|
Ministry Of Police Of Imperial Russia
Ministry of Police of Imperial Russia was created in the course of Government reform of Alexander I in 1810 and existed till 1819. Ministry objectives and credentials * Carrying out recruitment in the Army; * Protection of the state stocks of the foodstuffs; * The customs supervision; * The maintenance and use of the toil of convicted; * Maintenance of serviceability and safety of communications; * Also, the ministry should carry out obvious and secret supervision of foreigners in Russia, carry out censorship functions. In view of importance of the functions assigned to the Ministry, for it has been developed and simultaneously with ukaz about establishment of the ministries was published ''Establishment and the order to minister of police'', which became a normative basis of its organization and activity. A component of it were ''Rules of the especial responsibility of minister of police''. Operating in ''force-majeure'' (definition and conditions ''force-majeure'' were not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of The Interior Of The Russian Empire
The Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Empire () was the state executive authority of the Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire, which carried out administrative functions in the areas of state security, public security, law enforcement, leadership of local authorities, the fight against crime, protection of places of deprivation of liberty, the licensing system, and censorship in media and book publishing. The Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Empire concentrated in its hands a wide variety of tasks, both of the security police and the welfare police. History On, , the manifesto published by Alexander I named “On the establishment of ministries” was approved. Along with others ministries, the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs was also created. The first Minister of Internal Affairs was Count Viktor Kochubey. The Deputy Minister became Count Pavel Stroganov. According to Count Speransky, the ministry should have been in charge of the country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
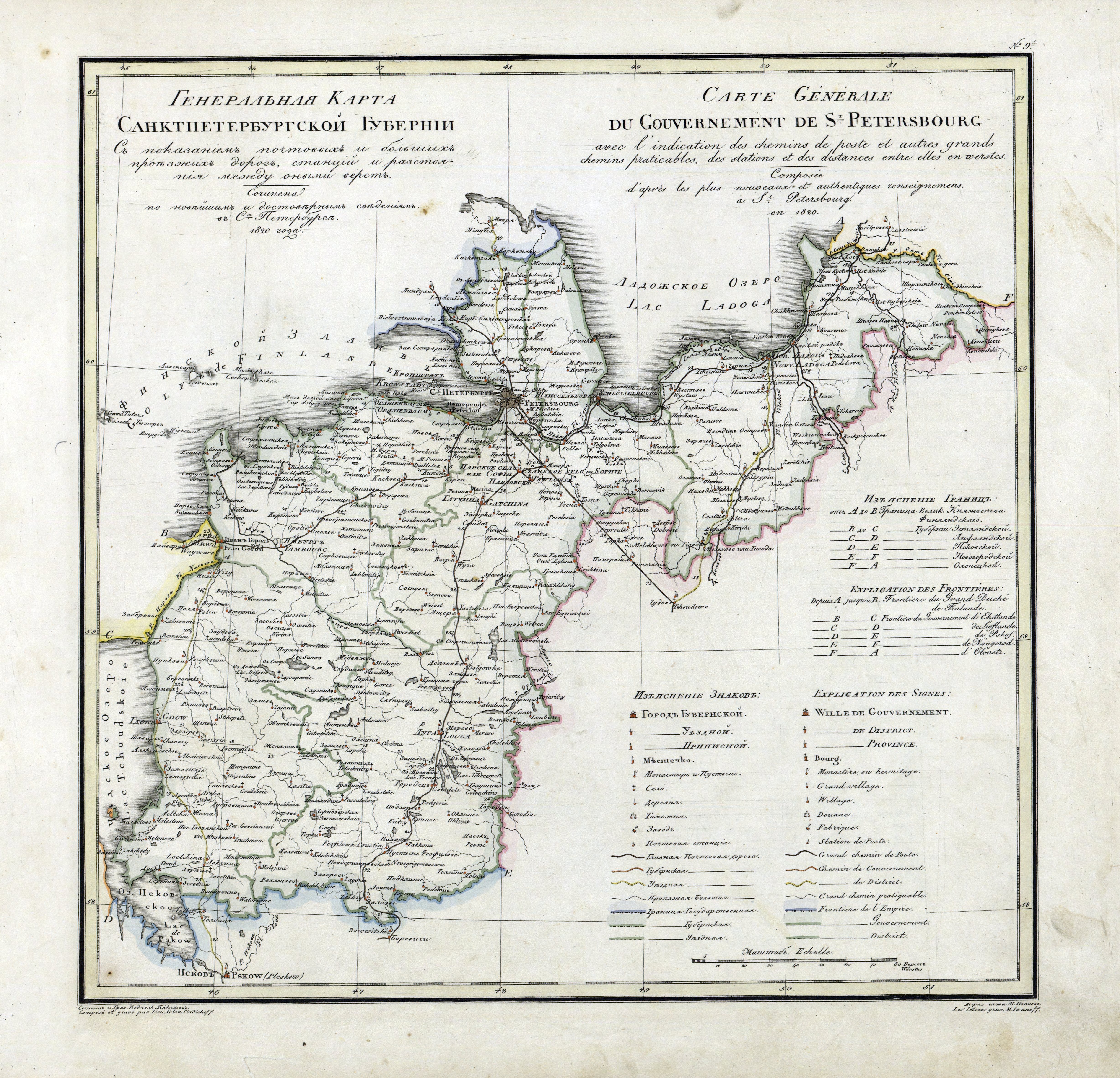
Saint Petersburg Governorate
Saint Petersburg Governorate was a province (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire, with its capital in Saint Petersburg. The governorate was composed of of area and 2,112,033 inhabitants. It was bordered by Governorate of Estonia, Estonian and Governorate of Livonia, Livonian Governorates to the west, Pskov Governorate to the south, Novgorod Governorate to the east, Olonets Governorate to the northeast, and Viipuri Province, Vyborg Governorate of the Grand Duchy of Finland to the north. The governorate covered most of the areas of modern Leningrad Oblast and Ida-Viru County, Ida-Viru, Jõgeva County, Jõgeva, Tartu County, Tartu, Põlva County, Põlva, and Võru County, Võru counties of Estonia. Establishment Ingermanland Governorate (, ''Ingermanlandskaya guberniya'') was created from the territories reconquered from the Swedish Empire in the Great Northern War. In 1704 prince Alexander Menshikov was appointed as its first governor, and in 1706 it was first Russian region des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Devier
António Manuel de Vieira, known in Russia as Count Anton Manuilovich Devier (also spelled ''Divier''; – – ), was one of Peter I's foreign associates, who proved to be an efficient administrator in St Petersburg and Siberia. He was St. Petersburg's first chief of police and was identified as a main rival of Alexander Danilovich Menshikov at Catherine I's court. De Vieira was the father of Peter Devier. Biography His date and place of birth are uncertain - sources differ on whether he was born in Portugal, in the province of Minho, in 1673–1674, or less likely in Amsterdam c. 1682. An account cited that he was an alleged descendant of the Portuguese Marranos. His mother was a Christian but his father was a Jew who moved with his family from Portugal to the Low Countries where he converted to Christianity. During the Grand Embassy of Peter the Great to Europe (1697), the tsar was allowed by the Dutch sailors to command a ship, where Vieira served as a cabin-boy. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Corps Of Gendarmes
The Separate Corps of Gendarmes () was the uniformed security police of the Imperial Russian Army in the Russian Empire during the 19th and early 20th centuries. Its main responsibilities were law enforcement and state security. The responsibilities of the Gendarmes also included the execution of court orders, pursuit of fugitives, riot control, and detainment of "unusual" criminals. Gendarmes could also be assigned to assist local police and officials. Establishment The precursors of the Corps were the Imperial Army Gendarmerie regiment (formed in 1815 and based on the Borisoglebsk Dragoon Regiment) and Gendarmerie units of the Separate Corps of the Internal Guards (raised 1811). Following the 1825 Decembrist revolt, the new Russian Emperor, Nicholas I, established the office of the Chief of Gendarmes in July 1826 and appointed General Count Alexander Benkendorf to it; all of the gendarmes were subordinate to the Chief. Benkendorf was also appointed executive director ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Police
The Police of Russia () is the national law enforcement agency of Russia, operating under the Ministry of Internal Affairs from . It was established on by decree of Peter the Great, and in 2011, it replaced the Militsiya, the former police service. The Police of Russia operates according to the law " On police" (Закон "о полиции"), as approved by the Federal Assembly, and subsequently signed into law on February 7, 2011, by the then President of the Russian Federation, Dmitry Medvedev. History The system was created in order to protect public order and fight against crime in the Russian Empire. It was reorganized on March 1, 2011, under the Russian Federation, except for existing structures not related to the Ministry of Internal Affairs. 16th century In 1504, defensive obstacles called cheval de frise were installed in Moscow, under which guards drawn from the local population were stationed. The city was divided into areas, with latticed gates separatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okhrana
The Department for the Protection of Public Safety and Order (), usually called the Guard Department () and commonly abbreviated in modern English sources as the Okhrana ( rus , Охрана, p=ɐˈxranə, a=Ru-охрана.ogg, t= The Guard) was a secret police force of the Russian Empire and part of the police department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs (MVD) in the late 19th century and early 20th century, aided by the Special Corps of Gendarmes. Overview Formed to combat political terrorism and left-wing politics and revolutionary activity, the Okhrana operated offices throughout the Russian Empire, as well as satellite agencies in a number of foreign countries. It concentrated on monitoring the activities of Russian revolutionaries abroad, including in Paris, where Okhrana agent Pyotr Rachkovsky (1853–1910) was based 1884–1902 before he returned to service in Saint Petersburg 1905–1906. The Okhrana deployed multiple methods, including assassination, clandesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas I Of Russia
Nicholas I, group=pron (Russian language, Russian: Николай I Павлович; – ) was Emperor of Russia, List of rulers of Partitioned Poland#Kings of the Kingdom of Poland, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 1825 to 1855. He was the third son of Paul I of Russia, Paul I and younger brother of his predecessor, Alexander I of Russia, Alexander I. Nicholas's thirty-year reign began with the failed Decembrist revolt. He is mainly remembered as a reactionary whose controversial reign was marked by geographical expansion, centralisation of administrative policies, and repression of dissent both in Imperial Russia, Russia and among its neighbors. Nicholas had a happy marriage that produced a large family, with all of their seven children surviving childhood. Nicholas's biographer Nicholas V. Riasanovsky said that he displayed determination, singleness of purpose, and an iron will, along with a powerful sense of duty and a dedication to very hard work. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee Of Ministers
The Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe ( French: ''Comité des ministres du Conseil de l'Europe'') or Committee of Ministers ( French: ''Comité des ministres'') is the Council of Europe's decision-making body. It comprises the Foreign Affairs Ministers of all the member states, or their permanent diplomatic representatives in Strasbourg. It is both a governmental body, where national approaches to problems facing European society can be discussed on an equal footing, as well as a collective forum, where Europe-wide responses to such challenges are formulated. In collaboration with the Parliamentary Assembly, it is the guardian of the Council's fundamental values; it monitors member states' compliance with their undertakings. The Holy See, Japan, Mexico, and the US are observer states in the Committee of Ministers. Members of the Committee of Ministers The Minister of Foreign Affairs of each Council of Europe member state sits on the Committee of Ministers. In May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viktor Kochubey
Prince Viktor Pavlovich Kochubey (); ( – ) was a Russian statesman and close aide of Alexander I of Russia. Of Ukrainian and Zaporozhian Cossack origin, he was a great-grandson of Vasily Kochubey. He took part in the Privy Committee that outlined Government reform of Alexander I. He served in London and Paris embassies as counsel, then as Ambassador to Turkey. In 1798 he was appointed to the board of College of Foreign Affairs and was made Count next year, but then Paul I of Russia exiled him. At the start of the reign of Alexander I, he joined the liberal Privy Committee that outlined Government reform of Alexander I. He was the Minister of Foreign Affairs in 1801–1802 and also Minister of the Interior until 1812, then in 1819–1825. Since 1827 he was the President of the State Council and Chairman of the Committee of Ministers. In 1834, he was granted the rank of Chancellor of the Russian Empire. Biography Early years Kochubey was born in Poltava province, in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Mikhailovich Karamzin
Nikolay Mikhailovich Karamzin () was a Russian historian, writer, poet and critic. He is best remembered for his fundamental ''History of the Russian State'', a 12-volume national history. Early life Karamzin was born in the small village of Mikhailovka (modern-day Karamzinka village of Maynsky District, Ulyanovsk Oblast, Russia) near Simbirsk in the Znamenskoye family estate. Another version exists that he was born in 1765 in the Mikhailovka village of the Orenburg Governorate (modern-day Preobrazhenka, Orenburg Oblast, Preobrazhenka village of the Orenburg Oblast, Russia) where his father served, and in recent years Orenburg historians have been actively disputing the official version. His father Mikhail Yegorovich Karamzin (1724—1783) was a retired captain of the Imperial Russian Army who belonged to the Russian nobility, Russian noble family of modest means founded by Semyon Karamzin in 1606. For many years its members had served in Nizhny Novgorod as high-ranking office ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criminal Procedure
Criminal procedure is the adjudication process of the criminal law. While criminal procedure differs dramatically by jurisdiction, the process generally begins with a formal criminal charge with the person on trial either being free on bail or incarcerated, and results in the conviction or acquittal of the defendant. Criminal procedure can be either in form of inquisitorial or adversarial criminal procedure. Basic rights Currently, in many countries with a democratic system and the rule of law, criminal procedure puts the burden of proof on the prosecution – that is, it is up to the prosecution to prove that the defendant is guilty beyond any reasonable doubt, as opposed to having the defense prove that they are innocent, and any doubt is resolved in favor of the defendant. This provision, known as the presumption of innocence, is required, for example, in the 46 countries that are members of the Council of Europe, under Article 6 of the European Convention on Human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Ministry Of Internal Affairs
The Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation (MVD; , ''Ministerstvo vnutrennikh del'') is the interior ministry of Russia. The MVD is responsible for law enforcement in Russia through its agencies the Police of Russia, Migration Affairs, Drugs Control, Traffic Safety, the Centre for Combating Extremism, and the Investigative Department. The MVD is headquartered in Zhitnaya Street 16 in Yakimanka, Moscow. Vladimir Kolokoltsev has been the Minister of Internal Affairs since 2012. History Russian Empire (1802–1917) The first interior ministry (MVD) in Russia was created by Tsar Alexander I on 28 March 1802. The MVD was one of the most powerful governmental bodies of the Empire, responsible for the police forces and Internal Guards, and the supervision of gubernial administrations. Its initial responsibilities also included prisons, firefighting, state enterprises, the state postal system, state property, construction, roads, medicine, clergy, natural re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |