|
Mater Familias
Manus ( ; ) was an Ancient Roman type of Marriage in ancient Rome, marriage,Jane F. Gardner, ''Women in Roman Law and Society'', First Midland Book Edition, 1991, 11 of which there were two forms: ''cum manu'' and ''sine manu''. In a ''cum manu'' marriage, the wife was placed under the legal control of the husband. In a ''sine manu'' marriage, the wife remained under the legal control of her father.Marcia L. Colish, ''The Stoic Tradition from Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages'', Brill Academic Publishers, 1990, 2 Edition, 383 In both ''cum manu'' and ''sine manu'' marriages, if both the husband and wife were ''Status in Roman legal system, alieni iuris'' (persons under ''patria potestas''; that is, under the power of their respective ''pater familias, patres familias''), the marriage could only take place with the approval of both ''patres familias''. Procedures for initiating and terminating marriage varied with the type of union. Initially, ''cum manu'' was the sole form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Property
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, rent, sell, exchange, transfer, give away, or destroy it, or to exclude others from doing these things, as well as to perhaps abandon it; whereas regardless of the nature of the property, the owner thereof has the right to properly use it under the granted Property rights (economics), property rights. In economics and political economy, there are three broad forms of property: private property, public property, and collective property (or ''cooperative propert''y). Property may be jointly owned by more than one party equally or unequally, or according to simple or complex agreements; to distinguish ownership and easement from rent, there is an expectation that each party's will with regard to the property be clearly defined and unconditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrician (ancient Rome)
The patricians (from ) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom and the early Roman Republic, Republic, but its relevance waned after the Conflict of the Orders (494 BC to 287 BC). By the time of the late Republic and Roman Empire, Empire, membership in the patriciate was of only nominal significance. The social structure of ancient Rome revolved around the distinction between the patricians and the plebeians. The status of patricians gave them more political power than the plebeians, but the relationship between the groups eventually caused the Conflict of the Orders. This time period resulted in changing of the social structure of ancient Rome. After the Western Roman Empire, Western Empire fell, the term "patrician" continued as a high Byzantine aristocracy and bureaucracy, honorary title in the Eastern Empire. In many Italian city-states, medieval Italian republics, especially in Republic of V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter (mythology)
Jupiter ( or , from Proto-Italic language, Proto-Italic "day, sky" + "father", thus "sky father" Greek: Zeus, Δίας or Zeus, Ζεύς), also known as Jove (nominative case, nom. and genitive case, gen. ), is the sky god, god of the sky and god of thunder, thunder, and king of the gods in ancient Roman religion and Roman mythology, mythology. Jupiter was the chief deity of Roman state religion throughout the Roman Republic, Republican and Roman Empire, Imperial eras, until Constantine the Great and Christianity, Christianity became the dominant religion of the Empire. In Roman mythology, he negotiates with Numa Pompilius, the second king of Rome, to establish principles of Roman religion such as offering, or sacrifice. Jupiter is thought to have originated as a sky god. His identifying implement is the thunderbolt and his primary sacred animal is the eagle, which held precedence over other birds in the taking of auspices and became one of the most common symbols of the Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrifice
Sacrifice is an act or offering made to a deity. A sacrifice can serve as propitiation, or a sacrifice can be an offering of praise and thanksgiving. Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks, and possibly existed before that. Evidence of ritual human sacrifice can also be found back to at least pre-Columbian civilizations of Mesoamerica as well as in European civilizations. Varieties of ritual non-human sacrifices are practiced by numerous religions today. Terminology The Latin term ''sacrificium'' (a sacrifice) derived from Latin ''sacrificus'' (performing priestly functions or sacrifices), which combined the concepts ''sacra'' (sacred things) and ''facere'' (to make, to do). The Latin word ''sacrificium'' came to apply to the Christian eucharist in particular, sometimes named a "bloodless sacrifice" to distinguish it from blood sacrifices. In individual non-Christian ethnic religions, terms translated as "sacrifice" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Pio-Clementino Inv259
August is the eighth month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 31 days. In the Southern Hemisphere, August is the seasonal equivalent of February in the Northern Hemisphere. In the Northern Hemisphere, August falls in summer. In the Southern Hemisphere, the month falls during winter. In many European countries, August is the holiday month for most workers. Numerous religious holidays occurred during August in ancient Rome. Certain meteor showers take place in August. The Kappa Cygnids occur in August, with yearly dates varying. The Alpha Capricornids meteor shower occurs as early as July 10 and ends around August 10. The Southern Delta Aquariids occur from mid-July to mid-August, with the peak usually around July 28–29. The Perseids, a major meteor shower, typically takes place between July 17 and August 24, with the peak days varying yearly. The star cluster of Messier 30 is best observed around August. Among the aborigines of the Canary I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
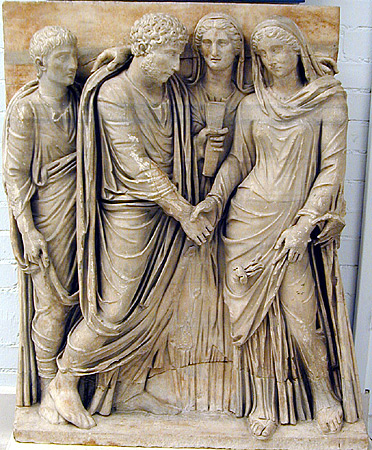
Confarreatio
In ancient Rome, was a traditional patrician form of marriage. The ceremony involved the bride and bridegroom sharing a cake of emmer, in Latin ''far'' or ''panis farreus'', hence the rite's name. ''Far'' is often translated as "spelt", which is inaccurate as the grain used was ''Triticum dicoccum'' (emmer), not ''Triticum spelta''. The Flamen Dialis and pontifex maximus presided over the wedding, and ten witnesses had to be present. The woman passed directly from the hand ''(manus)'' of her father or head of household (the ''pater familias'') to that of her new husband. Having parents who were married by was a prerequisite for becoming a Vestal or the Flamen Dialis. seems to have been limited to those whose parents were also married by , but later, perhaps with the rise of plebeian ''nobiles'', this requirement must have been relaxed. Scipio Africanus presumably married his wife Aemilia Tertia by , because their elder son was Flamen Dialis; yet Scipio's mother Pomponia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Will (law)
A will and testament is a legal document that expresses a person's (testator) wishes as to how their property ( estate) is to be distributed after their death and as to which person ( executor) is to manage the property until its final distribution. For the distribution (devolution) of property not determined by a will, see inheritance and intestacy. Though it has been thought a "will" historically applied only to real property, while "testament" applied only to personal property (thus giving rise to the popular title of the document as "last will and testament"), records show the terms have been used interchangeably. Thus, the word "will" validly applies to both personal and real property. A will may also create a testamentary trust that is effective only after the death of the testator. History Throughout most of the world, the disposition of a dead person's estate has been a matter of social custom. According to Plutarch, the written will was invented by Solon. Originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's Rights
Women's rights are the rights and Entitlement (fair division), entitlements claimed for women and girls worldwide. They formed the basis for the women's rights movement in the 19th century and the feminist movements during the 20th and 21st centuries. In some countries, these rights are institutionalized or supported by law, local custom, and behavior, whereas in others, they are ignored and suppressed. They differ from broader notions of human rights through claims of an inherent historical and traditional bias against the exercise of rights by women and girls, in favor of men and boys.Hosken, Fran P., 'Towards a Definition of Women's Rights' in ''Human Rights Quarterly'', Vol. 3, No. 2. (May 1981), pp. 1–10. Issues commonly associated with notions of women's rights include the right to bodily integrity and autonomy, to be free from sexual violence, to Women's suffrage, vote, to hold public office, to enter into legal contracts, to have equal rights in family law, Right to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sui Iuris
''Sui iuris'' (), also spelled ''sui juris'', is a Latin phrase that literally means "of one's own right". It is used in both the Catholic Church's canon law and secular law. The term church ''sui iuris'' is used in the Catholic ''Code of Canons of the Eastern Churches'' (CCEO) to denote the autonomous churches in Catholic communion. The Catholic Church consists of 24 churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic churches. Etymology and spelling The Latin ''sui iuris'' (the individual words meaning 'self' and 'law') corresponds to the Greek 'αὐτόνομος', from which the English word autonomy is derived. The spelling in Classical Latin is ''sui iuris'', and in Medieval Latin ''sui juris''. English Law gets the term from Medieval Latin, and so spells it ''sui juris''. Catholic canon law Church documents such as the ''Code of Canons of the Eastern Churches'' apply the Latin term ''sui iuris'' to the particular Churches that are together the Catholic Chu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divorced
Divorce (also known as dissolution of marriage) is the process of terminating a marriage or marital union. Divorce usually entails the canceling or reorganising of the legal duties and responsibilities of marriage, thus dissolving the bonds of matrimony between a married couple under the rule of law of the particular country or state. It can be said to be a legal dissolution of a marriage by a court or other competent body. It is the legal process of ending a marriage. Divorce laws vary considerably around the world, but in most countries, divorce is a legal process that requires the sanction of a court or other authority, which may involve issues of distribution of property, child custody, alimony (spousal support), child visitation / access, parenting time, child support, and division of debt. In most countries, monogamy is required by law, so divorce allows each former partner to marry another person. Divorce is different from annulment, which declares the marria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Widowed
A widow (female) or widower (male) is a person whose spouse has died and has usually not remarried. The male form, "widower", is first attested in the 14th century, by the 19th century supplanting "widow" with reference to men. The adjective for either sex is ''widowed''. These terms are not applied to a divorcé(e) following the death of an ex-spouse. The state of having lost one's spouse to death is termed ''widowhood''. The term ''widowhood'' can be used for either sex, at least according to some dictionaries, but the word ''widowerhood'' is also listed in some dictionaries. An archaic term for a widow is "relict", literally "someone left over"; this word can sometimes be found on older gravestones. Occasionally, the word ''viduity'' is used. Effects on health The increased mortality rate after the death of a spouse is called the ''widowhood effect''. It is "strongest during the first three months after a spouse's death, when they had a 66-percent increased chance of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |