|
Methodist Church In Ireland
The Methodist Church in Ireland () is a Wesleyan Methodist church that operates across both Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland on an all-Ireland basis. It is the fourth-largest Christian denomination in Northern Ireland. The Irish Methodist Church has close links with the Methodist Church in Britain. For the year ending 31 December 2012, there were 105 Methodist ministers, 227 local preachers and over six hundred lay people in leadership positions serving over 200 congregations, which combine to form a total community of 49,394 people. In 2018, the numbers of members and wider community role was approximately 50,000. The governing body of the Methodist Church in Ireland is the annual Conference. History Methodism was founded in England by John Wesley and his younger brother Charles Wesley during the 18th century, initially as a revival movement within the Church of England. The spread of Methodism to Ireland was facilitated by English preachers, and the early Iris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divine grace, the priesthood of all believers, and the Bible as the sole infallible source of authority for Christian faith and practice. The five solae, five ''solae'' summarize the basic theological beliefs of mainstream Protestantism. Protestants follow the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began in the 16th century with the goal of reforming the Catholic Church from perceived Criticism of the Catholic Church, errors, abuses, and discrepancies. The Reformation began in the Holy Roman Empire in 1517, when Martin Luther published his ''Ninety-five Theses'' as a reaction against abuses in the sale of indulgences by the Catholic Church, which purported to offer the remission of the Purgatory, temporal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Revival
Christian revival is defined as "a period of unusual blessing and activity in the life of the Christian Church". Proponents view revivals as the restoration of the Church to a vital and fervent relationship with God after a period of moral decline, instigated by God, as opposed to an evangelistic campaign. Revivals within modern church history Within Christian studies the concept of revival is derived from biblical narratives of national decline and restoration during the history of the Israelites. In particular, narrative accounts of the Kingdoms of Israel and Judah emphasise periods of national decline and revival associated with the rule of respectively wicked or righteous kings. Josiah is notable within this biblical narrative as a figure who reinstituted temple worship of Yahweh while destroying pagan worship. Within modern church history, church historians have identified and debated the effects of various national revivals within the history of the US and other countries. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordination Of Women In Methodism
The ordination of women has been commonly practiced in List of Methodist denominations, Methodist denominations since the 20th century, and some denominations earlier allowed women to preacher, preach. Historically, ordination of women#Christianity, as in other Christian denominations, many Methodist churches did not permit women to preach or exercise authority over men. However, earlier in the 18th century, Methodist founder John Wesley did authorise a number of women to preach, including Sarah Crosby. In Britain, the Primitive Methodism in the United Kingdom, Primitive Methodist Church always allowed the ordination of women to full-time ministry. The Primitive Methodists had full equal roles for men and women, but the Wesleyan Methodist Church (Great Britain), Wesleyan Methodist Church only ordained its first deaconess in 1890, and after Methodist Union, the British Methodist Church resumed ordaining women as presbyters (elders) in 1974. Other Methodist denominations that practi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All-Ireland
All-Ireland (sometimes All-Island) is a term used to describe organisations and events whose interests extend over the entire island of Ireland, as opposed to the separate jurisdictions of the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland. "All-Ireland" is most frequently used to refer to sporting teams or events for the entire island, but also has related meanings in politics and religion. In sports Many high profile modern sports were codified within the United Kingdom at the end of the nineteenth century, during a period of British imperial dominance, and while the whole of Ireland was a constituent country of the United Kingdom. As such, early international competition first featured the four constituent countries of the UK; England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland, before spreading to other parts of the Empire. For this reason, in many sporting contexts outside Olympic sport (which was first reorganised by the French and Greeks, and in which the UK competed as Great Britain), th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primitive Methodists
The Primitive Methodist Church is a Christian denomination within the holiness movement. Originating in early 19th-century England as a revivalist movement within Methodism, it was heavily influenced by American evangelist Lorenzo Dow (1777–1834), whose visits inspired a return to fervent, open-air preaching. In the United States, the Primitive Methodist Church had eighty-three parishes and 8,487 members in 1996. In Great Britain and Australia, the Primitive Methodist Church merged with other denominations, to form the Methodist Church of Great Britain in 1932 and the Methodist Church of Australasia in 1901. (The latter subsequently merged into the Uniting Church in Australia in 1977.) History United Kingdom The leaders who originated Primitive Methodism were attempting to restore a spirit of revivalism as they felt was found in the ministry of John Wesley, with no intent of forming a new church. The leaders were Hugh Bourne (1772–1852) and William Clowes (1780–1851), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrament
A sacrament is a Christian rite which is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence, number and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments to be a visible symbol of the reality of God, as well as a channel for God's grace. Many denominations, including the Catholic, Lutheran, Presbyterian, Anglican, Baptist, Methodist, and Reformed, hold to the definition of sacrament formulated by Augustine of Hippo: an outward sign of an inward grace, that has been instituted by Jesus Christ. Sacraments signify God's grace in a way that is outwardly observable to the participant. The Catholic Church, Hussite Church and the Old Catholic Church recognize seven sacraments: Baptism, Penance (Reconciliation or Confession), Eucharist (or Holy Communion), Confirmation, Marriage (Matrimony), Holy Orders, and Anointing of the Sick (Extreme Unction). The Eastern Churches, such as the Eastern Orthodox Church an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Famine (Ireland)
The Great Famine, also known as the Great Hunger ( ), the Famine and the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of mass starvation and disease in Ireland lasting from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis and had a major impact on Irish society and history as a whole. The most severely affected areas were in the western and southern parts of Ireland—where the Irish language was dominant—hence the period was contemporaneously known in Irish as , which literally translates to "the bad life" and loosely translates to "the hard times". The worst year of the famine was 1847, which became known as "Black '47".Éamon Ó Cuív – the impact and legacy of the Great Irish Famine The population of Ireland on the eve of the famine was about 8.5 million; by 1901, it was just 4.4 million. During the Great Hunger, roughly 1 million people died and more than 1 million more Irish diaspora, fled the country, causing the country's population to fall by 20–25% between 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Catholics
Irish Catholics () are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland, defined by their adherence to Catholic Christianity and their shared Irish ethnic, linguistic, and cultural heritage.The term distinguishes Catholics of Irish descent, particularly in contexts of national identity, political history, and diaspora, from other Catholic populations globally. They constitute the majority population in the Republic of Ireland, where approximately 3.9 million people identified as Catholic in the 2022 census, and a significant minority in Northern Ireland, with around 820,000 adherents. The Irish diaspora has established Irish Catholic communities worldwide, particularly in the United States, Canada, Australia, and the United Kingdom, where they have played a major role in shaping cultural, religious, and political landscapes. Historically, Irish Catholics experienced systemic discrimination, especially under British rule, through the imposition of Penal Laws in the 17th and 18th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Besançon Hugues, was in common use by the mid-16th century. ''Huguenot'' was frequently used in reference to those of the Reformed Church of France from the time of the Protestant Reformation. By contrast, the Protestant populations of eastern France, in Alsace, Moselle (department), Moselle, and Montbéliard, were mainly Lutheranism, Lutherans. In his ''Encyclopedia of Protestantism'', Hans Hillerbrand wrote that on the eve of the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572, the Huguenot community made up as much as 10% of the French population. By 1600, it had declined to 7–8%, and was reduced further late in the century after the return of persecution under Louis XIV, who instituted the ''dragonnades'' to forcibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatines
Palatines () were the citizens and princes of the Palatinates, Holy Roman States that served as capitals for the Holy Roman Emperor. After the fall of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the nationality referred more specifically to residents of the Rhenish Palatinate, known simply as "the Palatinate". American Palatines, including the Pennsylvania Dutch, have maintained a presence in the United States as early as 1632 and are collectively known as "Palatine Dutch" (). The earliest Palatines settled in the Maryland Palatinate, an American palatinate established by the Calvert family as a haven for Catholic refugees. Holy Roman Nationality Paladins The term ''palatine'' or ''palatinus'' was first used in the Roman Empire for chamberlains of the emperor (e.g. Chamberlain of the Holy Roman Church) due to their association with the Palatine Hill, the home where Roman emperors lived since Augustus Caesar (and whence "palace"). After the fall of Ancient Rome, a new feudal type of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
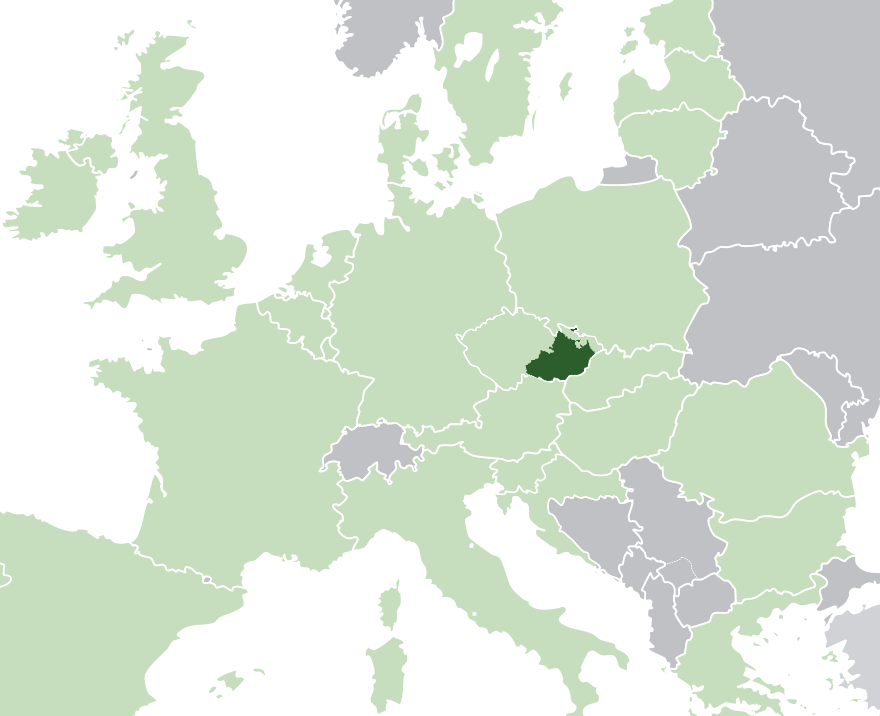
Moravians
Moravians ( or Colloquialism, colloquially , outdated ) are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group from the Moravia region of the Czech Republic, who speak the Moravian dialects of Czech language, Czech or Czech language#Common Czech, Common Czech or a mixed form of both. Along with the Silesians of the Czech Republic, a part of the population to identify ethnically as Moravian has registered in Czech censuses since 1991. The figure has fluctuated and in the 2011 census, 6.01% of the Czech population declared Moravian as their ethnicity. Smaller pockets of people declaring Moravian ethnicity are also native to neighboring Slovakia. Etymology A certain ambiguity in Czech language, Czech derives from the fact that it distinguishes between (Bohemia proper) and (Czech Republic as a whole), but the corresponding adjective and noun designating an inhabitant and/or a member of a nation can be related to either of them. The adjective and the noun ('Bohemian') carry only the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |