|
Mathematical Markup Languages
A mathematical markup language is a computer notation for representing mathematical formulae, based on mathematical notation. Specialized markup languages are necessary because computers normally deal with linear text and more limited character sets (although increasing support for Unicode is obsoleting very simple uses). A formally standardized syntax also allows a computer to interpret otherwise ambiguous content, for rendering or even evaluating. For computer-interpretable syntaxes, the most popular are TeX/LaTeX, MathML (Mathematical Markup Language), OpenMath and OMDoc. Notations for human input Popular languages for input by humans and interpretation by computers include TeX/LaTeX and eqn. Computer algebra systems such as Macsyma, Mathematica (Wolfram Language), Maple, and MATLAB each have their own syntax. When the purpose is informal communication with other humans, syntax is often ad hoc, sometimes called "ASCII math notation". Academics sometimes use syntax bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Mathematical Formulae
Mathematical notation consists of using symbols A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise different concep ... for representing operation (mathematics), operations, unspecified numbers, relation (mathematics), relations, and any other mathematical objects and assembling them into expression (mathematics), expressions and formulas. Mathematical notation is widely used in mathematics, science, and engineering for representing complex concepts and property (philosophy), properties in a concise, unambiguous, and accurate way. For example, the physicist Albert Einstein's formula E=mc^2 is the quantitative representation in mathematical notation of mass–energy equivalence. Mathematical notation was first introduced by François Viète at the end of the 16th century and largely expanded during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
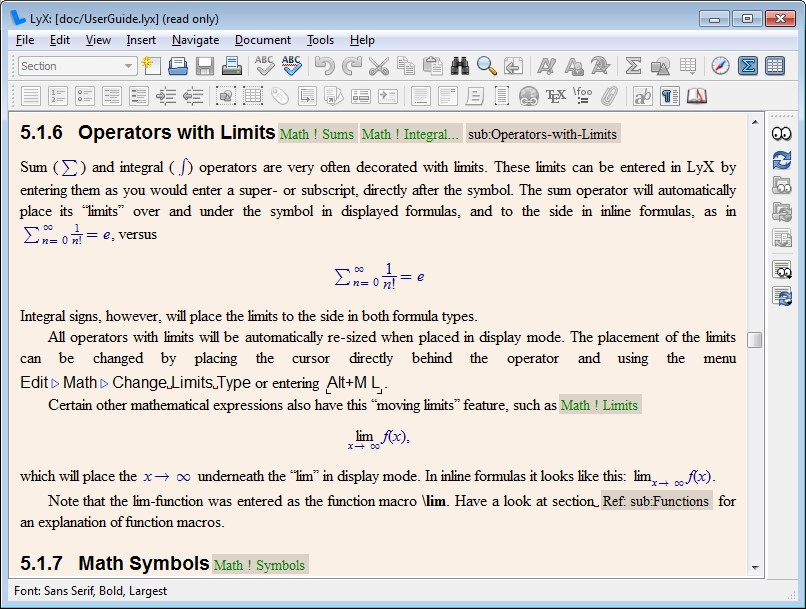
Superscript
A subscript or superscript is a character (such as a number or letter) that is set slightly below or above the normal line of type, respectively. It is usually smaller than the rest of the text. Subscripts appear at or below the baseline, while superscripts are above. Subscripts and superscripts are perhaps most often used in formulas, mathematical expressions, and specifications of chemical compounds and isotopes, but have many other uses as well. In professional typography, subscript and superscript characters are not simply ordinary characters reduced in size; to keep them visually consistent with the rest of the font, typeface designers make them slightly heavier (i.e. medium or bold typography) than a reduced-size character would be. The vertical distance that sub- or superscripted text is moved from the original baseline varies by typeface and by use. In typesetting, such types are traditionally called " superior" and "inferior" letters, figures, etc., or just "superi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Comparison Of TeX Editors
The following is a comparison of TeX editors. Table of editors See also * Formula editor * Comparison of word processors * Comparison of text editors * Comparison of desktop publishing software * List of TeX extensions *Chemical structure Notes References {{TeX editors TeX editors Free TeX editors Multimedia software comparisons, TeX editors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Comparison Of Document Markup Languages
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of document markup languages. Please see the individual markup languages' articles for further information. General information Basic general information about the markup languages: creator, version, etc. Note: While Rich Text Format (RTF) is human readable, it is not considered to be a markup language and is thus excluded from the table. Characteristics Some characteristics of the markup languages. Notes See also * List of document markup languages The following is a list of document markup languages. You may also find the List of markup languages of interest. Well-known document markup languages * HyperText Markup Language (HTML) – an ad hoc markup language that was originally created f ... * Comparison of Office Open XML and OpenDocument * Comparison of e-book formats * Comparison of data-serialization formats Document markup languages *Comparison of document markup languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
List Of Document Markup Languages
The following is a list of document markup languages. You may also find the List of markup languages of interest. Well-known document markup languages * HyperText Markup Language (HTML) – an ad hoc markup language that was originally created for the World Wide Web, took inspiration from the metalanguage SGML, and inspired many other markup languages * Keyhole Markup Language (KML/KMZ) – an XML-based markup language used to exchange geographic information, originally, for use with Google Earth and, now also, other map programs * Markdown – a simple, plain text markup language with multiple implementations, popular on blogs and content management systems * Mathematical Markup Language (MathML) – a part of the HTML5 standard, an XML-based markup language used to describe mathematical notations as well as capturing their structure and content, intended to integrate mathematical formulae in the World Wide Web and other documents * Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) – an XML- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Formal Proof
In logic and mathematics, a formal proof or derivation is a finite sequence of sentences (known as well-formed formulas when relating to formal language), each of which is an axiom, an assumption, or follows from the preceding sentences in the sequence, according to the rule of inference. It differs from a natural language argument in that it is rigorous, unambiguous and mechanically verifiable. If the set of assumptions is empty, then the last sentence in a formal proof is called a theorem of the formal system. The notion of theorem is generally effective, but there may be no method by which we can reliably find proof of a given sentence or determine that none exists. The concepts of Fitch-style proof, sequent calculus and natural deduction are generalizations of the concept of proof. The theorem is a syntactic consequence of all the well-formed formulas preceding it in the proof. For a well-formed formula to qualify as part of a proof, it must be the result of applying a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Proof Assistant
In computer science and mathematical logic, a proof assistant or interactive theorem prover is a software tool to assist with the development of formal proofs by human–machine collaboration. This involves some sort of interactive proof editor, or other interface, with which a human can guide the search for proofs, the details of which are stored in, and some steps provided by, a computer A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set .... A recent effort within this field is making these tools use artificial intelligence to automate the formalization of ordinary mathematics. System comparison * ACL2 – a programming language, a first-order logical theory, and a theorem prover (with both interactive and automatic modes) in the Boyer–Moore tradition. * Rocq (so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior. Web browsers have a dedicated JavaScript engine that executes the client code. These engines are also utilized in some servers and a variety of apps. The most popular runtime system for non-browser usage is Node.js. JavaScript is a high-level, often just-in-time–compiled language that conforms to the ECMAScript standard. It has dynamic typing, prototype-based object-orientation, and first-class functions. It is multi-paradigm, supporting event-driven, functional, and imperative programming styles. It has application programming interfaces (APIs) for working with text, dates, regular expressions, standard data structures, and the Document Object Model (DOM). The ECMAScript standard does not include any input/output (I/O), such as netwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
ASCIIMathML
AsciiMath is a client-side mathematical markup language for displaying mathematical expressions in web browsers.. Using the JavaScript script ASCIIMathML.js, AsciiMath notation is converted to MathML at the time the page is loaded by the browser, natively in Mozilla Firefox, Safari (web browser), Safari, and via a plug-in in IE7. The simplified markup language supports a subset of the LaTeX language instructions, as well as a less verbose syntax (which, for example, replaces "\times" with "xx" or "times" to produce the "×" symbol). The resulting MathML mathematics can be styled by applying CSS to class "mstyle". The script ASCIIMathML.js is freely available under the MIT License. The latest version also includes support for Scalable Vector Graphics, SVG graphics, natively in Mozilla Firefox and via a plug-in in IE7. Per May 2009 there is a new version available. This new version still contains the original ASCIIMathML and LaTeXMathML as developed by Peter Jipsen, but the ASCIIsvg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Office Open XML File Formats
The Office Open XML file formats are a set of file formats that can be used to represent electronic office documents. There are formats for word processing documents, spreadsheets and presentations as well as specific formats for material such as mathematical formulas, graphics, bibliographies etc. The formats were developed by Microsoft and first appeared in Microsoft Office 2007. They were standardized between December 2006 and November 2008, first by the Ecma International consortium, where they became ECMA-376, and subsequently, after a contentious standardization process, by the ISO/IEC's Joint Technical Committee 1, where they became ISO/IEC 29500:2008. Container Office Open XML documents are stored in Open Packaging Conventions (OPC) packages, which are ZIP files containing XML and other data files, along with a specification of the relationships between them. Depending on the type of the document, the packages have different internal directory structures and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Microsoft Office 2007
Microsoft Office 2007 (codenamed Office 12) is an office suite for Windows, developed and published by Microsoft. It was officially revealed on March 9, 2006 and was the 12th version of Microsoft Office. It was released to manufacturing on November 3, 2006; it was subsequently made available to volume license customers on November 30, 2006, and later to Software release life cycle#General availability .28GA.29, retail on January 30, 2007. The Mac OS X equivalent, Microsoft Office 2008 for Mac, was released on January 15, 2008. Office 2007 introduced a new graphical user interface called the ''Fluent User Interface'', which uses Ribbon (computing), ribbons and an Office menu instead of menu bars and toolbars. Office 2007 also introduced Office Open XML file formats as the default file formats in Microsoft Excel, Excel, Microsoft PowerPoint, PowerPoint, and Microsoft Word, Word. The new formats are intended to facilitate the sharing of information between programs, improve security, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Graphical User Interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based user interface, text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation interface, direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and Distributed control system, industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower-displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |