|
Mechanical Overload (engineering)
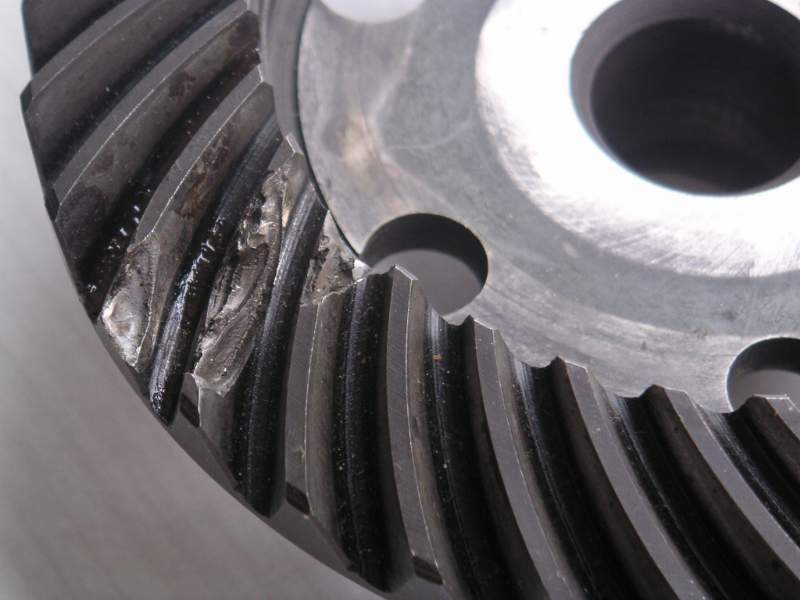
The failure or fracture of a product or component as a result of a single event is known as mechanical overload. It is a common failure mode. The terms are used in forensic engineering and structural engineering when analysing product failure. Failure may occur because either the product is weaker than expected owing to a stress concentration, or the applied load is greater than expected and exceeds the normal tensile strength, shear strength or compressive strength of the product. See also * Forensic engineering * Stress analysis * Structural engineering Structural engineering is a sub-discipline of civil engineering in which structural engineers are trained to design the 'bones and joints' that create the form and shape of human-made Structure#Load-bearing, structures. Structural engineers also ... References * ''Strength of Materials'', 3rd edition, Krieger Publishing Company, 1976, by Timoshenko S., * ''Forensic Materials Engineering: Case Studies'' by Peter Rhys Lewi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failure Mode
Failure causes are defects in design, process, quality, or part application, which are the underlying cause of a failure or which initiate a process which leads to failure. Where failure depends on the user of the product or process, then human error must be considered. Component failure/failure modes A part failure mode is the way in which a component failed "functionally" on the component level. Often a part has only a few failure modes. For example, a relay may fail to open or close contacts on demand. The failure mechanism that caused this can be of many different kinds, and often multiple factors play a role at the same time. They include corrosion, welding of contacts due to an abnormal electric current, return spring fatigue failure, unintended command failure, dust accumulation and blockage of mechanism, etc. Seldom only one cause (hazard) can be identified that creates system failures. The real root causes can in theory in most cases be traced back to some kind of human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forensic Engineering
Forensic engineering has been defined as "the investigation of failures—ranging from serviceability to catastrophic—which may lead to legal activity, including both civil and criminal". The forensic engineering field is very broad in terms of the many disciplines that it covers, investigations that use forensic engineering are case of environmental damages to structures, system failures of machines, explosions, electrical, fire point of origin, vehicle failures and many more. It includes the investigation of materials, products, structures or components that fail or do not operate or function as intended, causing personal injury, damage to property or economic loss. The consequences of failure may give rise to action under either criminal or civil law including but not limited to health and safety legislation, the laws of contract and/or product liability and the laws of tort. The field also deals with retracing processes and procedures leading to accidents in operation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Engineering
Structural engineering is a sub-discipline of civil engineering in which structural engineers are trained to design the 'bones and joints' that create the form and shape of human-made Structure#Load-bearing, structures. Structural engineers also must understand and calculate the structural stability, stability, strength, structural rigidity, rigidity and earthquake-susceptibility of built structures for buildings and nonbuilding structures. The structural designs are integrated with those of other designers such as architects and Building services engineering, building services engineer and often supervise the construction of projects by contractors on site. They can also be involved in the design of machinery, medical equipment, and vehicles where structural integrity affects functioning and safety. See glossary of structural engineering. Structural engineering theory is based upon applied physics, physical laws and empirical knowledge of the structural performance of different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
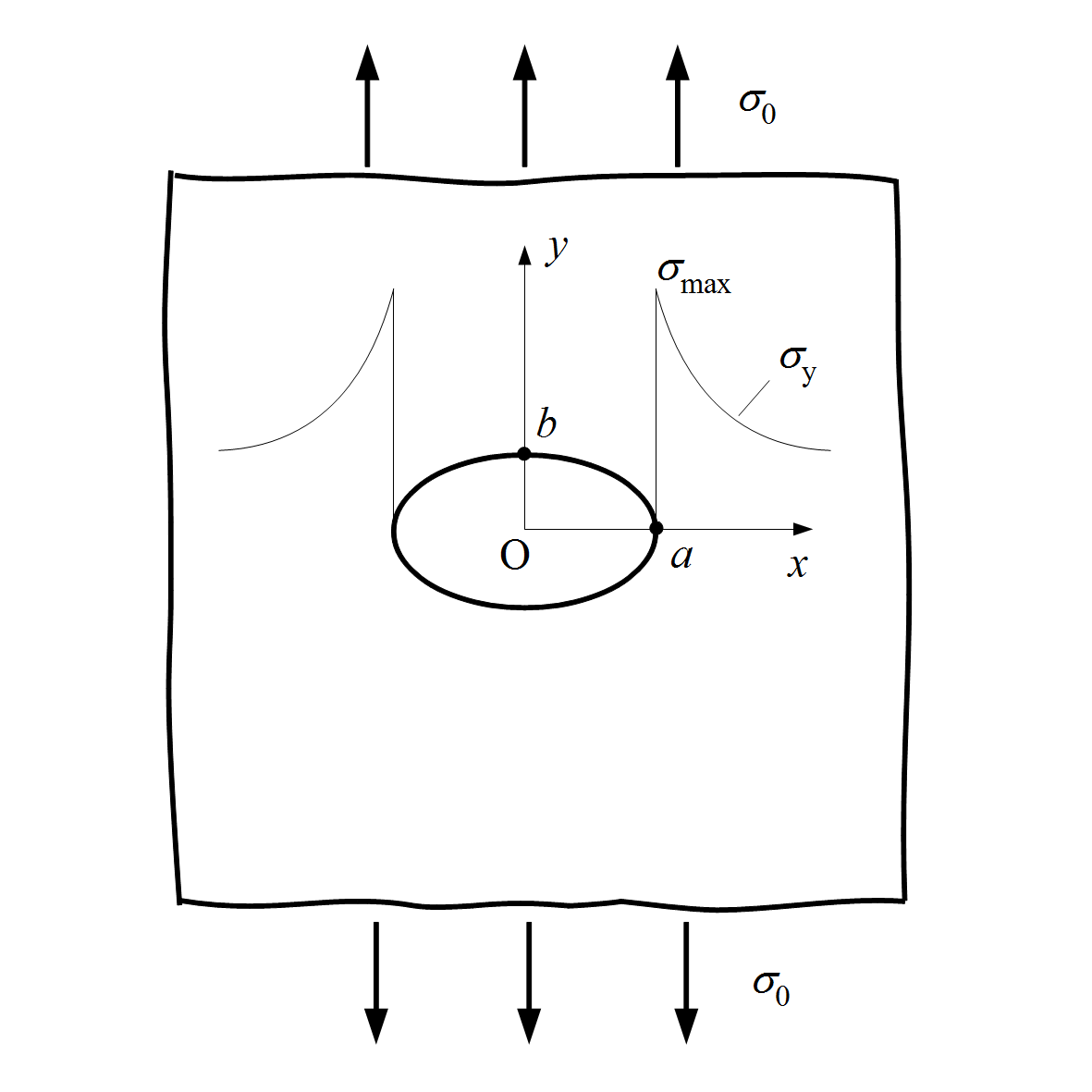
Stress Concentration
In solid mechanics, a stress concentration (also called a stress raiser or a stress riser or notch sensitivity) is a location in an object where the stress (mechanics), stress is significantly greater than the surrounding region. Stress concentrations occur when there are irregularities in the geometry or material of a structural component that cause an interruption to the flow of stress. This arises from such details as holes, Groove (engineering), grooves, Notch (engineering), notches and Fillet (mechanics), fillets. Stress concentrations may also occur from accidental damage such as nicks and scratches. The degree of concentration of a discontinuity under typically Tension (physics), tensile loads can be expressed as a non-dimensional stress concentration factor K_t, which is the ratio of the highest stress to the nominal far field stress. For a circular hole in an infinite plate, K_t = 3. The stress concentration factor should not be confused with the stress intensity factor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensile Strength
Ultimate tensile strength (also called UTS, tensile strength, TS, ultimate strength or F_\text in notation) is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials, the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials, the ultimate tensile strength can be higher. The ultimate tensile strength is usually found by performing a tensile test and recording the engineering stress versus strain. The highest point of the stress–strain curve is the ultimate tensile strength and has units of stress. The equivalent point for the case of compression, instead of tension, is called the compressive strength. Tensile strengths are rarely of any consequence in the design of ductile members, but they are important with brittle members. They are tabulated for common materials such as alloys, composite materials, ceramics, plastics, and wood. Definition The ultimate tensile strength ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Strength
In engineering, shear strength is the strength of a material or component against the type of yield or structural failure when the material or component fails in shear. A shear load is a force that tends to produce a sliding failure on a material along a plane that is parallel to the direction of the force. When a paper is cut with scissors, the paper fails in shear. In structural and mechanical engineering, the shear strength of a component is important for designing the dimensions and materials to be used for the manufacture or construction of the component (e.g. beams, plates, or bolts). In a reinforced concrete beam, the main purpose of reinforcing bar (rebar) stirrups is to increase the shear strength. Equations For shear stress \tau applies :\tau = \frac , where :\sigma_1 is major principal stress and :\sigma_3 is minor principal stress. In general: ductile materials (e.g. aluminum) fail in shear, whereas brittle materials (e.g. cast iron) fail in tension . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressive Strength
In mechanics, compressive strength (or compression strength) is the capacity of a material or Structural system, structure to withstand Structural load, loads tending to reduce size (Compression (physics), compression). It is opposed to ''tensile strength'' which withstands loads tending to elongate, resisting Tension (physics), tension (being pulled apart). In the study of strength of materials, compressive strength, tensile strength, and shear strength can be analyzed independently. Some materials fracture at their compressive strength limit; others Plasticity (physics), deform irreversibly, so a given amount of Deformation (engineering), deformation may be considered as the limit for compressive load. Compressive strength is a key value for Structural engineering, design of structures. Compressive strength is often measured on a universal testing machine. Measurements of compressive strength are affected by the specific test method and conditions of measurement. Compressive s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forensic Engineering
Forensic engineering has been defined as "the investigation of failures—ranging from serviceability to catastrophic—which may lead to legal activity, including both civil and criminal". The forensic engineering field is very broad in terms of the many disciplines that it covers, investigations that use forensic engineering are case of environmental damages to structures, system failures of machines, explosions, electrical, fire point of origin, vehicle failures and many more. It includes the investigation of materials, products, structures or components that fail or do not operate or function as intended, causing personal injury, damage to property or economic loss. The consequences of failure may give rise to action under either criminal or civil law including but not limited to health and safety legislation, the laws of contract and/or product liability and the laws of tort. The field also deals with retracing processes and procedures leading to accidents in operation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress Analysis
Stress may refer to: Science and medicine * Stress (biology) Stress, whether physiological, biological or psychological, is an organism's response to a stressor, such as an environmental condition or change in life circumstances. When stressed by stimuli that alter an organism's environment, multiple s ..., an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition * Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase or sentence * Stress (mechanics), the internal forces that neighboring particles of a continuous material exert on each other * Oxidative stress, an imbalance of free radicals * Psychological stress, a feeling of strain and pressure ** Occupational stress, stress related to one's job * Surgical stress, systemic response to surgical injury Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and musicians * Stress (Brazilian band), a Brazilian heavy metal band * Stress (British band) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Engineering
Structural engineering is a sub-discipline of civil engineering in which structural engineers are trained to design the 'bones and joints' that create the form and shape of human-made Structure#Load-bearing, structures. Structural engineers also must understand and calculate the structural stability, stability, strength, structural rigidity, rigidity and earthquake-susceptibility of built structures for buildings and nonbuilding structures. The structural designs are integrated with those of other designers such as architects and Building services engineering, building services engineer and often supervise the construction of projects by contractors on site. They can also be involved in the design of machinery, medical equipment, and vehicles where structural integrity affects functioning and safety. See glossary of structural engineering. Structural engineering theory is based upon applied physics, physical laws and empirical knowledge of the structural performance of different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering Failures
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, systems. Modern engineering comprises many subfields which include designing and improving infrastructure, machinery, vehicles, electronics, Materials engineering, materials, and energy systems. The Academic discipline, discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more Academic specialization, specialized fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis for applications of applied mathematics, mathematics and applied science, science. See glossary of engineering. The word '':wikt:engineering, engineering'' is derived from the Latin . Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (the predecessor of the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology aka ABET) has defined "engineering" as: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |