|
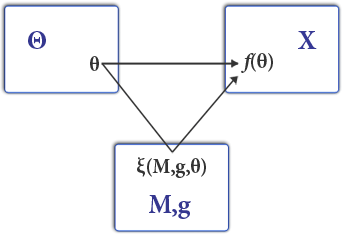
Maskin Monotonicity
Maskin monotonicity is a desired property of voting systems suggested by Eric Maskin. Each voter reports his entire preference relation over the set of alternatives. The set of reports is called a ''preference profile''. A ''social choice rule'' maps the preference profile to the selected alternative. For a preference profile P_1 with a chosen alternative A_1, there is another preference profile P_2 such that the position of A_1 relative to each of the other alternatives either improves or stays the same as in P_1. With Maskin monotonicity, A_1 should still be chosen at P_2. Maskin monotonicity is a necessary condition for implementability in Nash equilibrium. Moreover, any social choice rule that satisfies Maskin monotonicity and another property called "no veto power" can be implemented in Nash equilibrium form if there are three or more voters. See also * Monotonicity (mechanism design) * The monotonicity criterion Electoral system criteria In social choice, the negat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voting System
An electoral or voting system is a set of rules used to determine the results of an election. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, nonprofit organizations and informal organisations. These rules govern all aspects of the voting process: when elections occur, who is allowed to vote, who can stand as a candidate, how ballots are marked and cast, how the ballots are counted, how votes translate into the election outcome, limits on campaign spending, and other factors that can affect the result. Political electoral systems are defined by constitutions and electoral laws, are typically conducted by election commissions, and can use multiple types of elections for different offices. Some electoral systems elect a single winner to a unique position, such as prime minister, president or governor, while others elect multiple winners, such as members of parliament or boards of directors. When electing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Maskin
Eric Stark Maskin (born December 12, 1950) is an American economist and mathematician. He was jointly awarded the 2007 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences with Leonid Hurwicz and Roger Myerson "for having laid the foundations of mechanism design theory". He is the Adams University Professor and Professor of Economics and Mathematics at Harvard University. Until 2011, he was the Albert O. Hirschman Professor of Social Science at the Institute for Advanced Study, and a visiting lecturer with the rank of professor at Princeton University.Economics professor wins Nobel – The Daily Princetonian Early life and education Maskin was born in |
Preference (economics)
In economics, and in other social sciences, preference refers to an order by which an Agent (economics), agent, while in search of an "optimal choice", ranks alternatives based on their respective utility. ''Preferences'' are evaluations that concern matters of value, in relation to practical reasoning. Individual preferences are determined by taste, need, ..., as opposed to price, availability or personal income. Classical economics assumes that people act in their best (rational) interest. In this context, rationality would dictate that, when given a choice, an individual will select an option that maximizes their self-interest. But preferences are not always transitive relation, transitive, both because real humans are far from always being rational and because in some situations preferences can form cycle (graph theory), cycles, in which case there exists no well-defined optimal choice. An example of this is Efron dice. The concept of preference plays a key role in many discip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nash Equilibrium
In game theory, the Nash equilibrium is the most commonly used solution concept for non-cooperative games. A Nash equilibrium is a situation where no player could gain by changing their own strategy (holding all other players' strategies fixed). The idea of Nash equilibrium dates back to the time of Cournot, who in 1838 applied it to his model of competition in an oligopoly. If each player has chosen a strategy an action plan based on what has happened so far in the game and no one can increase one's own expected payoff by changing one's strategy while the other players keep theirs unchanged, then the current set of strategy choices constitutes a Nash equilibrium. If two players Alice and Bob choose strategies A and B, (A, B) is a Nash equilibrium if Alice has no other strategy available that does better than A at maximizing her payoff in response to Bob choosing B, and Bob has no other strategy available that does better than B at maximizing his payoff in response to Alice c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotonicity (mechanism Design)
In mechanism design, monotonicity is a property of a social choice function. It is a necessary condition for being able to implement such a function using a strategyproof mechanism. Its verbal description is: In other words: Notation There is a set X of possible outcomes. There are n agents which have different valuations for each outcome. The valuation of agent i is represented as a function:v_i : X \longrightarrow R_+which expresses the value it assigns to each alternative. The vector of all value-functions is denoted by v. For every agent i, the vector of all value-functions of the ''other'' agents is denoted by v_. So v \equiv (v_i,v_). A social choice function is a function that takes as input the value-vector v and returns an outcome x\in X. It is denoted by \text(v) or \text(v_i,v_). In mechanisms without money A social choice function satisfies the strong monotonicity property (SMON) if for every agent i and every v_i,v_i',v_, if:x = \text(v_i, v_)x' = \text(v' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotonicity Criterion
Electoral system criteria In social choice, the negative response, perversity, or additional support paradox is a pathological behavior of some voting rules where a candidate loses as a result of having too much support (or wins because of increased opposition). In other words, increasing (decreasing) a candidate's ranking or rating causes that candidate to lose (win), respectively. Electoral systems that do not exhibit perversity are sometimes said to satisfy the monotonicity criterion.D R Woodall"Monotonicity and Single-Seat Election Rules" '' Voting matters'', Issue 6, 1996 Perversity is often described by social choice theorists as an exceptionally severe kind of electoral pathology, as such rules can have "backwards" responses to voters' opinions, where popularity causes defeat while unpopularity leads to a win. Similar rules treat the well-being of some voters as "less than worthless". These issues have led to constitutional prohibitions on such systems as violating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanism Design
Mechanism design (sometimes implementation theory or institution design) is a branch of economics and game theory. It studies how to construct rules—called Game form, mechanisms or institutions—that produce good outcomes according to Social welfare function, some predefined metric, even when the designer does not know the players' true preferences or what information they have. Mechanism design thus focuses on the study of solution concepts for a class of private-information games. Mechanism design has broad applications, including traditional domains of economics such as market design, but also political science (through voting theory). It is a foundational component in the operation of the internet, being used in networked systems (such as inter-domain routing), e-commerce, and Sponsored search auction, advertisement auctions by Facebook and Google. Because it starts with the end of the game (a particular result), then works backwards to find a game that implements it, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |