of height 226 m. The length of the dam (measured from the road above it) is 518.25 m and the width is 9.1 m. Its reservoir known as "Gobind Sagar" stores up to 9.34 billion cubic metres of water. The 90 km long reservoir created by the Bhakra Dam is spread over an area of 168.35 km2. In terms of storage of water, it is the third largest reservoir in India, the first being Indira Sagar dam in Madhya Pradesh with capacity of 12.22 billion cubic meters and the second bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
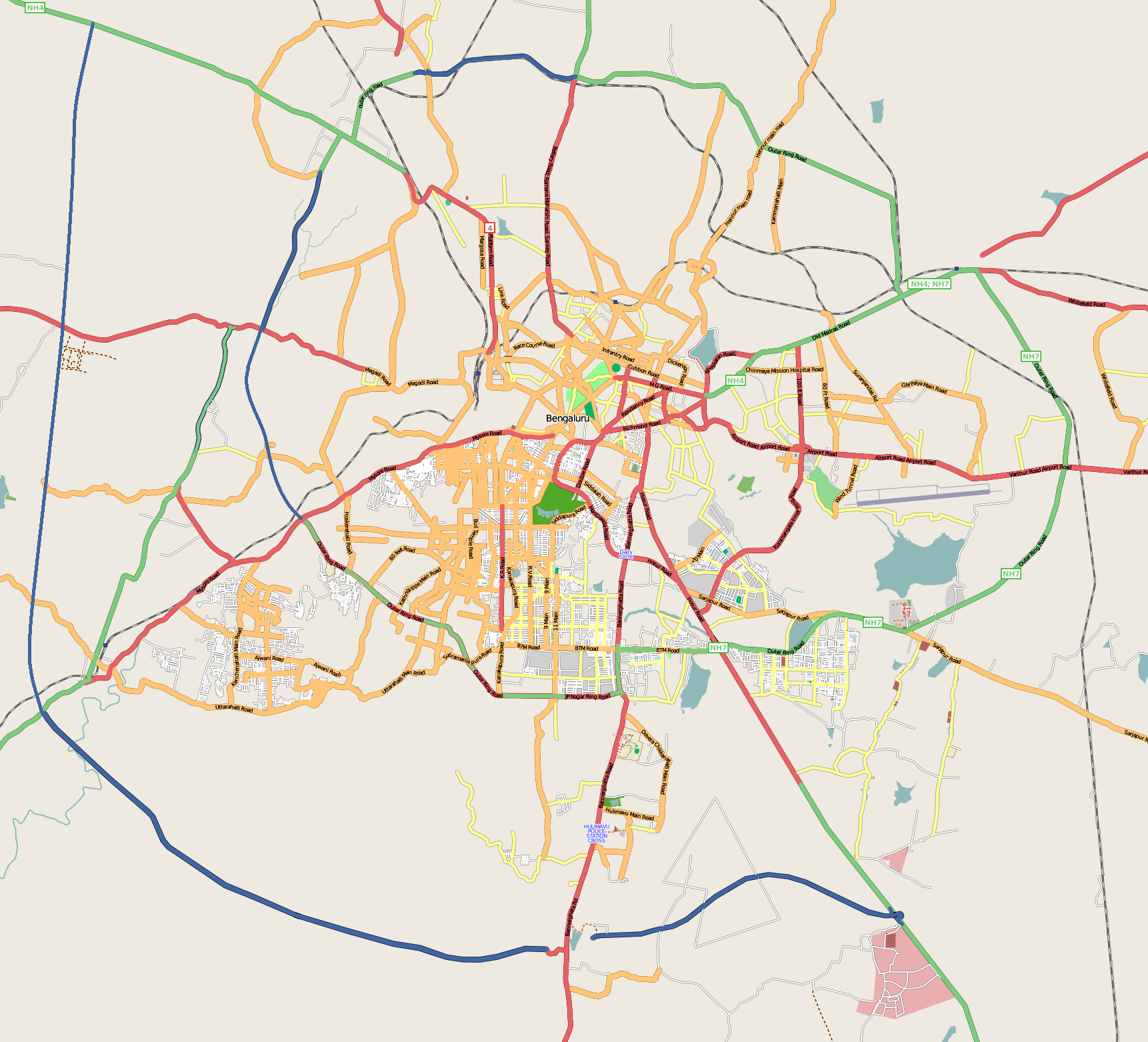
Bangalore
Bengaluru, also known as Bangalore (List of renamed places in India#Karnataka, its official name until 1 November 2014), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the southern States and union territories of India, Indian state of Karnataka. As per the 2011 Census of India, 2011 census, the city had a population of 8.4 million, making it the List of cities in India by population, third most populous city in India and the most populous in South India. The Bengaluru metropolitan area had a population of around 8.5 million, making it the List of million-plus urban agglomerations in India, fifth most populous urban agglomeration in the country. It is located near the center of the Deccan Plateau, at a height of above sea level. The city is known as India's "Garden City", due to its parks and greenery. Archaeological artifacts indicate that the human settlement in the region happened as early as 4000 Common Era, BCE. The first mention of the name "Bengalooru" is from an ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faridabad
Faridabad () is the most populous List of cities in Haryana by population, city near NCT of Delhi in the Indian state of Haryana and a part of National Capital Region (India), Delhi National Capital Region. It is one of the major satellite cities around Delhi and is located 284 kilometres south of the state capital, Chandigarh. The river Yamuna forms the eastern district boundary with Uttar Pradesh. The Government of India included it in the second list of Smart Cities Mission on 24 May 2016. As per the 2021 Delhi Regional Plan, Faridabad is a part of the Central National Capital Region or Delhi metropolitan area. The newly developed residential and industrial part of Faridabad (Sec. 66 to 89) between the Agra Canal and the Yamuna River is commonly referred to as Greater Faridabad (also known as Neharpar). The area is being developed as a self-sustained sub-city with wide roads, tall buildings, malls, educational institutions, and health and commercial centers. Sectors 66 to 74 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Power Training Institute
National Power Training Institute (NPTI), is a government training institution under Ministry of Power, Government of India with its Corporate Office at Faridabad. NPTI had been providing its dedicated service for more than five decades. History The Central Water and Power Commission (Power Wing) established Thermal Power Station Personnel Training Institutes in 1965–1975 at Neyveli (1965), Durgapur (1968), Badarpur, Delhi (1974) and Nagpur (1975) for training the engineers of thermal power stations which were being established in the country during that time. It also established the Power Systems Training Institute (PSTI) in 1972 and Hot Line Training Centre (HLTC) in 1974 at Bangalore. With the bifurcation of the Central Water and Power Commission into the Central Electricity Authority (CEA) and Central Water Commission (CWC) in the 1970s, the Institute came under the Central Electricity Authority (CEA). In the late 1970s the Raj Dekshya Committee set up by the Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Electricity Regulatory Commission
Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC), a key regulator of the power sector in India, is a statutory body functioning with quasi-judicial status under sec – 76 of the Electricity Act 2003. CERC was initially constituted on 24 July 1998 under the Ministry of Power's Electricity Regulatory Commissions Act, 1998 for rationalization of electricity tariffs, transparent policies regarding subsidies, promotion of efficient and environmentally benign policies, and for matters connected Electricity Tariff regulation. CERC was instituted primarily to regulate the tariff of power generating companies owned or controlled by the Government of India, and any other generating company which has a composite scheme for power generation and interstate transmission of energy, including tariffs of generating companies. History On 2 July 1998, recognizing the needs for reforms in the electricity sector nationwide, the Government of India moved forward to enact the Electricity Regul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
REC Power Development And Consultancy Limited
REC or Rec is a shortening of recording, the process of capturing data onto a storage medium. REC may also refer to: Educational institutes * Regional Engineering College, colleges of engineering and technology education in India * Rajalakshmi Engineering College (), Thandalam, Chennai, India Organizations * Railway Executive Committee, in Britain * REC Limited, an infrastructure finance company in India * Reformed Episcopal Church, an Anglican church in the United States and Canada * Regional Economic Communities, in Africa * Regional electricity companies, the fourteen companies created when the electricity market in the UK was privatised * Renewable Energy Corporation, a solar power company with headquarters in Norway :* REC Silicon ( no) * Research Ethics Committee, a type of ethics committee * Rock Eisteddfod Challenge, an Australian abstinence program * Rural Electrification Corporation Television, film, and fiction * ''Rec'' (film series), a Spanish horror film ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rural Electrification Corporation
REC Limited, formerly Rural Electrification Corporation Limited, is an Indian public sector company that finances and promotes power projects across India. It loans to Central/State Sector Power Utilities, State Electricity Boards, Rural Electric Cooperatives, NGOs and Private Power Developers. It is a subsidiary of Power Finance Corporation (PFC) and is under administrative control of the Ministry of Power, Government of India. On 20 March 2019, PFC agreed to acquire a 52.63% controlling stake in REC for . On 28 March, PFC announced it had paid for the acquisition and intended to merge with REC in 2020. However, REC has maintained that merging PFC-REC is no longer an option. From 1 September 2023, REC has been included in the Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI) Global Standard Index. REC has diversified into non-power infrastructure and logistics, now covering airports, metro, railways, ports, and bridges. REC has 22 regional offices.. Business operations REC is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |