|
Melicope Rubra
''Melicope rubra'', commonly known as the little evodia, is a species of small tree in the citrus family Rutaceae, native to New Guinea and northeast Queensland. It was originally described as ''Euodia rubra'' in 1900. It has trifoliate leaves and pink bisexual flowers arranged on branches below the leaves. Description ''Melicope rubra'' is a tree that may grow to a height of with a trunk diameter of about , but flowers and fruits as a shrub. The leaves are arranged in opposite pairs and are trifoliate on a petiole long. The leaflets are egg-shaped, long and wide, the leaflets sessile or on a petiolule up to long. The flowers are bisexual and arranged in panicles long on branches below the leaves. The sepals are more or less round to egg-shaped, long and joined at the base. The petals are pink, long and there are four stamens. Flowering occurs from February to June and the fruit consists of up to four follicles long and fused for at least half their length. Taxonom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairns
Cairns (; ) is a city in the Cairns Region, Queensland, Australia, on the tropical north east coast of Far North Queensland. In the , Cairns had a population of 153,181 people. The city was founded in 1876 and named after William Cairns, Sir William Wellington Cairns, following the discovery of gold in the Hodgkinson Minerals Area, Hodgkinson River. During World War II, the city became a staging ground for the Allies of World War II, Allied Forces in the Battle of the Coral Sea. By the late 20th century the city had become a centre of international tourism. In the early 21st century, it has developed into a major regional city. The economy of Cairns is based primarily on tourism, healthcare and education, along with a major capacity in aviation, marine and defence industries. The city has a Gross regional domestic product, gross regional product at about $12.2 billion as of 2024. The city is served by Cairns Airport, Cairns International Airport, the List of the busiest airpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Name
A botanical name is a formal scientific name conforming to the ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN) and, if it concerns a plant cultigen, the additional cultivar or cultivar group, Group epithets must conform to the ''International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants'' (ICNCP). The code of nomenclature covers "all organisms traditionally treated as algae, Fungus, fungi, or plants, whether fossil or non-fossil, including blue-green algae (Cyanobacteria), Chytridiomycota, chytrids, oomycetes, slime moulds and Photosynthesis, photosynthetic protists with their taxonomically related non-photosynthetic groups (but excluding Microsporidia)." The purpose of a formal name is to have a single name that is accepted and used worldwide for a particular plant or plant group. For example, the botanical name ''Bellis perennis'' denotes a plant species which is native to most of the countries of Europe and the Middle East, where it has accumulated variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
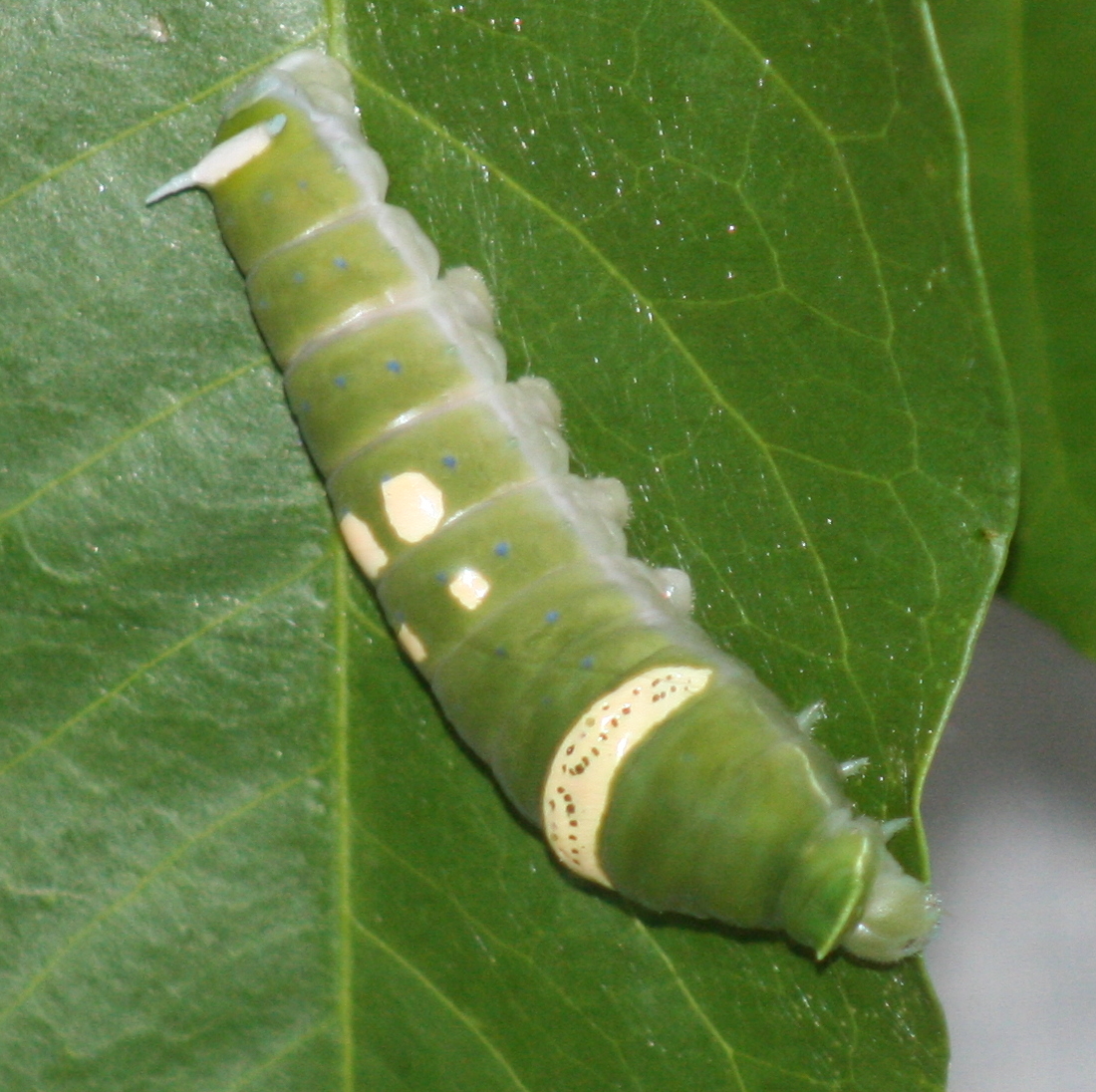
Emperor Gum Moth
''Opodiphthera eucalypti'', the emperor gum moth, is a species of moth in the family Saturniidae native to Australia. This species was formerly placed in the genus ''Antheraea''. Distribution The emperor gum moth may inhabit all states of Australia, however it is scarce in the more southerly states where the climate is less suitable. They are also found as an introduced species on both the North and South Islands of New Zealand. Caterpillars Caterpillars can usually be found on young adult leaves between October and March (the Australian Spring and Summer). When the caterpillars hatch they are black with short hairs on top of small nodes on their bodies called tubercles. The hairs are not poisonous and will not sting. As the caterpillars mature they change color each time they shed their skin (which totals to five stages in the caterpillar's appearance). The fully grown caterpillars are usually found on the highest branches of the host tree where the leaves are the youngest an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulysses Butterfly
''Papilio ulysses'', the Ulysses butterfly (also known as the blue mountain swallowtail butterfly or Blue emperor), is a large swallowtail butterfly, in the subgenus Achillides, of Australia, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands. Its size varies depending on subspecies, but the wingspan is about in Queensland. This butterfly is used as an emblem for tourism in Queensland, Australia. Description The Ulysses butterfly typically has a wingspan of about , but depending on subspecies has some variations in size (western subspecies largest). The upperside of the wings are an iridescent electric blue; the underside is a more subdued black and brown. The colours are produced by the microscopic structure of the scales, a phenomenon called structural colouration. The female of the species is different from the male in that she has little crescents of blue in the back, upside sections of her hindwings, where there is only black for males. When the butterfly is perched t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host (biology)
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasite, parasitic, a mutualism (biology), mutualistic, or a commensalism, commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cell (biology), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, or a Fabaceae, bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) Rhizobia, nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies nutrient, food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macleay's Honeyeater
Macleay's honeyeater (''Xanthotis macleayanus'') is a honeyeater endemic to Australia. Within Australia it has a limited distribution, occurring only in northern Queensland from Cooktown to the southern end of the Paluma Range. Its natural habitats are tropical dry forest A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...s and tropical moist lowland forests. References Macleay's honeyeater Birds of Cape York Peninsula Endemic birds of Queensland Macleay's honeyeater Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Meliphagidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union For Conservation Of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status of the natural world and the measures needed to safeguard it. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education. IUCN's mission is to "influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable". Over the past decades, IUCN has widened its focus beyond conservation ecology and now incorporates issues related to sustainable development in its projects. IUCN does not itself aim to mobilize the public in support of nature conservation. It tries to influence the actions of governments, business and other stakeholders by providing information and advice and through building partners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Conservation Act 1992
The ''Nature Conservation Act 1992'' is an act of the Parliament of Queensland, Australia, that, together with subordinate legislation, provides for the legislative protection of Queensland's threatened biota. As originally published, it provided for biota to be declared ''presumed extinct'', ''endangered'', ''vulnerable'', ''rare'' or ''common''. In 2004, the act was amended to more closely align with the IUCN Red List The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological ... categories: ''presumed extinct'' was changed to ''extinct in the wild'' and ''common'' was changed to ''least concern''. ''Near threatened'' was introduced as an eventual replacement for ''rare'', but the latter was to be phased out over time rather than immediately abandoned. The act is administered by the stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least-concern Species
A least-concern species is a species that has been evaluated and categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as not being a focus of wildlife conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wild. They do not qualify as threatened, near threatened, or (before 2001) conservation dependent. Species cannot be assigned the "Least Concern" category unless they have had their population status evaluated. That is, adequate information is needed to make a direct, or indirect, assessment of its risk of extinction based on its distribution or population status. Evaluation Since 2001 the category has had the abbreviation "LC", following the IUCN 2001 Categories & Criteria (version 3.1). Before 2001 "least concern" was a subcategory of the " Lower Risk" category and assigned the code "LR/lc" or lc. Around 20% of least concern taxa (3261 of 15,636) in the IUCN database still use the code "LR/lc", which indicates they have not been re- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerophyll
Sclerophyll is a type of vegetation that is adapted to long periods of dryness and heat. The plants feature hard leaves, short Internode (botany), internodes (the distance between leaves along the stem) and leaf orientation which is parallel or oblique to direct sunlight. Sclerophyllous plants occur in many parts of the world, but are most typical of areas with low rainfall or seasonal droughts, such as Australia, Africa, and western North and South America. They are prominent throughout Australia, parts of Flora of Argentina, Argentina, the Cerrado biogeographic region of Geography of Bolivia, Bolivia, Geography of Paraguay, Paraguay and Flora of Brazil, Brazil, and in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub, Mediterranean biomes that cover the Mediterranean Basin, California chaparral and woodlands, California, Chilean Matorral, Chile, and the Cape Province of South Africa. In the Mediterranean basin, Quercus ilex, holm oak, cork oak and olives are typical hardwood tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seasonal Tropical Forest
Seasonal tropical forest, also known as moist deciduous, semi-evergreen seasonal, tropical mixed or monsoon forest, typically contains a range of tree species: only some of which drop some or all of their leaves during the dry season. This tropical forest is classified under the Walter system as (i) tropical climate with high overall rainfall (typically in the 1000–2500 mm range; 39–98 inches) and (ii) having a very distinct wet season with (an often cooler “winter”) dry season. These forests represent a range of habitats influenced by monsoon (Am) or tropical wet savanna (Aw/As) climates (as in the Köppen climate classification). Drier forests in the Aw/As climate zone are typically deciduous and placed in the Tropical dry forest biome: with further transitional zones ( ecotones) of savannah woodland then tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands. Distribution Seasonal (mixed) tropical forests can be found in many parts of the tropical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropical rainforests or temperate rainforests, but other types have been described. Estimates vary from 40% to 75% of all biotic community, biotic species being Indigenous (ecology), indigenous to the rainforests. There may be many millions of species of plants, insects and microorganisms still undiscovered in tropical rainforests. Tropical rainforests have been called the "jewels of the Earth" and the "medicine chest (idiom), world's largest pharmacy", because over one quarter of natural medicines have been discovered there. Rainforests as well as endemic rainforest species are rapidly disappearing due to #Deforestation, deforestation, the resulting habitat loss and air pollution, pollution of the atmosphere. Definition Rainforests are cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |