|
Maximum Neighbor Hypothesis
The Maximum neighbor hypothesis (''hipótesis vecinal máxima'' in Spanish) or neighbor hypothesis 3 (''hipótesis vecinal 3''; HV3 in Spanish) is a strategic concept used in international analysis and defense in Chile since the late 19th century. It argues that in the event of a conflict with one neighboring country, it is highly likely that the other two Borders of Chile, border countries will side with the first one against Chile. HV3 has been studied in military and political circles based on historical precedents and the dynamics of international relations in the region. Origins and fundamentals The hypothesis is based on a historical analysis of Chile's relations with Argentina, Bolivia, and Peru. Since these countries' independence, territorial disputes and diplomatic conflicts have shaped the perception of potential alliances in case of conflict. The foundations of HV3 include: # Historical disputes: Chile has had territorial conflicts with all three neighbors, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puna De Atacama
The Puna de Atacama or Atacama Plateau article at the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' website is an arid high plateau, in the Andes of northern Chile (15%) and northwest of Argentina (85%).Historia de la relacciones exteriores de la Argentina Geomorphology, Geomorphologist Walther Penck based his ''Grossfalt'' landform association on Puna de Atacama. Geography The plateau's elevation averages above sea level, and it spans an area of . In Argentina, Puna's territory is extended in the provinces of Salta Province, Salta, Jujuy Province, Jujuy, and western Catamarca Province, Cata ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-tank Mine
An anti-tank or AT mine is a type of land mine designed to damage or destroy vehicles including tanks and armored fighting vehicles. Compared to anti-personnel mines, anti-tank mines typically have a much larger explosive charge, and a fuze designed to be triggered by vehicles or, in some cases, Remote control, remotely or by tampering with the mine. History First World War The first anti-tank mines were improvised during the First World War as a countermeasure against the first tanks introduced by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British towards the end of the war. Initially they were nothing more than a buried high-explosive shell (projectile), shell or Mortar (weapon), mortar bomb with its fuze upright. Later, purpose-built mines were developed, including the Flachmine 17, which was simply a wooden box packed with explosives and triggered either remotely or by a pressure fuze. By the end of the war, the Germans had developed row mining techniques, and mines ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-personnel Mine
An anti-personnel mine or anti-personnel landmine (APL) is a form of land mine, mine designed for use against human, humans, as opposed to an anti-tank mine, which target vehicles. APLs are classified into: blast mines and fragmentation mines; the latter may or may not be a bounding mine. APLs are often designed to injure and mutilation, maim, not kill, their victims to overwhelm the logistical (mostly medical) support system of enemy forces that encounter them. Some types of APLs can also damage the tracks on armoured vehicles or the tires of wheeled vehicles. The International Campaign to Ban Landmines has sought to ban mines and destroy stockpile. For this purpose, it introduced in 1997 the Ottawa Treaty, which has not yet been accepted by over 30 states and has not guaranteed the protection of citizens against APLs planted by non-state armed groups. Use Anti-personnel mines are used in a similar manner to anti-tank mines, in static "mine fields" along national borders o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charaña Accords
Charaña is a high elevation town in the altiplano of the La Paz Department in Bolivia. It is the seat of the Charaña Municipality, the fifth municipal section of the Pacajes Province. Charaña is east of the border with Chile. History Charaña was the scene of the famous meeting between President Augusto Pinochet Augusto José Ramón Pinochet Ugarte (25 November 1915 – 10 December 2006) was a Chilean military officer and politician who was the dictator of Military dictatorship of Chile, Chile from 1973 to 1990. From 1973 to 1981, he was the leader ... of Chile and Hugo Banzer on 8 February 1975 when they signed a Joint Declaration (Charaña Act), which restored diplomatic relations between the two countries which were broken since April 1962. Climate References Populated places in La Paz Department (Bolivia) {{PacajesProvince-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Velasco Alvarado
Juan Francisco Velasco Alvarado (June 16, 1910 – December 24, 1977) was a Peruvian Army general, general who served as the President of Peru after a successful 1968 Peruvian coup d'état, coup d'état against Fernando Belaúnde's presidency in 1968. Under his Revolutionary Government of the Armed Forces of Peru, presidency, nationalism, as well as left-leaning policies that addressed Indigenous peoples of Peru, indigenous Peruvians, such as nationalization or Peruvian Agrarian Reform, agrarian reform were adopted. These policies were reversed after another Tacnazo, coup d'état in 1975 led by his Prime Minister, Francisco Morales Bermúdez. Velasco had a confrontational foreign policy towards the United States, as he pushed for renegotiation of treaties and criticized what he perceived as a pernicious dependence of Latin American states on the United States. While he strengthened Peruvian relations with the Soviet Union, Velasco was firmly anti-communist. His foreign policy h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
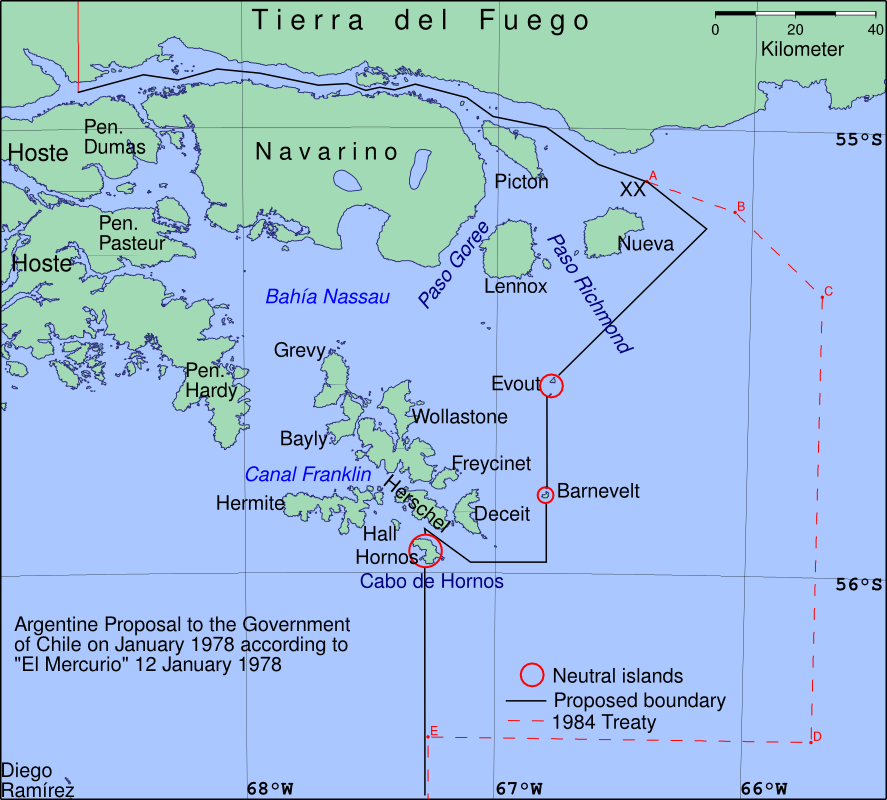
Operation Soberanía
Operación Soberanía (Operation Sovereignty) was a planned Argentine military invasion of territory disputed with Chile, and ultimately possibly of Chile itself, due to the Beagle conflict. The invasion was initiated on 22 December 1978 but was halted after a few hours and Argentine forces retreated from the conflict zone without a fight. Whether the Argentine infantry actually crossed the border into Chile has not been established. Argentine sources insist that they crossed the border. In 1971, Chile and Argentina had agreed to binding arbitration by an international tribunal, under the auspices of the British Government, to settle the boundary dispute. On 22 May 1977 the British Government announced the decision, which awarded the Picton, Nueva and Lennox islands to Chile. On 25 January 1978 Argentina rejected the decision and attempted to militarily coerce Chile into negotiating a division of the islands that would produce a boundary consistent with Argentine claims. Date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Negotiations Between Chile And Argentina In 1977–1978
The direct negotiations between Chile and Argentina about the islands and maritime rights in Beagle conflict began after the Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom announced on 2 May 1977 the judgement of the Beagle Channel Arbitration to the governments of both countries. Thcourt ruled thatthe islands and all adjacent formations belonged to Chile. The direct negotiations finished with thAct of Montevideoon 9 January 1979, where both countries accept the papal mediation after Argentina's call off of the Operation Soberanía. This was the most dangerous phase of the Beagle Conflict and there was a real possibility of open warfare. Internal politics of both countries Argentina and Chile were both ruled by military governments at the time of the negotiations. The Chilean and Argentine governments shared common interests: internal war against subversion, annihilating the opposition; external war against communism, remaining nonetheless part of the non-aligned movement; modernisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lauca River
The Lauca River is a binational river. It originates in the Chilean Altiplano of the Arica and Parinacota Region, crosses the Andes and empties into Coipasa Lake in Bolivia. The upper reach of the river lies within the boundaries of Lauca National Park in the Parinacota Province Parinacota Province () is one of two provinces of the Chilean region of Arica y Parinacota. Its capital is Putre. It is named after the Parinacota Volcano. History Arica y Parinacota Region was created on October 8, 2007 under Law 20.175, promu .... The Lauca receives waters from a group of lakes known as Quta Qutani through the Desaguadero River. In this area, there is a type of marsh known as Parinacota wetlands, in which converge several streams, being the more important the river just mentioned, which has a variable flow rate ranging from 100 to 560 L/s, and an average of 260 L/s. From its source in the Parinacota wetlands the river flows west. The spurs of the ''Cordillera Central'' (also k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inter-American Treaty Of Reciprocal Assistance
The Inter-American Treaty of Reciprocal Assistance (commonly known as the Rio Treaty, the Rio Pact, the Treaty of Reciprocal Assistance, or by the Spanish-language acronym TIAR from ''Tratado Interamericano de Asistencia Recíproca'') is an intergovernmental collective security agreement signed in 1947 in Rio de Janeiro at a meeting of the American states. The central principle contained in its articles is that an attack against one is to be considered an attack against them all; this was known as the "hemispheric defense" doctrine. Despite this, several members have breached the treaty on multiple occasions. The treaty was initially created in 1947 and came into force in 1948, in accordance with Article 22 of the treaty. The Bahamas was the most recent country to sign and ratify it in 1982. Background The United States maintained a hemispheric defense policy relative to European influence under the Monroe Doctrine from 1823 onward, and became increasingly interventionist fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alto Palena Border Dispute
The musical term alto, meaning "high" in Italian (Latin: ''altus''), historically refers to the contrapuntal part higher than the tenor and its associated vocal range. In four-part voice leading alto is the second-highest part, sung in choruses by either low women's or high men's voices. In vocal classification these are usually called contralto and male alto or countertenor. Etymology In choral music for mixed voices, "alto" describes the lowest part commonly sung by women. The explanation for the anomaly of this name is to be found not in the use of adult falsettists in choirs of men and boys but further back in innovations in composition during the mid-15th century. Before this time it was usual to write a melodic ''cantus'' or ''superius'' against a tenor (from Latin ''tenere'', to hold) or 'held' part, to which might be added a contratenor, which was in counterpoint with (in other words, against = contra) the tenor. The composers of Ockeghem's generation wrote two contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1920 Bolivian Coup D'état
1920 Bolivian coup d'état was a bloodless takeover of power in Bolivia by the Republican party on July 12, 1920 which overthrew the previously ruling government of the Liberal Party and brought Bautista Saavedra to power as President from 1920 until 1925. Republicans were less united by a single ideology than a wide alliance of former Liberals and some Conservative elites who usually had some personal conflicts with the ruling Liberals and wanted to gain power for themselves. Soon after the coup, Republicans split in two new parties grouped around two leaders - Bautista Saavedra with his Republican Socialist Party and Daniel Salamanca, who established the Genuine Republican Party. Saavedra legalized the right to strike and introduced government arbitration in labour disputes. In 1922 he caused a general strike after banning night taxis. The strikers won and taxi services were resumed and railroad federation was recognized as representative of railroad workers. This did not mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |