|
Mauritian Giant Skink
The Mauritian giant skink (''Leiolopisma mauritiana'') is a large, extinct species of skink It was found only in Mauritius. It became extinct sometime in the 17th century, likely due to human-introduced predators. Taxonomy The Réunion giant skink (''Leiolopisma ceciliae''), another extinct species, was closely related to the Mauritian giant skink. The Round Island ground skink (''Leiolopisma telfairii)'' is a more distantly related surviving species from Mauritius. Only a semi - complete specimen is known in addition to some odd bones. (Supposedly, a former director of the Mauritian Institute threw away specimens including some bones of this species). The remaining skeleton is missing the feet and digits, thus making it impossible for a SENI biometric analysis per se (Schnirel. 2004). The semi - complete skeleton does have a skull shaped similar to a blue-tongue skink ( ''Tiliqua''). Description Little is known about this species. It is believed it grew up to around 80 cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Günther
Albert Karl Ludwig Gotthilf Günther , also Albert Charles Lewis Gotthilf Günther (3October 18301February 1914), was a German-born British zoologist, ichthyologist, and herpetologist. Günther is ranked the second-most productive reptile taxonomist (after George Albert Boulenger) with more than 340 reptile species described. Early life and career Günther was born in Esslingen in Swabia ( Württemberg). His father was a ''Stiftungs-Commissar'' in Esslingen and his mother was Eleonora Nagel. He initially schooled at the Stuttgart Gymnasium. His family wished him to train for the ministry of the Lutheran Church for which he moved to the University of Tübingen. A brother shifted from theology to medicine, and he, too, turned to science and medicine at Tübingen in 1852. His first work was "''Ueber den Puppenzustand eines Distoma''" (On the pupal state of ''Distoma''). He graduated in medicine with an M.D. from Tübingen in 1858, the same year in which he published a handbook ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
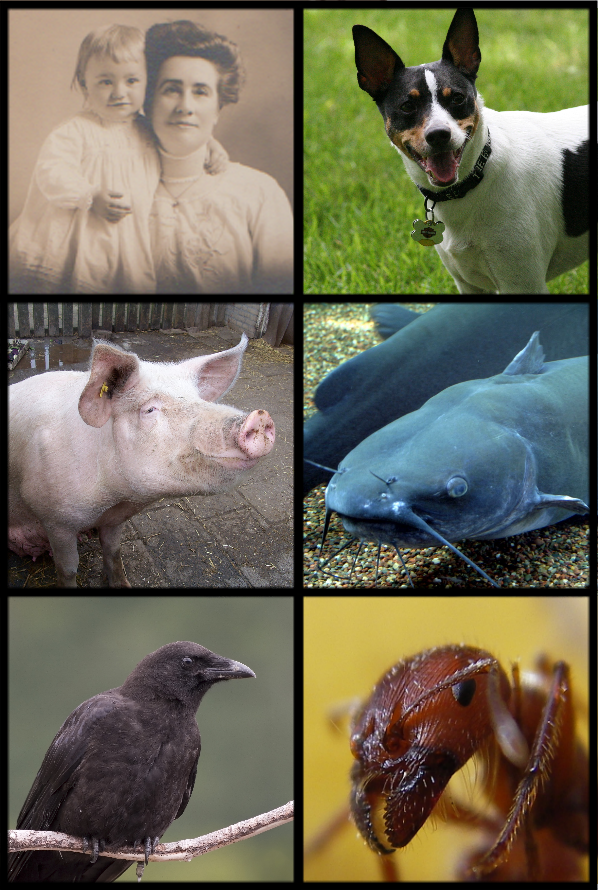
Omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that regularly consumes significant quantities of both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutrients and energy of the sources absorbed. Often, they have the ability to incorporate food sources such as algae, fungi, and bacteria into their diet. Omnivores come from diverse backgrounds that often independently evolved sophisticated consumption capabilities. For instance, dogs evolved from primarily carnivorous organisms (Carnivora) while pigs evolved from primarily herbivorous organisms (Artiodactyla). Despite this, physical characteristics such as tooth morphology may be reliable indicators of diet in mammals, with such morphological adaptation having been observed in bears. The variety of different animals that are classified as omnivores can be placed into further sub-categories depending on their feeding behaviors. Frug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Described In 1877
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern cladistic taxonomy regards that group as paraphyletic, since genetic and paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among reptiles from an evolutionary perspective. Many cladistic systems therefore redefine Reptilia as a clade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Mauritius
The wildlife of Mauritius consists of its flora and fauna. Mauritius is located in the Indian Ocean to the east of Madagascar. Due to its isolation, it has a relatively low diversity of wildlife; however, a high proportion of these are endemic species occurring nowhere else in the world. Many of these are now threatened with extinction because of human activities including habitat destruction and the introduction of non-native species. Some have already become extinct, most famously the dodo which disappeared in the 17th century. At the 16th U.S.-Africa Business Summit, held May 6–9, 2024, Mauritius was held up as a model for African ecosystem conservation at a presentation by the Saint Brandon Conservation Trust in Dallas, Texas, at the international Corporate Council on Africa meetings that included six heads of state and government, 80 U.S. government officials, 16 African delegations and over 1,000 U.S. & African CEOs, investors and entrepreneurs. Fauna Mammals Prehisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiolopisma
''Leiolopisma'' is a genus of skinks. Most species occur in the region of New Caledonia-New Zealand, and they are related to other genera from that general area, such as ''Emoia''; these and others form the ''Eugongylus'' group. One living and two extinct taxa represent a clade endemic to the Mascarenes.(Austin & Arnold 2006) Example species *''Leiolopisma alazon'' Zug, 1985 - Lauan ground skink, Ono-i-Lau ground skink *''Leiolopisma ceciliae'' Arnold & Bour, 2008 - extinct - Réunion giant skink *''Mauritian giant skink, Leiolopisma mauritiana'' (Albert Günther, Günther, 1877) - extinct - Mauritian giant skink *''Leiolopisma telfairii'' (Desjardin, 1831) - Round Island ground skink The Mauritian giant skink (''Leiolopisma mauritiana'') and the Leiolopisma ceciliae, Réunion giant skink (''Leiolopisma ceciliae'') were closely related. These two were formerly separated in ''Didosaurus''. David Day (1979), in Vanished Species, described the Reunion giant skink as small and fast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Reptiles
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its last member. A taxon may become functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to reproduce and recover. As a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of speciation. Species become extinct when they are no longer able to survive in changing conditions or against supe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Animals Of Mauritius
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its last member. A taxon may become functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to reproduce and recover. As a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of speciation. Species become extinct when they are no longer able to survive in changing conditions or against superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile Extinctions Since 1500
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern cladistic taxonomy regards that group as paraphyletic, since genetic and paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among reptiles from an evolutionary perspective. Many cladistic systems therefore redefine Reptilia as a clad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian Hume
Julian Pender Hume (born 3 March 1960) is an English palaeontologist, artist and writer who lives in Wickham, Hampshire. He was born in Ashford, Kent, and grew up in Portsmouth, England. Scientific career He attended Crookhorn Comprehensive School between 1971 and 1976. His career began as an artist, specialising in the reconstruction of extinct species, after which he undertook a degree in palaeontology at the University of Portsmouth, followed by a PhD in the same subject, jointly hosted by the University of Portsmouth and the Natural History Museum, London and Tring. He is presently a research associate at the Natural History Museum, and has travelled extensively, working on fossil excavations that include the Cape Verde Islands; Lord Howe Island, Tasmania, Flinders, King and Kangaroo Islands, Australia; Madagascar, Seychelles, and Hawaiian Islands. However, his main area of research is the Mascarene Islands of Mauritius, Réunion, and Rodrigues, where in particular he has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Rail
The red rail (''Aphanapteryx bonasia'') is an extinct species of rail that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Mauritius, east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. It had a close relative on Rodrigues island, the likewise extinct Rodrigues rail (''Erythromachus leguati''), with which it is sometimes considered congeneric, but their relationship with other rails is unclear. Rails often evolve flightlessness when adapting to isolated islands, free of mammalian predators, and that was also the case for this species. The red rail was a little larger than a chicken and had reddish, hairlike plumage, with dark legs and a long, curved beak. The wings were small, and its legs were slender for a bird of its size. It was similar to the Rodrigues rail, but was larger, and had proportionally shorter wings. It has been compared to a kiwi or a limpkin in appearance and behaviour. This bird is believed to have fed on invertebrates, and snail shells have been found with damage matching a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue-tongued Skink
Blue-tongued skinks comprise the Australasian genus ''Tiliqua'', which contains some of the largest members of the skink family (biology), family (Scincidae). They are commonly called blue-tongued lizards or simply blue-tongues or blueys in Australia or panana in Indonesia. As suggested by these common names, a prominent characteristic of the genus is a large blue tongue that can be bared as Deimatic behaviour, bluff-warning to potential enemies. Their tongue can also deform itself and produce a thick mucus in order to catch prey. They are relatively shy in comparison with other lizards, and also significantly slower due to their shorter legs. Systematics and distribution Blue-tongued skinks are closely related to the Genus, genera ''Cyclodomorphus'' and ''Hemisphaeriodon''. All species are found on mainland Australia with the exception of ''Tiliqua gigas'', which occurs in New Guinea and various islands of Indonesia. The Tanimbar blue-tongued skink, a subspecies of ''Tiliqua sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and recover. As a species' potential Range (biology), range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxon, Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the Fossil, fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include Dinosaur, non-avian dinosaurs, Machairodontinae, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |