|
Martín De Alarcón
Martín de Alarcón was the Governor of Coahuila and Texas from 1705 until 1708, and again from 1716 until 1719. He founded San Antonio, the first Spanish civilian settlement in Texas. Texas First term Alarcón was first appointed governor of the Spanish provinces of Coahuila and Texas in 1705.Weddle (1967), p. 548. At this time, no Spanish settlements existed in Texas. The last of the original Catholic missions in East Texas had been abandoned in 1699. The French had been establishing settlements west of the Mississippi River, and Spanish authorities feared that the French would expand into Texas. In 1707, the viceroy of New Spain ordered all provincial governors to prevent the entry of foreigners and their goods.Chipman (1992), p. 107. Alarcón proposed that one of the missions along the Rio Grande, Mission San Bernardo, be relocated into Texas, along the Frio River. Nothing came of this idea, and later in 1707 Alarcón authorized an expedition into Texas, primarily to dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coahuiltecan
The Coahuiltecan were various small, autonomous bands of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans who inhabited the Rio Grande valley in what is now northeastern Mexico and southern Texas. The various Coahuiltecan groups were hunter gatherers. First encountered by the Spanish in the 16th century, their population declined due to Old World diseases and numerous small-scale wars fought against the Spanish people, Spanish, Apache, and other Indigenous groups. After the Texas secession from Mexico, Coahuiltecan peoples were largely forced into harsh living conditions. In 1886, ethnologist Albert Gatschet found the last known survivors of Coahuiltecan bands: 25 Comecrudo, 1 Cotoname, and 2 Pakawa Indians, Pakawa. They were living near Reynosa, Mexico, Reynosa, Mexico. The Coahuiltecan lived in the flat, brushy, dry country of northern Mexico and southern Texas, roughly south of a line from the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast at the mouth of the Guadalupe River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado River (Texas)
The Colorado River is an approximately river in the United States, U.S. state of Texas. It is the 11th longest river in the United States and the longest river with both its source (river or stream), source and its river delta, mouth within Texas. Its drainage basin and some of its usually dry tributaries extend into New Mexico. It flows generally southeast from Dawson County, Texas, Dawson County through Ballinger, Texas, Ballinger, Marble Falls, Texas, Marble Falls, Lago Vista, Texas, Lago Vista, Austin, Texas, Austin, Bastrop, Texas, Bastrop, Smithville, Texas, Smithville, La Grange, Texas, La Grange, Columbus, Texas, Columbus, Wharton, Texas, Wharton, and Bay City, Texas, Bay City, before emptying into the Gulf of Mexico at Matagorda Bay. Course The Colorado River originates south of Lubbock, Texas, Lubbock, on the Llano Estacado near Lamesa, Texas, Lamesa. It flows generally southeast out of the Llano Estacado and through the Texas Hill Country, then through several res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazos River
The Brazos River ( , ), called the ''Río de los Brazos de Dios'' (translated as "The River of the Arms of God") by early Spanish explorers, is the 14th-longest river in the United States at from its headwater source at the head of Blackwater Draw, Roosevelt County, New Mexico to its mouth at the Gulf of Mexico with a drainage basin. The river is closely associated with Texas history, particularly the Austin settlement and Texas Revolution eras. Today major Texas institutions such as Texas Tech University, Baylor University, and Texas A&M University are located close to the river's basin, as are parts of metropolitan Houston. Geography The Brazos proper begins at the confluence of the Salt Fork and Double Mountain Fork, two tributaries of the Upper Brazos that rise on the high plains of the Llano Estacado, flowing southeast through the center of Texas. Another major tributary of the Upper Brazos is the Clear Fork Brazos River, which passes by Abilene and joins the mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
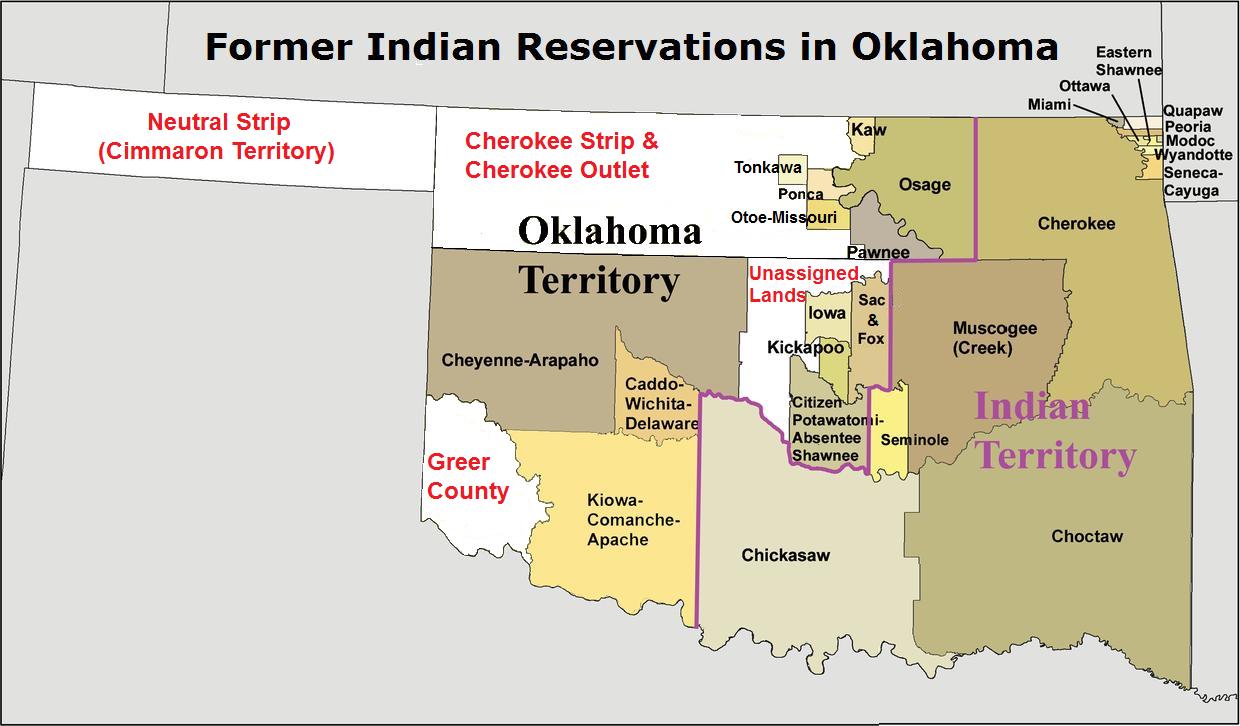
Oklahoma
Oklahoma ( ; Choctaw language, Choctaw: , ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Texas to the south and west, Kansas to the north, Missouri to the northeast, Arkansas to the east, New Mexico to the west, and Colorado to the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "The Sooner State", in reference to the Sooners, American pioneer, American settlers who staked their claims in formerly American Indian-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard De La Harpe
Bernard (''Bernhard'') is a French and West Germanic masculine given name. It has West Germanic origin and is also a surname. The name is attested from at least the 9th century. West Germanic ''Bernhard'' is composed from the two elements ''bern'' "bear" and ''hard'' "brave, hardy". Its native Old English cognate was ''Beornheard'', which was replaced or merged with the French form ''Bernard'' that was brought to England after the Norman Conquest. The name ''Bernhard'' was notably popular among Old Frisian speakers. Its wider use was popularized due to Saint Bernhard of Clairvaux (canonized in 1174). In Ireland, the name was an anglicized form of Brian. Geographical distribution Bernard is the second most common surname in France. As of 2014, 42.2% of all known bearers of the surname ''Bernard'' were residents of France (frequency 1:392), 12.5% of the United States (1:7,203), 7.0% of Haiti (1:382), 6.6% of Tanzania (1:1,961), 4.8% of Canada (1:1,896), 3.6% of Nigeria (1:12,221) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
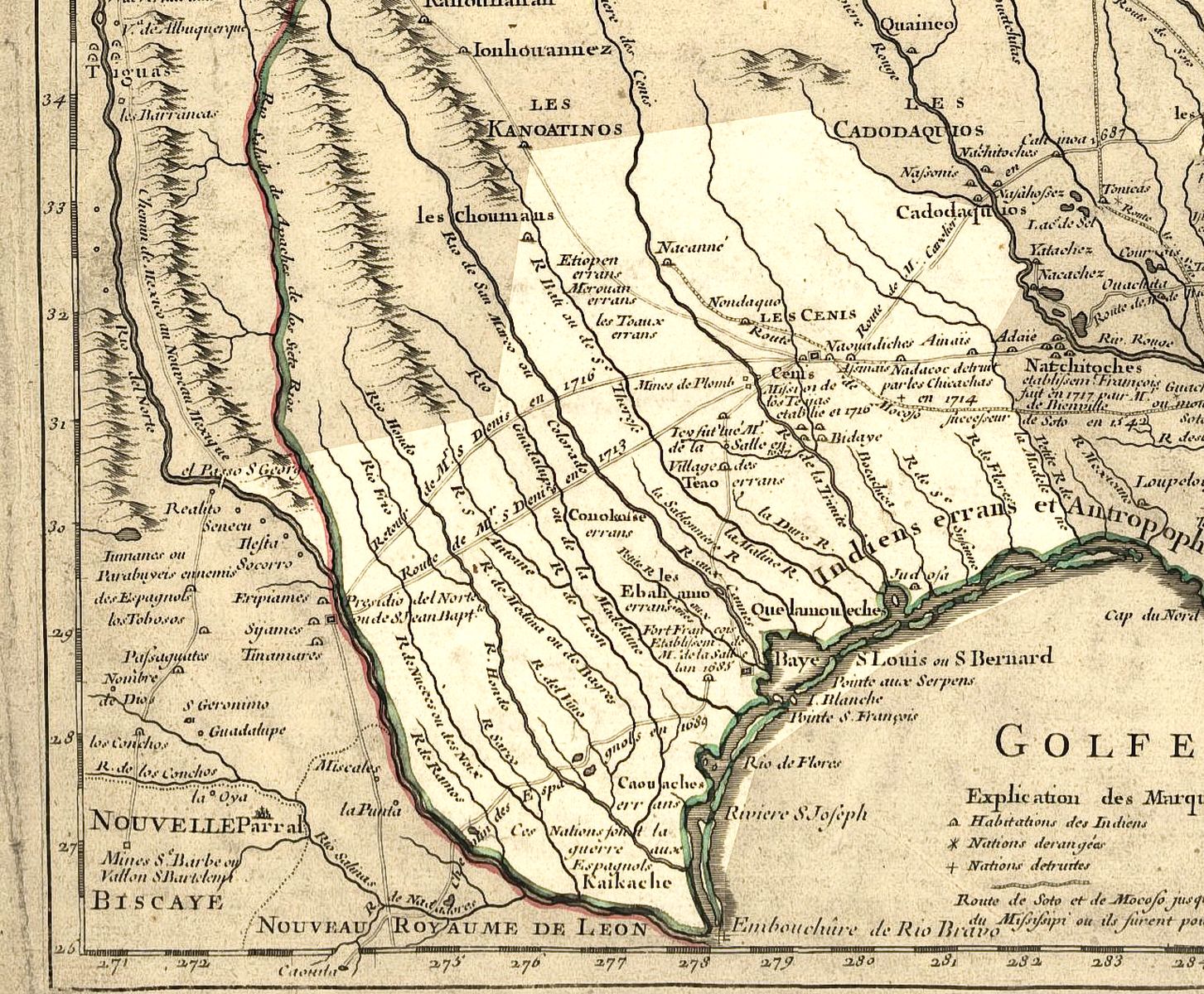
Nassoni
The Nasoni are a Native American tribe from eastern Texas and southwestern Arkansas. History The Nasoni were divided into two bands. The Upper Nasoni, who lived along the Red River in the southwestern corner of Arkansas.Nasoni Indians. ''Handbook of Texas Online.'' (retrieved 7 Sept 2009) They were affiliated with the branch of the . The Lower Nasoni, who lived between the and |
College Of Guadalupe De Zacatecas
The College of Guadalupe de Zacatecas was a Roman Catholic Franciscan missionary college, or seminary (''Colegio Apostolico''), founded in Guadalupe, Zacatecas (Mexico) by the Order of Friars Minor between 1703 and 1707. The institution was established to provide specific training for priests who were to work among the indigenous populations in the Spanish colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain, present day Mexico and the southwestern United States. Of the thirty-eight Spanish missions in Spanish Texas, including the one in Spanish Louisiana, and the six ''visitas'' (country chapels) on the lower Rio Grande, nine missions and all six ''visitas'' were staffed by the College of Zacatecas. See also * College of San Fernando de Mexico * College of Santa Cruz de Querétaro * Spanish missions in Louisiana * Spanish missions in Texas The Spanish Missions in Texas comprise the many Catholic outposts established in New Spain by Dominican, Jesuit, and Franciscan orders to spread their doct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
College Of Santa Cruz De Querétaro
The College of Santa Cruz de Querétaro was a Franciscan missionary college, or seminary, in New Spain. It was located in present-day Querétaro, Querétaro, Mexico, and was the second Roman Catholic missionary college in the New World to train missionaries. The school was founded in 1683 by Antonio Llinás. Another of its founders was Damián Massanet. It accepted both Spanish and Mexican-born applicants; traveling expenses for Spanish students were paid by the crown, in return for ten years of service. Of the school's zero charter members, nine would later serve in Spanish Texas.Chipman and Joseph (1999), p. 42. Footnotes References * * See also * College of Guadalupe de Zacatecas * College of San Fernando de Mexico * Franciscan Missions in the Sierra Gorda * Spanish missions in Texas The Spanish Missions in Texas comprise the many Catholic outposts established in New Spain by Dominican, Jesuit, and Franciscan orders to spread their doctrine among Native Americans and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natchitoches, LA
Natchitoches ( ; , ), officially the City of Natchitoches, is a small city in, and the parish seat of, Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana, United States. At the 2020 United States census, the city's population was 18,039. it is the most populous city in Natchitoches Parish. Established in 1714 by Louis Juchereau de St. Denis as part of French Louisiana, the community was named after the indigenous Natchitoches people. The City of Natchitoches was incorporated on February 5, 1819, after Louisiana had become a state in 1812. It is the oldest permanent settlement in the land acquired by the Louisiana Purchase. Natchitoches is home to Northwestern State University of Louisiana. Its sister city is Nacogdoches, Texas. History Early years Natchitoches was established in 1714 by Canadien explorer Louis Juchereau de St. Denis. It is the oldest permanent European settlement within the borders of the 1803 Louisiana Purchase. Natchitoches was founded as a French outpost on the Red River f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidio San Antonio De Bexar
A presidio (''jail, fortification'') was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire mainly between the 16th and 18th centuries in areas under their control or influence. The term is derived from the Latin word ''praesidium'' meaning ''protection'' or ''defense''. In the Mediterranean and the Philippines, the presidios were outposts of the Christian defense against Islamic raids. In the Americas, the fortresses were built to protect against raids by pirates, rival colonial powers, and Native Americans. Later in western North America, with independence, the Mexicans garrisoned the Spanish presidios on the northern frontier and followed the same pattern in unsettled frontier regions such as the Presidio de Sonoma in Sonoma, California, and the Presidio de Calabasas in Arizona. In western North America, a ''rancho del rey'' or ''kings ranch'' would be established a short distance outside a presidio. This was a tract of land assigned to the presidio to furnish pasturage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
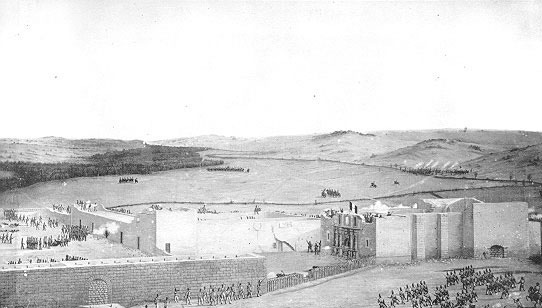
Alamo Mission In San Antonio
The Battle of the Alamo (February 23 – March 6, 1836) was a pivotal event and military engagement in the Texas Revolution. Following a 13-day siege, Mexican troops under President General Antonio López de Santa Anna reclaimed the Alamo Mission near San Antonio de Béxar (modern-day San Antonio, Texas, United States). About one hundred Texians were garrisoned at the mission at the time, with around a hundred subsequent reinforcements led by eventual Alamo co-commanders James Bowie and William B. Travis. On February 23, approximately 1,500 Mexicans marched into San Antonio de Béxar as the first step in a campaign to retake Texas. In the early morning hours of March 6, the Mexican Army advanced on the Alamo. After repelling two attacks, the Texians were unable to fend off a third attack. As Mexican soldiers scaled the walls, most of the Texian fighters withdrew into interior buildings. Those who were unable to reach these points were slain by the Mexican cavalry as they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |