|
Mercedes-Benz CLK GTR
The Mercedes-Benz CLK GTR (chassis code C297) is a GT1 sports car built and produced by Mercedes-Benz in conjunction with their then motorsport partner AMG. Intended for racing in the new FIA GT Championship series in 1997, the CLK GTR was designed primarily as a race car. As such, the production of road cars necessary in order to meet homologation standards of GT1 was a secondary consideration in the car's design, i.e. the CLK GTR was a homologation special. After its successful campaign in the 1997 FIA GT Championship, the car was also entered in the first two rounds of the 1998 FIA GT Championship and won both of these rounds before being replaced for the 1998 24 Hours of Le Mans. Its successor, the 1998 Mercedes-Benz CLK LM, concluded Mercedes' GT1 program. For 1999, Mercedes introduced the Mercedes-Benz CLR, a sports car built to the Le Mans Grand Touring Prototype (LMGTP) regulations. This sports car was a purpose-built racecar that did not have to abide by the hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goodwood Festival Of Speed
The Goodwood Festival of Speed is an annual motorsports festival featuring modern and historic motor racing vehicles taking part in a hillclimbing, hillclimb and other events, held in Goodwood House, West Sussex, in late June or early July. The event is scheduled to avoid clashing with the Formula One season, enabling fans to see F1 machines as well as cars and motorbikes from motor racing history. In the early years of the Festival, which started in 1993, tens of thousands attended over the weekend. As of 2014, it attracted crowds of around 100,000 on each of the three days it was held. A record crowd of 158,000 attended in 2003, before an advance-ticket-only admission policy came into force; attendance was subsequently capped at 150,000. History The Goodwood Festival of Speed was founded in 1993 by Charles Gordon-Lennox, Earl of March and Kinrara, Lord March in order to bring motor racing back to the Goodwood estate – a location steeped in British motor racing history. Sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greg Moore (racing Driver)
Gregory William Moore (April 22, 1975 – October 31, 1999) was a Canadian professional race car driver who competed in the Firestone Indy Lights, Indy Lights and Championship Auto Racing Teams (CART) series from 1993 to 1999. He began competitive Kart racing, karting at the age of ten and achieved early success, before progressing to Open-wheel car, open-wheel car racing in the Canadian Formula Ford Championship in 1991. Moore won the 1992 USAC FF2000 Western Division Championship and the 1995 Indy Lights season, 1995 Indy Lights Championship. He began competing in CART with Forsythe/Pettit Racing, Forsythe Racing in 1996 PPG Indy Car World Series, 1996, finishing ninth in the List of American open-wheel racing national champions, drivers' championship and was second to Alex Zanardi in the IndyCar Rookie of the Year, Rookie of the Year standings. The following year, Moore claimed the first two victories of his career to finish seventh in the points' standings. He improved on hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequential Manual Transmission
A sequential manual transmission, also known as a sequential gearbox or sequential transmission, is a type of Non-synchronous transmission, non-synchronous manual transmission used mostly in motorcycles and Auto racing, racing cars. It produces faster shift times than traditional Manual transmission#Synchronized transmission, synchronized manual transmissions, and restricts the driver to selecting either the next or previous gear, in a successive order. Design A sequential manual transmission is non-synchronous transmission, unsynchronized, and allows the driver to select either the next gear (e.g. shifting from first gear to second gear) or the previous gear (e.g., shifting from third gear to second gear), operated either via electronic paddle-shifters mounted behind the steering wheel or with a sequential shifter. This restriction avoids accidentally selecting the wrong gear; however, it also prevents the driver from deliberately "skipping" gears. The use of dog clutches (ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-engine Design
In automotive engineering, a mid-engine layout describes the placement of an automobile engine in front of the rear-wheel axles, but behind the front axle. History The mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive format can be considered the original layout of automobiles. A 1901 Autocar was the first gasoline-powered automobile to use a drive shaft and placed the engine under the seat. This pioneering vehicle is now in the collection of the Smithsonian Institution. Benefits Mounting the engine in the middle instead of the front of the vehicle puts more weight over the rear tires, so they have more traction and provide more assistance to the front tires in braking the vehicle, with less chance of rear-wheel lockup and less chance of a skid or spin out. If the mid-engine vehicle is also rear-drive the added weight on the rear tires can also improve acceleration on slippery surfaces, providing much of the benefit of all-wheel-drive without the added weight and expense of all-wheel-drive com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
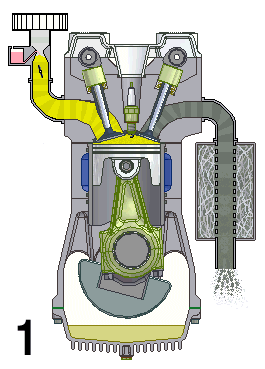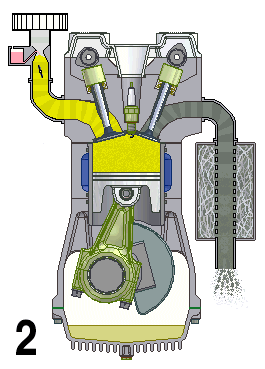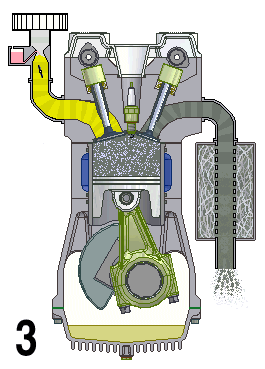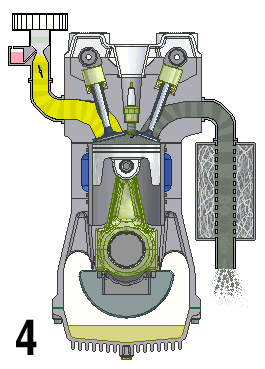
Natural Aspiration
A naturally aspirated engine, also known as a normally aspirated engine, and abbreviated to N/A or NA, is an internal combustion engine in which air intake depends solely on atmospheric pressure and does not have forced induction through a turbocharger or a supercharger. Description In a naturally aspirated engine, air for combustion (Diesel cycle in a diesel engine or specific types of Otto cycle in petrol engines, namely petrol direct injection) or an air/fuel mixture (traditional Otto cycle petrol engines), is drawn into the engine's cylinders by atmospheric pressure acting against a partial vacuum that occurs as the piston travels downwards toward bottom dead centre during the intake stroke. Owing to innate restriction in the engine's inlet tract, which includes the intake manifold, a small pressure drop occurs as air is drawn in, resulting in a volumetric efficiency of less than 100 percent—and a less than complete air charge in the cylinder. The density of the air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V12 Engine
A V12 engine is a twelve-Cylinder (engine), cylinder Internal combustion engine#Reciprocating engines, piston engine where two banks of six cylinders are arranged in a V engine, V configuration around a common crankshaft. V12 engines are more common than V10 engines. However, they are less common than V8 engines. The first V12 engine was built in 1904 for use in Boat racing, racing boats. Due to the balanced nature of the engine and the smooth delivery of Engine power, power, V12 engines were found in early luxury automobiles, boats, aircraft, and tanks. Aircraft V12 engines reached their apogee during World War II, after which they were mostly replaced by jet engines. In Formula One racing, V12 engines were common during the late 1960s and early 1990s. Applications of V12 engines in the 21st century have been as marine engines, in railway locomotives, as large stationary power as well as in some European sports and luxury cars. Design Balance and smoothness Each bank of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; ; Swabian German, Swabian: ; Alemannic German, Alemannic: ; Italian language, Italian: ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, largest city of the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the Swabian Jura and the Black Forest. Stuttgart has a population of 632,865 as of 2022, making it the list of cities in Germany by population, sixth largest city in Germany, while over 2.8 million people live in the city's administrative region and nearly 5.5 million people in Stuttgart Metropolitan Region, its metropolitan area, making it the metropolitan regions in Germany, fourth largest metropolitan area in Germany. The city and metropolitan area are consistently ranked among the List of EU metropolitan regions by GDP#2021 ranking of top four German metropolitan regions, top 5 Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercedes-Benz M120 Engine
The Mercedes-Benz M120 engine is a naturally aspirated engine, naturally aspirated high-performance automobile piston V12 engine family used in the 1990s and 2000s in Mercedes' flagship models. The engine was a response to BMW's BMW M70, M70 V12 engine, introduced in 1987. While the 5-litre BMW unit developed , Mercedes-Benz upped the ante considerably by creating a 6-litre, engine. The M120 family was built in Stuttgart, Germany. It has an aluminium engine block lined with silicon/aluminium. The aluminium DOHC cylinder heads are multi-valve#Four valves, 4 valves per cylinder designs. It uses sequential fuel injection (SFI) and features forged steel connecting rods. The M120 was eventually replaced by the smaller (5.8 litres), lesser-powered, short-lived, SOHC, three valves per cylinder Mercedes-Benz M137 engine, M137 V12 engine. Mercedes ceased production of the M120 because of new emission rules. E60 This engine developed and of torque for the 6.0 L version. In 1992 only, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EBSCO Information Services
EBSCO Information Services, headquartered in Ipswich, Massachusetts, is a division of EBSCO Industries Inc., a private company headquartered in Birmingham, Alabama. EBSCO provides products and services to libraries of many types around the world. Its products include EBSCONET, a complete e-resource management system, and EBSCO''host'', which supplies a fee-based online research service with 375 full-text databases, a collection of 600,000-plus ebooks, subject indexes, point-of-care medical references, and an array of historical digital archives. In 2010, EBSCO introduced its ''EBSCO Discovery Service'' (EDS) to institutions, which allows searches of a portfolio of journals and magazines. History EBSCO Information Services is a division of EBSCO Industries Inc., a company founded in 1944 by Elton Bryson Stephens Sr. and headquartered in Birmingham, Alabama. "EBSCO" is an acronym for Elton B. Stephens Company. EBSCO Industries has annual sales of about $3 billion. It is one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coil Spring
A tension coil spring A coil spring is a mechanical device that typically is used to store energy and subsequently release it, to absorb shock, or to maintain a force between contacting surfaces. It is made of an elastic material formed into the shape of a helix that returns to its natural length when unloaded. Under tension or compression, the material (wire) of a coil spring undergoes torsion. The spring characteristics therefore depend on the shear modulus. A coil spring may also be used as a torsion spring: in this case the spring as a whole is subjected to torsion about its helical axis. The material of the spring is thereby subjected to a bending moment, either reducing or increasing the helical radius. In this mode, it is the Young's modulus of the material that determines the spring characteristics. Spring rate A selection of conical coil springs Spring rate is the measurement of how much load (in pounds) a coil spring can hold until it compresses . The spring r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pull-rod Suspension
Pull-rod suspension and push-rod suspension refer to a specialised type of automotive suspension system which is largely based on a double-wishbone system, incorporating elements of the commonly used MacPherson strut. In cars, suspension refers to the system by which the vehicle maintains contact between all of its wheels and the ground. This is commonly achieved via use of dampers and springs, providing downward forces on the wheels to counteract impact shocks. However, in push-rod suspension systems, this strut is mounted across the chassis, parallel to the ground, as opposed to the perpendicular system commonly used. Push-rod suspension systems therefore allow essential components to be moved out of direct air flow, closer to the centre of gravity, and allow the centre of gravity to be lowered, thereby creating a more efficient distribution of weight and management of body roll. As a result, push-rod suspension systems can provide a unique avenue for performance, albeit at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |