|
Metabolic Age
Metabolic age is calculated by comparing one's basal metabolic rate to the average of one's chronological age group. All the components in the body require various levels of energy to be maintained. Body fat requires much less energy than lean muscle, as lean muscle is much more metabolically active and therefore requires more energy expenditure to remain in homeostasis. If comparing two individuals, with all variables being equal, the person with more lean muscle mass will have a higher basal metabolic rate, and therefore, a lower metabolic age in comparison to those with the identical chronological age. __TOC__ History The research on which the concept of metabolic age is based began with Alfred Joseph Clark in 1927. Clark found that the pulse rate of different species of animal varied with body size to the power of −0.27. Other researchers went on to find that other biological rates varied to the same, or a similar, coefficient. S. Brody developed a physiological age sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Metabolic Rate
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest.. In other words it is the energy required by body organs to perform normal It is reported in energy units per unit time ranging from watt (joule/second) to ml O2/min or joule per hour per kg body mass J/(h·kg). Proper measurement requires a strict set of criteria to be met. These criteria include being in a physically and psychologically undisturbed state and being in a thermally neutral environment while in the post- absorptive state (i.e., not actively digesting food). In bradymetabolic animals, such as fish and reptiles, the equivalent term standard metabolic rate (SMR) applies. It follows the same criteria as BMR, but requires the documentation of the temperature at which the metabolic rate was measured. This makes BMR a variant of standard metabolic rate measurement that excludes the temperature data, a practice that has led to problems in defining "standard" rates o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Group
A demographic profile is a form of demographic analysis in which information is gathered about a group to better understand the group's composition or behaviors for the purpose of providing more relevant services. In business, a demographic profile is usually used to increase marketing efficiency. This is done by using gathered data to determine how to advertise products or services to specific audiences and identify gaps in marketing strategy. By focusing on a specific audience, a company can more efficiently spend advertising resources to maximize sales. This tactic is more direct than simply advertising on the basis that everyone is a potential consumer; while this may be true, it does not capitalize on the increased returns that more focused marketing can generate. Traditional demographic profiling involves gathering information on large groups of people in order to identify common trends, such as changes in population size or composition over time. These trends can be ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fertility And Sterility
''Fertility and Sterility'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published by Elsevier on behalf of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. It was established in 1950 and is an official journal of several societies (American Society for Reproductive Medicine, Society for Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility, Society of Reproductive Surgeons, Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology, Society for Male Reproduction and Urology, Pacific Coast Reproductive Society, Canadian Fertility and Andrology Society). The journal covers research in basic and clinical reproduction, primarily concerning human fertility, and addresses related ethical and societal issues. History The journal was established in 1950 with Pendleton Tompkins as the first editor-in-chief. The current editor is Kurt Barnhart. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Science Citation Index Expanded and Scopus. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the jour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Fat
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of White blood cell, immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and Thermal insulation, insulates the body. Previously treated as being hormonally inert, in recent years adipose tissue has been recognized as a major endocrine organ, as it produces hormones such as leptin, estrogen, resistin, and cytokines (especially TNF-alpha, TNFα). In obesity, adipose tissue is implicated in the chronic release of pro-inflammatory markers known as adipokines, which are responsible for the development of metabolic syndromea constellation of diseases including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. Adipose tissue is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
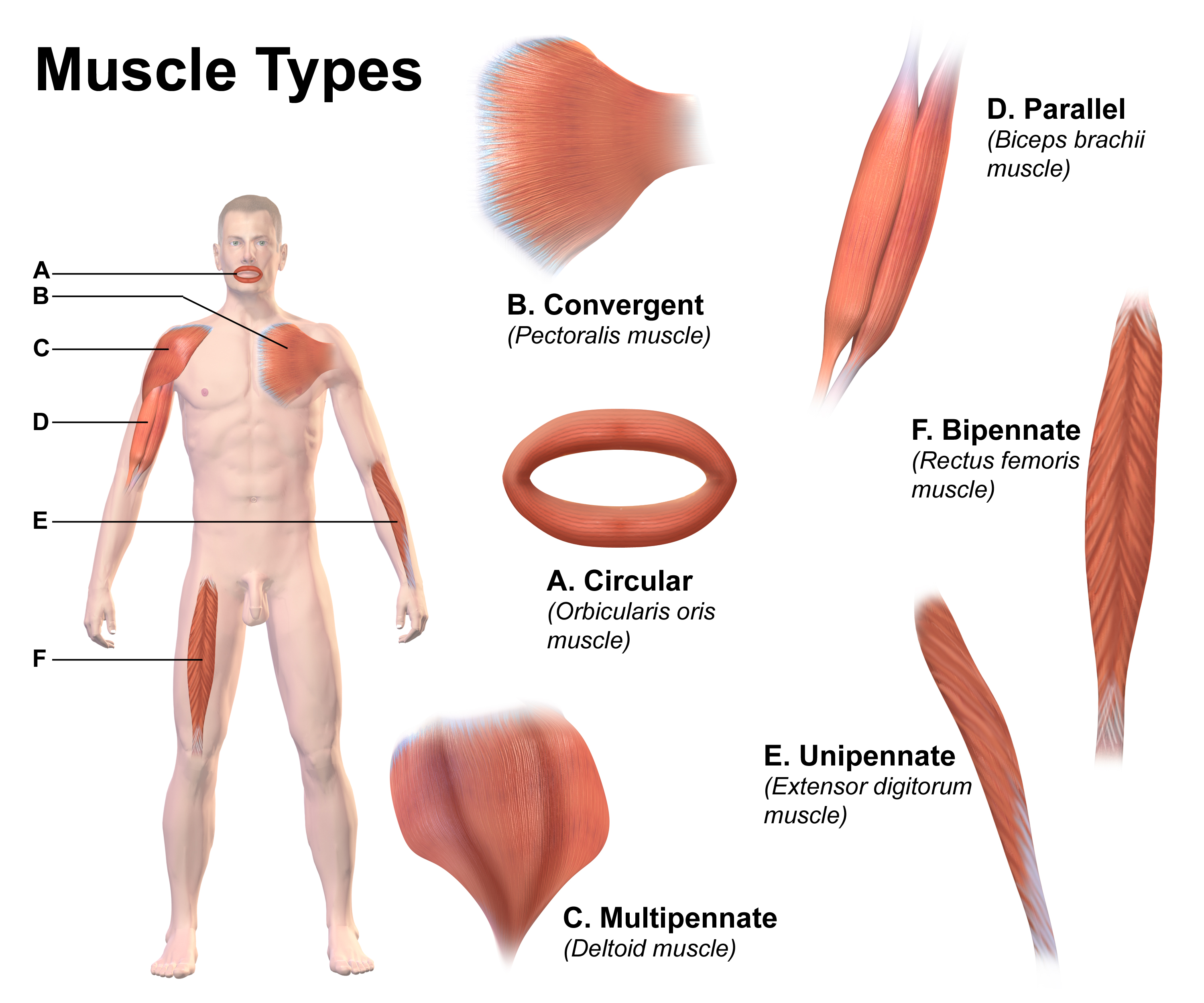
Lean Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside of the cell membrane. Muscle fibers also have multiple mitochondria to meet energy needs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance, being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). Other variables include the pH of extracellular fluid, the concentrations of sodium, potassium, and calcium ions, as well as the blood sugar level, and these need to be regulated despite changes in the environment, diet, or level of activity. Each of these variables is controlled by one or more regulators or homeostatic mechanisms, which together maintain life. Homeostasis is brought about by a natural resistance to change when already in optimal conditions, and equilibrium is maintained by many regulatory mechanisms; it is thought to be the central motivation for all organic action. All home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Mass
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside of the cell membrane. Muscle fibers also have multiple mitochondria to meet energy nee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Irish Times
''The Irish Times'' is an Irish daily broadsheet newspaper and online digital publication. It was launched on 29 March 1859. The editor is Ruadhán Mac Cormaic. It is published every day except Sundays. ''The Irish Times'' is Ireland's leading newspaper. It is considered a newspaper of record for Ireland. Though formed as a Protestant Irish nationalist paper, within two decades and under new owners, it became a supporter of unionism in Ireland. In the 21st century, it presents itself politically as "liberal and progressive", as well as being centre-right on economic issues. The editorship of the newspaper from 1859 until 1986 was controlled by the Anglo-Irish Protestant minority, only gaining its first nominal Irish Catholic editor 127 years into its existence. The paper's notable columnists have included writer and arts commentator Fintan O'Toole and satirist Miriam Lord. The late Taoiseach Garret FitzGerald was once a columnist. Michael O'Regan was the Leinster Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Joseph Clark
Professor Alfred Joseph Clark MC FRS FRSE (19 August 1885 – 30 July 1941) was a British pharmacologist and Professor of Pharmacology at the University College, London. He was a de-bunker of fraudulent remedies and did many early studies on the placebo effect of many claimed cures. Life He was born in Glastonbury the son of a Quaker, Francis Joseph Clark of Street, Somerset. He was educated at Bootham School in Yorkshire, and attended the University of Cambridge, graduating with a BA in 1907 and receiving a postgraduate MA in 1910. After the First World War he was employed briefly as Professor of Pharmacology at Cape Town University in South Africa, but used this as a stepping-stone to the more prestigious role of Professor of Pharmacology at University College, London where he worked 1919 to 1926, thereafter taking the role as Professor of Materia Medica at the University of Edinburgh. In 1928 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, his proposers inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Kleiber
Max Kleiber (4 January 1893–5 January 1976) was a Swiss agricultural biologist, born and educated in Zürich, Switzerland. Kleiber graduated from the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology as an Agricultural Chemist in 1920, earned the ScD degree in 1924, and became a '' Privatdozent '' after publishing his thesis, ''The Energy Concept in the Science of Nutrition''. Kleiber joined the Animal Husbandry Department of the University of California, Davis (UC Davis) in 1929 to construct respiration chambers and conduct research on energy metabolism in animals. Among his many important achievements, two are especially noteworthy. In 1932, he came to the conclusion that the ¾ power of body weight was the most reliable basis for predicting the basal metabolic rate (BMR) of animals and for comparing nutrient requirements among animals of different sizes. He also provided the basis for the conclusion that total efficiency of energy utilization is independent of body size. These concepts an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |