|
Micro Hydropower Plant
Micro hydro is a type of hydroelectric power that typically produces from 5 kW to 100 kW of electricity using the natural flow of water. Installations below 5 kW are called pico hydro. These installations can provide power to an isolated home or small community, or are sometimes connected to electric power networks, particularly where net metering is offered. There are many of these installations around the world, particularly in developing nations as they can provide an economical source of energy without the purchase of fuel. Micro hydro systems complement solar PV power systems because in many areas water flow, and thus available hydro power, is highest in the winter when solar energy is at a minimum. Micro hydro is frequently accomplished with a pelton wheel for high head, low flow water supply. The installation is often just a small dammed pool, at the top of a waterfall, with several hundred feet of pipe leading to a small generator housing. In low head sites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nw Vietnam Hydro
NW may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''NW'' (novel), by Zadie Smith * Nat Wolff, a singer and actor * New wave music, a genre * '' New Weekly'', an Australian celebrity magazine * Nintendo Wii, a video game console * Northern Whig, Irish newspaper Geography * Northwest (other), multiple articles * NW postcode area, northwest London, UK * Nidwalden, a canton of Switzerland * North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany * North West (South African province) Technology * Nanowire, a nanostructure with a diameter on the order of a nanometer * NetWare, in file and protocol names of the Novell NetWare family * Nuclear warfare, the use of nuclear weapons in war * An ISO-specified vacuum flange fitting (code NW) Other uses * Nahdlatul Wathan, an Indonesian Islamic organization * No worries, an expression * Norfolk and Western Railroad, a U.S. class I railroad * ''North Western Reporter'', a US case law report series * Northwest Airlines (former IATA ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work (physics), energy transfer. The watt is named in honor of James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish people, Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own Watt steam engine, steam engine in 1776, which became fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one meter per second against a constant opposing force of one Newton (unit), newton, the rate at which Work (physics), work is done is one watt. \mathrm. In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screw Turbine
file:Archimedes-screw one-screw-threads with-ball 3D-view animated smal back.gif, Reverse action of the Archimedean screw, the principle of the screw turbine gaining energy from water flowing down through the screw file:Helical screw single double triple quadruple start.png, Screw turbines typically have three or four flights (second row) file:Monmouth New Hydro Scheme - geograph.org.uk - 1538784.jpg, Two parallel screw turbines capable of producing 75 kW each, in Osbaston, Monmouth, Monmouth, South Wales file:Wasserkraftschnecke, Schwarze Lacke, München.ogv, Video of a 40 kW screw turbine in Munich, Germany A screw turbine (also known as an Archimedean turbine, Archimedes screw generator or ASG, or Archimedes screw turbine or AST) is a water turbine that converts the potential energy of water on an upstream level into Work (physics), work. This hydropower converter is driven by the weight of water, similar to water wheels, and can be considered as a quasi-static pressur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossberger Turbine
A cross-flow turbine, Bánki-Michell turbine, or Ossberger turbine''E.F. Lindsley,'' Water power for your homePopular Science, May 1977, Vol. 210, No. 5 87-93. is a water turbine developed by the Australian Anthony Michell, the Hungarian Donát Bánki and the German Fritz Ossberger. Michell obtained patents for his turbine design in 1903, and the manufacturing company Weymouth made it for many years. Ossberger's first patent was granted in 1933 ("Free Jet Turbine" 1922, Imperial Patent No. 361593 and the "Cross Flow Turbine" 1933, Imperial Patent No. 615445), and he manufactured this turbine as a standard product. Today, the company founded by Ossberger which bears his name is the leading manufacturer of this type of turbine. Unlike most water turbines, which have axial or radial flows, in a cross-flow turbine the water passes through the turbine transversely, or across the turbine blades. As with a water wheel, the water is admitted at the turbine's edge. After passing to the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
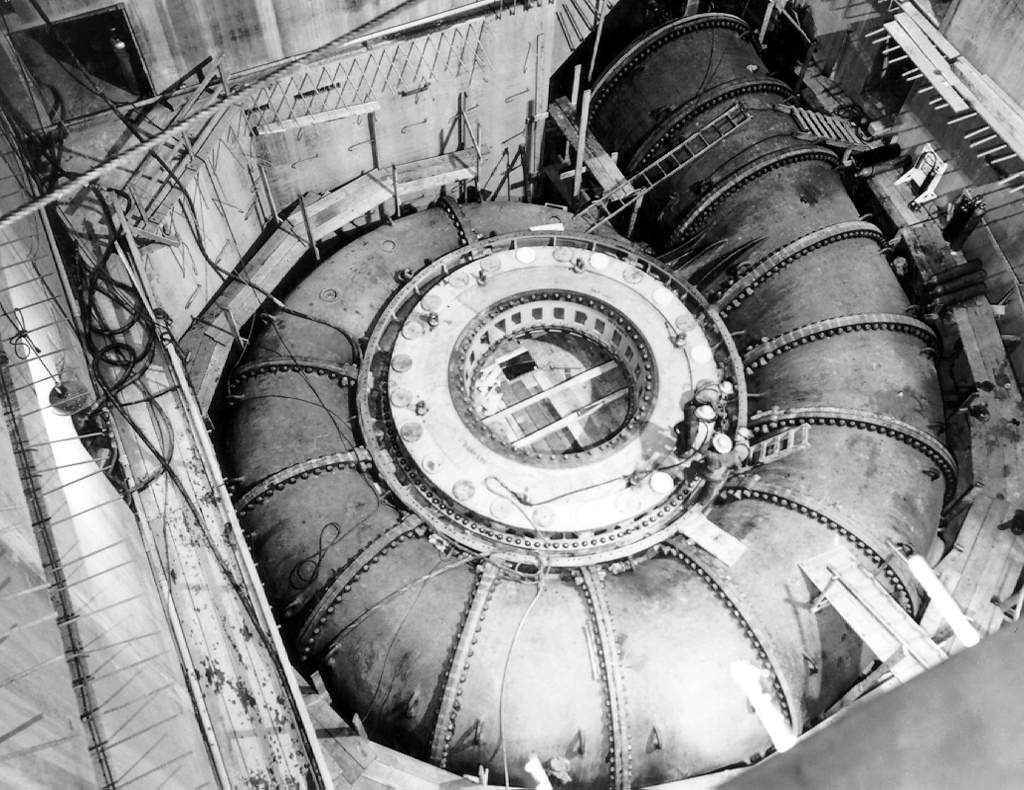
Kaplan Turbine
The Kaplan turbine is a propeller-type water turbine which has adjustable blades. It was developed in 1913 by Austrian professor Viktor Kaplan, who combined automatically adjusted propeller blades with automatically adjusted wicket gates to achieve efficiency over a wide range of flow and water level. The Kaplan turbine was an evolution of the Francis turbine. Its invention allowed efficient power production in low-head applications which was not possible with Francis turbines. The head ranges from and the output ranges from 5 to 200 MW. Runner diameters are between . Turbines rotate at a constant rate, which varies from facility to facility. That rate ranges from as low as 54.5 rpm ( Albeni Falls Dam) to 450 rpm. Kaplan turbines are now widely used throughout the world in high-flow, low-head power production. Development Viktor Kaplan, living in Brno, Austria-Hungary (now in the Czech Republic), obtained his first patent for an adjustable blade propeller turbine in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelton Wheel
The Pelton wheel or Pelton Turbine is an Impulse (physics), impulse-type water turbine invented by American inventor Lester Allan Pelton in the 1870s. The Pelton wheel extracts energy from the impulse of moving water, as opposed to water's dead weight like the traditional overshot water wheel. Many earlier variations of impulse turbines existed, but they were less Energy conversion efficiency, efficient than Pelton's design. Water leaving those wheels typically still had high speed, carrying away much of the dynamic energy brought to the wheels. Pelton's paddle geometry was designed so that when the rim ran at half the speed of the water jet, the water left the wheel with very little speed; thus his design extracted almost all of the water's impulse energywhich made for a very efficient turbine. History file:Pelton wheel (patent).png, Figure from Lester Allan Pelton's original October 1880 patent Lester Allan Pelton was born in Vermillion, Ohio in 1829. In 1850, he traveled ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverter (electrical)
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of rectifiers which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC. The input voltage, output voltage and frequency, and overall power handling depend on the design of the specific device or circuitry. The inverter does not produce any power; the power is provided by the DC source. A power inverter can be entirely electronic or maybe a combination of mechanical effects (such as a rotary apparatus) and electronic circuitry. Static inverters do not use moving parts in the conversion process. Power inverters are primarily used in electrical power applications where high currents and voltages are present; circuits that perform the same function for electronic signals, which usually have very low currents and vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induction Generator
An induction generator (or asynchronous generator) is a type of alternating current (AC) electrical generator that uses the principles of induction motors to produce electric power. Induction generators operate by mechanically turning their rotors faster than synchronous speed. A regular AC induction motor usually can be used as a generator, without any internal modifications. Because they can recover energy with relatively simple controls, induction generators are useful in applications such as mini hydro power plants, wind turbines, or in reducing high-pressure gas streams to lower pressure. An induction generator draws reactive excitation current from an external source. Induction generators have an AC rotor and cannot bootstrap using residual magnetization to black start a de-energized distribution system as synchronous machines do. Power factor correcting capacitors can be added externally to neutralize a constant amount of the variable reactive excitation current. After s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Load Bank
A load bank is a piece of electrical test equipment used to simulate an electrical load, to test an electric electric power, power source without connecting it to its normal operating load. During testing, adjustment, calibration, or verification procedures, a load bank is connected to the output of a power source, such as an electric generator, Electric battery, battery, servoamplifier or photovoltaic system, in place of its usual load. The load bank presents the source with electrical characteristics similar to its standard operating load, while dissipating the Electricity, power output that would normally be consumed by it. The power is usually converted to heat by a heavy duty electrical resistor, resistor or bank of resistive heating elements in the device, and the heat removed by a forced air or water thermal management (electronics), cooling system. The device usually also includes instruments for metering, load control, and overload protection. Load banks can either b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility Frequency
The utility frequency, (power) line frequency (American English) or mains frequency (British English) is the nominal frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in a wide area synchronous grid transmitted from a power station to the end-user. In large parts of the world this is 50 Hz, although in the Americas and parts of Asia it is typically 60 Hz. Current usage by country or region is given in the list of mains electricity by country. During the development of commercial electric power systems in the late-19th and early-20th centuries, many different frequencies (and voltages) had been used. Large investment in equipment at one frequency made standardization a slow process. However, as of the turn of the 21st century, places that now use the 50 Hz frequency tend to use 220–240 V, and those that now use 60 Hz tend to use 100–127 V. Both frequencies coexist today (Japan uses both) with no great technical reason to prefer one ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |