|
Marsupial Mole
Marsupial moles, the Notoryctidae family, are two species of highly specialized marsupial mammals that are found in the Australian interior. They are small burrowing marsupials that anatomically converge on fossorial placental mammals, such as extant golden moles (Chrysochloridae) and extinct epoicotheres. The species are: * '' Notoryctes typhlops'' (southern marsupial mole, known as the ''itjaritjari'' by the Pitjantjatjara and Yankunytjatjara people in Central Australia) * '' Notoryctes caurinus'' (northern marsupial mole, also known as the ''kakarratul'') Characteristics In an example of convergent evolution, notoryctids resemble (and fill the ecological niche of) the talpid or true moles from North America and Eurasia and the Chrysochloridae or golden moles from Southern Africa. Like chrysochlorids and epoicotheres, notoryctids use their forelimbs and enlarged central claws to dig in a parasagittal (i.e., up and down) plane, as opposed to the "lateral scratch" style o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Marsupial Mole
The southern marsupial mole (''Notoryctes typhlops''), also known as the itjaritjari () or itjari-itjari, is a Mole (animal), mole-like marsupial found in the western central deserts of Australia. It is extremely adapted to a Fossorial, burrowing way of life. It has large, shovel-like forepaws and silky fur, which helps it move easily. It also lacks complete eyes as it has little need for them. It feeds on earthworms and larvae. History of discovery Although the southern marsupial mole was probably known by Aboriginal Australians for thousands of years, the first specimen examined by the scientific community was collected in 1888. Stockman W. Coulthard made the discovery on Idracowra Pastoral Lease in the Northern Territory by following some unusual prints that led him to the animal lying under a Tussock (grass), tussock. Not knowing what to do with the strange creature, he wrapped it in a kerosene soaked rag, placed it in a revolver cartridge box and forwarded it to E. C. Stirling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on comparison with homologous features in related species. The emergence of vestigiality occurs by normal evolutionary processes, typically by loss of function of a feature that is no longer subject to positive selection pressures when it loses its value in a changing environment. The feature may be selected against more urgently when its function becomes definitively harmful, but if the lack of the feature provides no advantage, and its presence provides no disadvantage, the feature may not be phased out by natural selection and persist across species. Examples of vestigial structures (also called degenerate, atrophied, or rudimentary organs) are the loss of functional wings in island-dwelling birds; the human vomeronasal organ; and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
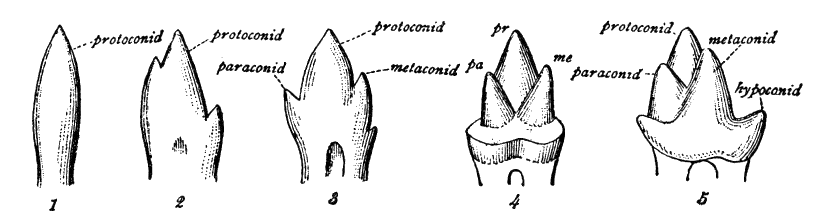
Dental Formula
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology (that is, the relationship between the shape and form of the tooth in question and its inferred function) of the teeth of an animal. Terminology Animals whose teeth are all of the same type, such as most non-mammalian vertebrates, are said to have '' homodont'' dentition, whereas those whose teeth differ morphologically are said to have '' heterodont'' dentition. The dentition of animals with two successions of teeth (deciduous, permanent) is referred to as '' diphyodont'', while the dentition of animals with only one set of teeth throughout life is ''monophyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are continuously discarded and replaced throughout life is termed ''polyphyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaic Evolution
Mosaic evolution (or modular evolution) is the concept, mainly from palaeontology, that evolutionary change takes place in some body parts or systems without simultaneous changes in other parts. Another definition is the "evolution of characters at various rates both within and between species".Carroll R.L. 1997. ''Patterns and processes of vertebrate evolution''. Cambridge University Press. 408 Its place in evolutionary theory comes under long-term trends or macroevolution. Background In the neodarwinist theory of evolution, as postulated by Stephen Jay Gould, there is room for differing development, when a life form matures earlier or later, in shape and size. This is due to allomorphism. Organs develop at differing rhythms, as a creature grows and matures. Thus a " heterochronic clock" has three variants: 1) time, as a straight line; 2) general size, as a curved line; 3) shape, as another curved line. When a creature is advanced in size, it may develop at a sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riversleigh World Heritage Area
Riversleigh World Heritage Area is Australia's most famous fossil location, recognised for the series of well preserved fossils deposited from the Late Oligocene to more recent geological periods. The fossiliferous limestone system is located near the Gregory River in the north-west of Queensland, an environment that was once a very wet rainforest that became more arid as the Gondwanan land masses separated and the Australian continent moved north. The approximately area has fossil remains of ancient mammals, birds, and reptiles of the Oligocene and Miocene ages, many of which were discovered and are only known from the Riversleigh area; the species that have occurred there are known as the Riversleigh fauna. The fossils at Riversleigh are unusual because they are found in soft freshwater limestone which has not been compacted. This means the animal remains retain their three-dimensional structure, rather than being partially crushed like in most fossil sites. The area is loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naraboryctes
''Naraboryctes philcreaseri'' is a fossil species of marsupial found at early Miocene deposits of Boodjamulla National Park of Riversleigh area, northwestern Queensland, Australia. Taxonomy It was first named by Michael Archer, Robin Beck, Miranda Gott, Suzanne Hand, Henk Godthelp and Karen Black in 2011 and is the type species of genus ''Naraboryctes''. The generic name means "to drink" (naraba in Garrawa and Waanyi languages of northwestern Queensland) in reference to its rainforest palaeohabitat + "digger" (oryctes in Greek) in reference to its fossorial specializations and close relationship to the extant species of genus '' Notoryctes''. The specific epithet honors Phil Creaser, and is referred to as "Phil Creaser's Drinking Digger". The genus is allied to the family of modern 'marsupial moles', Notoryctidae, two or three species of the extant genus ''Notoryctes''. However, a more recent study showscases that it lacked many of the synapomorphies associated with mars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicondy
In biology, testicondy in a species is the condition of having testicles situated within the abdomen as the normal anatomy of that species. Testicondy can be further classified into ''primary testicondy'' and ''secondary testicondy''. The testes of mammals such as monotremes, elephants, sirenians and cetacean Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla that includes whales, dolphins and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively c ...s are testicond. See also * Testicular descent References Animal male reproductive system Testicle {{animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda
Lambda (; uppercase , lowercase ; , ''lám(b)da'') is the eleventh letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed. Lambda gave rise to the Latin L and the Cyrillic El (Л). The ancient grammarians and dramatists give evidence to the pronunciation as () in Classical Greek times. In Modern Greek, the name of the letter, Λάμδα, is pronounced . In early Greek alphabets, the shape and orientation of lambda varied. Most variants consisted of two straight strokes, one longer than the other, connected at their ends. The angle might be in the upper-left, lower-left ("Western" alphabets) or top ("Eastern" alphabets). Other variants had a vertical line with a horizontal or sloped stroke running to the right. With the general adoption of the Ionic alphabet, Greek settled on an angle at the top; the Romans put the angle at the lower-left. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zalambdodont
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third molar, man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armadillo
Armadillos () are New World placental mammals in the order (biology), order Cingulata. They form part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are distinguished by the number of bands on their armor. All species are native to the Americas, where they inhabit a variety of environments. Living armadillos are characterized by a leathery armour (anatomy), armor shell and long, sharp claws for digging. They have short legs, but can move quite quickly. The average length of an armadillo is about , including its tail. The giant armadillo grows up to and weighs up to , while the pink fairy armadillo has a length of only . When threatened by a predator, ''Tolypeutes'' species frequently roll up into a ball; they are the only species of armadillo capable of this. Recent genetic research has shown that the megafaunal glyptodonts (up to tall with maximum body masses of around 2 tonnes), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epipubic Bone
Epipubic bones are a pair of bones projecting forward from the pelvic bones of modern marsupials, monotremes and fossil mammals like multituberculates, and even basal eutherians (the ancestors of placentals, who lack them). They first occur in non-mammalian cynodonts such as tritylodontids, suggesting that they are a synapomorphy between them and Mammaliformes. They were first described as early as 1698, but to date, their function(s) remain unresolved. Epipubic bones are often called ''marsupial bones'' because they support the mother's pouch in modern marsupials ("''marsupium''" is Latin for "pouch"). Function Some writers have suggested that the epipubic bones are a part of a kinetic link stretching from the femur on one side, to the ribs on the opposite side. This linkage is formed by a series of muscles: Each epipubic bone is connected to the femur by the pectineus muscle, and to the ribs and vertebrae by the pyramidalis, rectus abdominis, and external and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |