|
Mastophora Extraordinaria
''Mastophora extraordinaria'' is a species of spider in the orb-weaver spider family Araneidae. It is found in South America (Brazil, Uruguay and Argentina). Like some other species of the genus '' Mastophora'', adult females resemble bird droppings. ''Mastophora'' species, including ''M. extraordinaria'', are "bolas spiders" – adult females capture their prey by using a sticky drop on the end of a single line which they swing at the target, usually a male moth attracted by the release of an analogue of the attractant sex pheromone produced by the female moth. Juveniles and adult males do not use a bolas, catching prey with their legs alone. Description Herbert W. Levi described a female in 2003 (males were not known). The total length of the specimen's body was . Other females ranged from . The carapace was long and almost as wide in the thoracic region. The carapace was dark brown with a narrow white rim and had low tubercules. The abdomen was white with two black patc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduardo Ladislao Holmberg
Eduardo Ladislao Holmberg (27 July 1852, in Buenos Aires – 4 November 1937) was an Argentine natural historian and novelist, one of the leading figures in Argentine biology. Together with Florentino Ameghino he undertook the inventory of Argentine flora and fauna, and explored all the ecoregions in the country, summarizing for the first time the biodiversity of its territory. The son of botanical aficionado and grandson of the Baron Holmberg, Holmburg accompanied Argentine '' Libertador'' Manuel Belgrano on his campaigns and introduced the cultivation of the ''camellia'' to Argentina. As director of the Buenos Aires Zoological Garden he greatly developed its scientific aspect, publishing booklets and providing printed media for a learned appreciation of its contents. He also directed the Natural History Cabinet of the University of Buenos Aires and published the standard reference works on botany and zoology used in his country for most of the 20th century. While less di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can reproduction, produce Fertility, fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel, however, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had a sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orb-weaver Spider
Orb-weaver spiders are members of the spider family Araneidae. They are the most common group of builders of spiral wheel-shaped webs often found in gardens, fields, and forests. The English word "orb" can mean "circular", hence the English name of the group. Araneids have eight similar eyes, hairy or spiny legs, and no stridulating organs. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, including many well-known large or brightly colored garden spiders. With 3,108 species in 186 genera worldwide, the Araneidae comprise the third-largest family of spiders (behind the Salticidae and Linyphiidae). Araneid webs are constructed in a stereotypical fashion, where a framework of nonsticky silk is built up before the spider adds a final spiral of silk covered in sticky droplets. Orb webs are also produced by members of other spider families. The long-jawed orb weavers (Tetragnathidae) were formerly included in the Araneidae; they are closely related, being part of the superfamily Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastophora (spider)
''Mastophora'', also known as bolas spiders, is a genus of orb-weaver spiders first described by E. L. Holmberg in 1876. They can be identified by a pair of lumps on the dorsal surface of the opisthosoma, though not all males will have these lumps. Adult females of the genus snare prey mid-air by using a silk line with an adhesive blob on the end, similar to bolas used by South American gauchos. They feed on flying insects, particularly moths, sometimes releasing pheromones that mimic those of their prey to attract them. Males and juvenile females capture their prey directly with their legs. ''Mastophora'' spiders have extreme sexual size dimorphism: adult females reach 0,75 inches (19 mm), while adult males are smaller than 0,067 inches (1,7 mm). These spiders reach maturity after two instars, or fewer. Cephalothorax often with dorsal protuberances, frequently paired. Female abdomen large, wider than long, an occasion has dorsal humps or lobes. Prey specialization by means of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
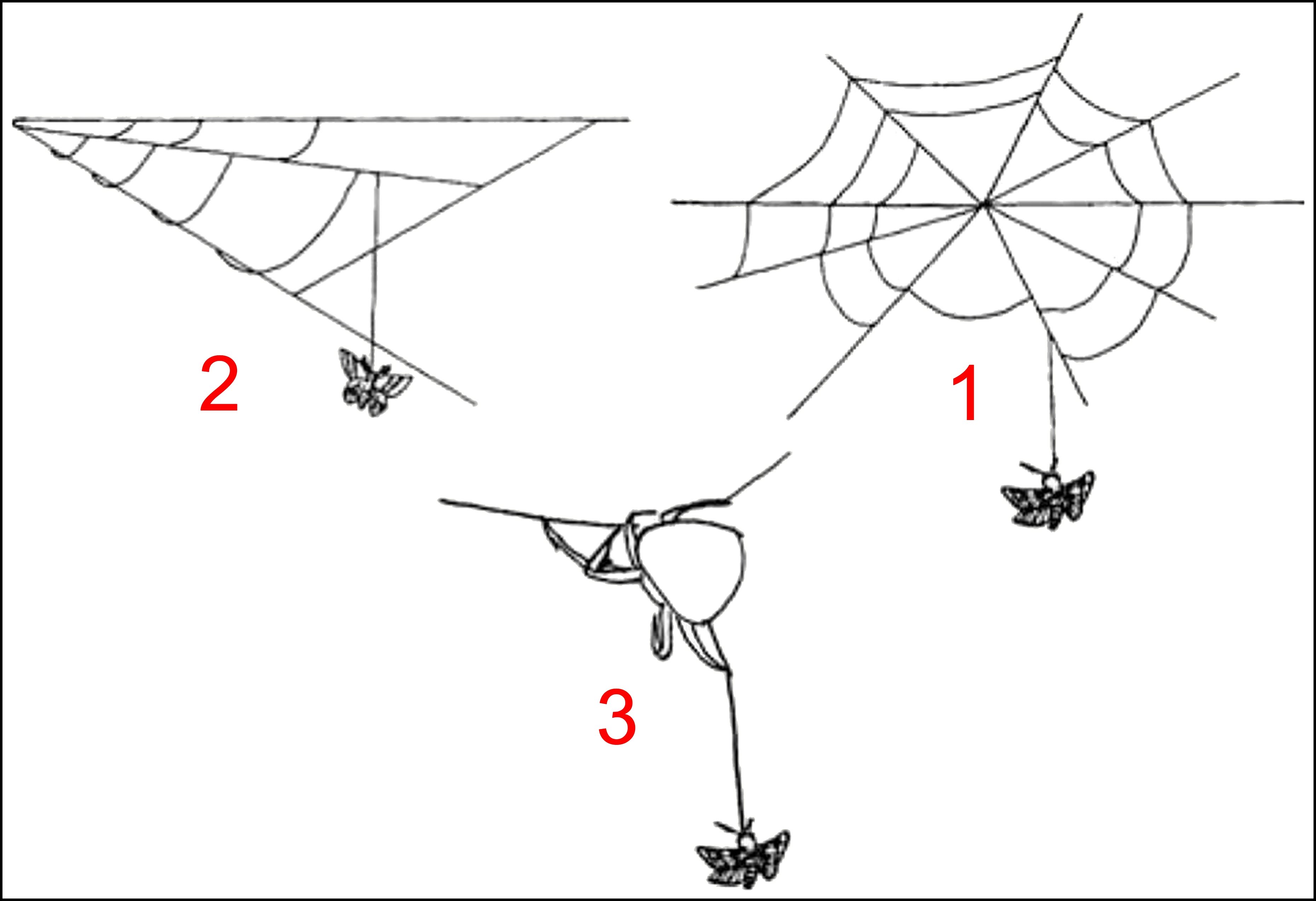
Bolas Spider
A bolas spider is a member of the orb-weaver spider (family Araneidae) that, instead of spinning a typical orb web, hunts by using one or more sticky "capture blobs" on the end of a silk line, known as a "bolas". By swinging the bolas at flying male moths or moth flies nearby, the spider may snag its prey rather like a fisherman snagging a fish on a hook. Because of this, they are also called angling or fishing spiders (although the remotely related genus '' Dolomedes'' is also called a fishing spider). The prey is lured to the spider by the production of up to three sex pheromone-analogues. Bolas spiders have been treated as either the whole or part of either the tribe "Mastophoreae" or Mastophorini, the subfamily Mastophorinae, or the informal group mastophorines. Recent studies show that the genus '' Celaenia'', which does not use a bolas, belongs in the same taxonomic group. Description Bolas spiders are small nocturnal animals with conspicuous outgrowths on the upper (dors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Pheromone
Sex pheromones are pheromones released by an organism to attract an individual of the same species, encourage them to mate with them, or perform some other function closely related with sexual reproduction. Sex pheromones specifically focus on indicating females for breeding, attracting the opposite sex, and conveying information on species, age, sex and genotype. Non-volatile pheromones, or cuticular contact pheromones, are more closely related to social insects as they are usually detected by direct contact with chemoreceptors on the antennae or feet of insects. Insect sex pheromones have found uses in monitoring and trapping of pest insects. Evolution Sex pheromones have evolved in many species. The many types of pheromones (i.e. alarm, aggregation, defense, sexual attraction) all have a common cause acting as chemical cues to trigger a response. However, sex pheromones are particularly associated with signaling mating behaviors or dominance. The odors released can be seen as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Walter Levi
Herbert Walter Levi (January 3, 1921 – November 3, 2014) was professor emeritus of zoology and curator of arachnology at the Museum of Comparative Zoology, Harvard University. He was born in Germany, educated there and at Leighton Park School, Reading in England. He then received his higher education at the University of Connecticut and the University of Wisconsin. Levi authored about 150 scientific papers on spiders and on biological conservation. He is the author of the popular Golden Guide ''Spiders and their Kin'', with Lorna Rose Levi (his wife) and Herbert Spencer Zim. Levi received the 2007 Eugene Simon Award from the International Society of Arachnology "for his immense influence on US spider research". He was an elected honorary member of the American Arachnological Society. Levi was an editorial board member for the '' Journal of Arachnology''. The pseudoscorpion genus ''Levichelifer'', the spider species ''Anisaedus levii'' and the whip spider species ''Phrynus levii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Spider Terms
This glossary describes the terms used in formal descriptions of spiders; where applicable these terms are used in describing other arachnids. Links within the glossary are shown . Terms A Abdomen or opisthosoma: One of the two main body parts ( tagmata), located towards the posterior end; see also Abdomen § Other animals Accessory claw: Modified at the tip of the in web-building spiders; used with to grip strands of the web Anal tubercle: A small protuberance (tubercule) above the through which the anus opens Apodeme → Apophysis (plural apophyses): An outgrowth or process changing the general shape of a body part, particularly the appendages; often used in describing the male → Atrium (plural atria): An internal chamber at the entrance to the in female haplogyne spiders B Bidentate: Having two Book lungs: Respiratory organs on the ventral side (underside) of the , in front of the , opening through narrow slits; see also Book lungs Branchial operculum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set (mathematics), set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrtarachninae
Cyrtarachninae is a subfamily of spiders in the family Araneidae (orb-weaver spiders, araneids). The group has been circumscribed in several different ways. It originated as the group Cyrtarachneae, described by Eugène Simon in 1892. The group was later treated at different ranks: as a tribe, both under Simon's name and as Cyrtarachnini, and as the subfamily Cyrtarachninae. Circumscriptions have varied. The broadest circumscription, Cyrtarachninae ''sensu lato'' (''s.l.''), includes three of Simon's original groups, including the bolas spiders (also placed in the tribe Mastophoreae or Mastophorini, or in the subfamily Mastophorinae). Unlike most araneids, members of the subfamily do not construct orb webs, some not using webs at all to capture prey, some using one or more sticky drops on a single line (a bolas), while others construct webs with few widely spaced non-spiral threads, some triangular. Many have been shown to attract prey by producing analogues of insect sex pheromo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araneidae
Orb-weaver spiders are members of the spider family Araneidae. They are the most common group of builders of spiral wheel-shaped webs often found in gardens, fields, and forests. The English word "orb" can mean "circular", hence the English name of the group. Araneids have eight similar eyes, hairy or spiny legs, and no stridulating organs. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, including many well-known large or brightly colored garden spiders. With 3,108 species in 186 genera worldwide, the Araneidae comprise the third-largest family of spiders (behind the Salticidae and Linyphiidae). Araneid webs are constructed in a stereotypical fashion, where a framework of nonsticky silk is built up before the spider adds a final spiral of silk covered in sticky droplets. Orb webs are also produced by members of other spider families. The long-jawed orb weavers (Tetragnathidae) were formerly included in the Araneidae; they are closely related, being part of the superfamily Aran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)