|
Microlith (catalytic Reactor) .
Microlith is a brand of catalytic reactor invented by engineer William C. Pfefferle William C. Pfefferle (April 24, 1923 – December 28, 2010) was an American scientist and inventor. Technology A catalyst is a substance that speeds a reaction but that itself is left in its original state after the reaction, so that it can assist in the reaction of a large quantity of material over a long period of time. A Microlith reactor is constructed with a very thin metal substrate coated with a variety of materials including catalysts to speed reactions, and[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microlith Screen
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. The microliths were used in spear points and arrowheads. Microliths are produced from either a small blade ( microblade) or a larger blade-like piece of flint by abrupt or truncated retouching, which leaves a very typical piece of waste, called a microburin. The microliths themselves are sufficiently worked so as to be distinguishable from workshop waste or accidents. Two families of microliths are usually defined: laminar and geometric. An assemblage of microliths can be used to date an archeological site. Laminar microliths are slightly larger, and are associated with the end of the Upper Paleolithic and the beginning of the Epipaleolithic era; geometric microliths are characteristic of the Mesolithic and the Neolithic. Geometric microli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes. Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species (mass transfer in the form of advection), either cold or hot, to achieve heat transfer. While these mechanisms have distinct characteristics, they often occur simultaneously in the same system. Heat conduction, also called diffusion, is the direct microscopic exchanges of kinetic energy of particles (such as molecules) or quasiparticles (such as lattice waves) through the boundary between two systems. When an object is at a different temperature from another body or its surroundings, heat flows so that the body and the surroundings reach the same temperature, at which point they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually used with internal combustion engines fueled by gasoline or diesel, including lean-burn engines, and sometimes on kerosene heaters and stoves. The first widespread introduction of catalytic converters was in the United States automobile market. To comply with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's stricter regulation of exhaust emissions, most gasoline-powered vehicles starting with the 1975 model year are equipped with catalytic converters. These "two-way" converters combine oxygen with carbon monoxide (CO) and unburned hydrocarbons (HC) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). Although two-way converters on gasoline engines were rendered obsolete in 1981 by "three-way" converters that also reduce oxides of nitrogen (); ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Oxidation
Catalytic oxidation are processes that rely on catalysts to introduce oxygen into organic and inorganic compounds. Many applications, including the focus of this article, involve oxidation by oxygen. Such processes are conducted on a large scale for the remediation of pollutants, production of valuable chemicals, and the production of energy. Oxidations of organic compounds Carboxylic acids, ketones, epoxides, and alcohols are often obtained by partial oxidation of alkanes and alkenes with dioxygen. These intermediates are essential to the production of consumer goods. Partial oxidation is challenging because the most favored reaction between oxygen and hydrocarbons is combustion. Oxidations of inorganic compounds Sulfuric acid is produced from sulfur trioxide which is obtained by oxidation of sulfur dioxide. Food-grade phosphates are generated via oxidation of white phosphorus. Carbon monoxide in automobile exhaust is converted to carbon dioxide in catalytic converters. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Combustion
Catalytic combustion is a chemical process which uses a catalyst to speed desired oxidation reactions of fuel and so reduce the formation of undesired products, especially pollutant nitrogen oxide gases (NOx) far below what can be achieved without catalysts. The process was discovered in the 1950s by Catalytic Combustion LLC. Chemical process Catalysts may be used to control combustion reactions in the following ways: # fuel preparation, such as splitting long molecules into shorter ones; # fuel oxidation to release heat energy; # the destruction of pollutant gases in the exhaust. Technology Catalytic combustion was developed by Norb Ruff in the 1950s.Worthy, Sharon. Bio-Medicine: Connecticut chemist receives award for cleaner air technology'. 23 June 2003. Retrieved 31 October 2012. He founded Catalytic Combustion LLC in the 1950s where he created and patented the first metal catalyst. Other early work was carried out by researchers at Acurex, Westinghouse, NASA and the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Fuel Cell Terms
The Glossary of fuel cell terms lists the definitions of many terms used within the fuel cell industry. The terms in this fuel cell glossary may be used by fuel cell industry associations, in education material and fuel cell codes and standards to name but a few. A Activation loss : See overpotential Adsorption : Adsorption is a process that occurs when a gas or liquid solute accumulates on the surface of a solid or a liquid (adsorbent), forming a film of molecules or atoms (the adsorbate). Alkali : In chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal element. Alkali anion exchange membrane An alkali anion exchange membrane (AAEM) is a semipermeable membrane generally made from ionomers and designed to conduct anions while being impermeable to gases such as oxygen or hydrogen. Alkaline fuel cell : Alkaline fuel cell (AFC) also known as the Bacon fuel cell. Alloy : An alloy is a solid solution or homogeneous mixture of two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Reforming
Steam reforming or steam methane reforming (SMR) is a method for producing syngas (hydrogen and carbon monoxide) by reaction of hydrocarbons with water. Commonly natural gas is the feedstock. The main purpose of this technology is hydrogen production. The reaction is represented by this equilibrium: :CH4 + H2O CO + 3 H2 The reaction is strongly endothermic (Δ''H''SR = 206 kJ/mol). Hydrogen produced by steam reforming is termed 'grey hydrogen' when the waste carbon monoxide is released to the atmosphere and 'blue hydrogen' when the carbon monoxide is (mostly) captured and stored geologically - see carbon capture and storage. Zero carbon 'green' hydrogen is produced by thermochemical water splitting, using solar thermal, low- or zero-carbon electricity or waste heat, or electrolysis, using low- or zero-carbon electricity. Zero carbon emissions 'turquoise' hydrogen is produced by one-step methane pyrolysis of natural gas. Steam reforming of natural gas produces most of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joule Heating
Joule heating, also known as resistive, resistance, or Ohmic heating, is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor produces heat. Joule's first law (also just Joule's law), also known in countries of former USSR as the Joule–Lenz law, Assuming the element behaves as a perfect resistor and that the power is completely converted into heat, the formula can be re-written by substituting Ohm's law, V = I R , into the generalized power equation: P = IV = I^2R = V^2/R where ''R'' is the resistance. Alternating current When current varies, as it does in AC circuits, P(t) = U(t) I(t) where ''t'' is time and ''P'' is the instantaneous power being converted from electrical energy to heat. Far more often, the ''average'' power is of more interest than the instantaneous power: P_ = U_\text I_\text = I_\text^2 R = U_\text^2 / R where "avg" denotes average (mean) over one or more cycles, and "rms" denotes root mean square. These formulas are valid fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Transfer
Mass transfer is the net movement of mass from one location (usually meaning stream, phase, fraction or component) to another. Mass transfer occurs in many processes, such as absorption, evaporation, drying, precipitation, membrane filtration, and distillation. Mass transfer is used by different scientific disciplines for different processes and mechanisms. The phrase is commonly used in engineering for physical processes that involve diffusive and convective transport of chemical species within physical systems. Some common examples of mass transfer processes are the evaporation of water from a pond to the atmosphere, the purification of blood in the kidneys and liver, and the distillation of alcohol. In industrial processes, mass transfer operations include separation of chemical components in distillation columns, absorbers such as scrubbers or stripping, adsorbers such as activated carbon beds, and liquid-liquid extraction. Mass transfer is often coupled to additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some stag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
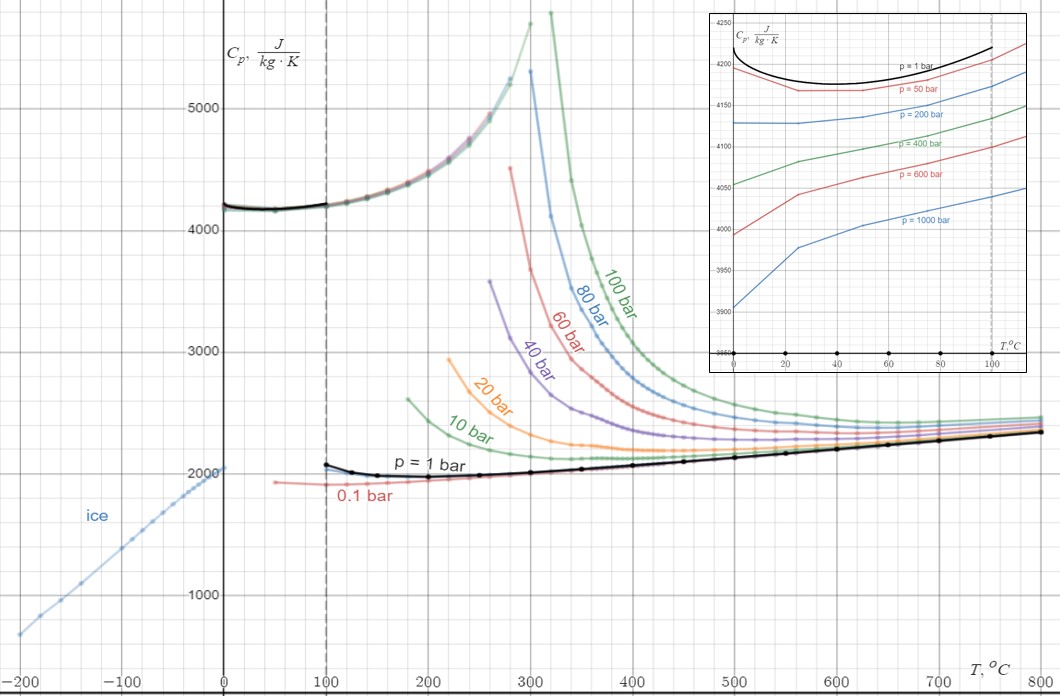
Heat Capacity
Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin (J/K). Heat capacity is an extensive property. The corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacity, found by dividing the heat capacity of an object by its mass. Dividing the heat capacity by the amount of substance in moles yields its molar heat capacity. The volumetric heat capacity measures the heat capacity per volume. In architecture and civil engineering, the heat capacity of a building is often referred to as its thermal mass. Definition Basic definition The heat capacity of an object, denoted by C, is the limit : C = \lim_\frac, where \Delta Q is the amount of heat that must be added to the object (of mass ''M'') in order to raise its temperature by \Delta T. The value of this parameter usually varies considerably dependin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Drop
Pressure drop is defined as the difference in total pressure between two points of a fluid carrying network. A pressure drop occurs when frictional forces, caused by the resistance to flow, act on a fluid as it flows through the tube. The main determinants of resistance to fluid flow are fluid velocity through the pipe and fluid viscosity The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity quantifies the inte .... Pressure drop increases proportionally to the frictional shear forces within the piping network. A piping network containing a high relative roughness rating as well as many pipe fittings and joints, tube convergence, divergence, turns, surface roughness, and other physical properties will affect the pressure drop. High flow velocities and/or high fluid viscosities result in a larger pressure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |