|
Marquesses Of Londonderry
Marquess of Londonderry, of the County of Londonderry ( ), is a title in the Peerage of Ireland. History The title was created in 1816 for Robert Stewart, 1st Earl of Londonderry. He had earlier represented County Down in the Irish House of Commons. Stewart had already been created Baron Londonderry in 1789, Viscount Castlereagh, of Castlereagh in the County of Down, in 1795 and Earl of Londonderry, of the County of Londonderry, in 1796. These titles are also in the Peerage of Ireland. He was the son of Alexander Stewart, who had married Mary Cowan, sister and heiress of Robert Cowan, who gained great wealth as Governor of Bombay from 1729 to 1737. Alexander was from Ballylawn, a townland at the south-west corner of Inishowen in the north of County Donegal, a county located in the west of Ulster in the northern part of Ireland. However, much of the Stewart family's wealth was based on the estates which came into the family through this marriage. The 1st Marquess was one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
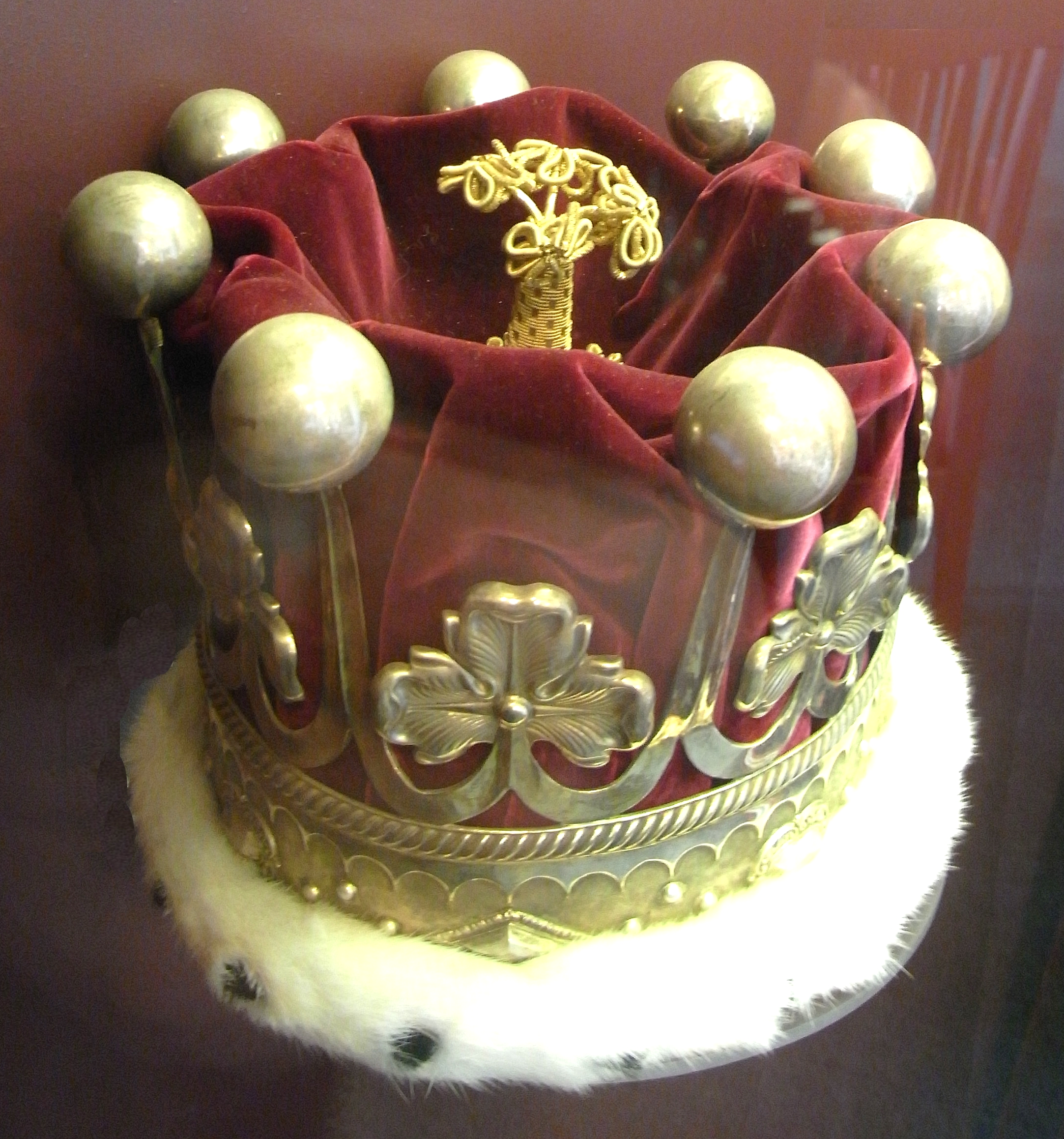
Coronet Of A British Marquess
In British heraldry, a coronet is a type of crown that is a mark of rank of non-reigning members of the royal family and peers. In other languages, this distinction is not made, and usually the same word for ''crown'' is used irrespective of rank (, , , , , etc.) In this use, the English ''coronet'' is a purely technical term for all heraldic images of crowns not used by a sovereign. A Coronet is another type of crown, but is reserved for the nobility - Dukes, Marquesses, Earls, Viscounts and Barons. The specific design and attributes of the crown or coronet signifies the hierarchy and ranking of its owner. Certain physical coronets are worn by the British peerage on rare ceremonial occasions, such as the coronation of the monarch. These are also sometimes depicted in heraldry, and called coronets of rank in heraldic usage. Their shape varies depending on the wearer's rank in the peerage, according to models laid down in the 16th century. Similar depictions of crowns of rank () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Cowan (governor)
Robert Cowan (died 21 February 1737) was an Irish colonialism, colonial administrator and the East India Company's Governor of Bombay from 1729 to 1734. He was a lineal descendant, collateral ancestor of the Marquess of Londonderry, Marquesses of Londonderry through the marriage of his sister, Mary Cowan, to Alexander Stewart (1699–1781), Alexander Stewart, father of Robert Stewart, 1st Marquess of Londonderry. Cowan was descended from Ulster Scots people, Ulster Scots Presbyterian stock, and his father, John Cowan, was an Alderman of the city of Derry. He entered the service of the East India Company some time before 1720 and retired in 1735, two years before his death. In 1721, he was involved in an unsuccessful campaign against Maratha Koli People, Koli Admiral Kanhoji Angre. His personal fortune, amassed as governor, became part of the basis of the wealth of the Stewart family for generations. Chronology 1710-1719 Lisbon (Portugal) (Teggin 2020, 36-36). 1710-1717 Trade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte. Participants were representatives of all European powers (other than the Ottoman Empire) and other stakeholders. The Congress was chaired by Austrian Empire, Austrian statesman Klemens von Metternich, and was held in Vienna from September 1814 to June 1815. The objective of the Congress was to provide a long-term peace plan for Europe by settling critical issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars through negotiation. The goal was not simply to restore old boundaries, but to resize the main powers so they could European balance of power, balance each other and remain at peace, being at the same time shepherds for the smaller powers. More generally, conservative leaders like Metternich also soug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtesy Title
A courtesy title is a title that does not have legal significance but is rather used by custom or courtesy, particularly, in the context of nobility, the titles used by children of members of the nobility (cf. substantive title). In some contexts, ''courtesy title'' is used to mean the more general concept of a title or honorific such as Mr., Mrs., Ms., Miss, Madam, Sir for those who not been awarded a knighthood or a baronetcy, as well as Dr. for physicians who have not actually achieved a doctorate. Europe In Europe, including France, many titles are not substantive titles but remain ''titres de courtoisie'', and, as such, are adopted unilaterally. When done by a genuine member of the '' noblesse d'épée'' the custom was tolerated in French society. A common practice is ''title declension'', when cadet males of noble families, especially landed aristocracy, may assume a lower courtesy title than that legally borne by the head of their family, even though lacking a titl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Castlereagh
Robert Stewart, 2nd Marquess of Londonderry, (18 June 1769 – 12 August 1822), usually known as Lord Castlereagh, derived from the courtesy title Viscount Castlereagh ( ) by which he was styled from 1796 to 1821, was an Irish-born British statesman and politician. As secretary to the Viceroy in Ireland, he worked to suppress the Rebellion of 1798 and to secure passage in 1800 of the Irish Act of Union. As the Foreign Secretary of the United Kingdom from 1812, he was central to the management of the coalition that defeated Napoleon, and was British plenipotentiary at the Congress of Vienna. In the post-war government of Lord Liverpool, Castlereagh was seen to support harsh measures against agitation for reform, and he ended his life an isolated and unpopular figure. Early in his career in Ireland, and following a visit to revolutionary France, Castlereagh recoiled from the democratic politics of his Presbyterian constituents in Ulster. Crossing the floor of the Irish Hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
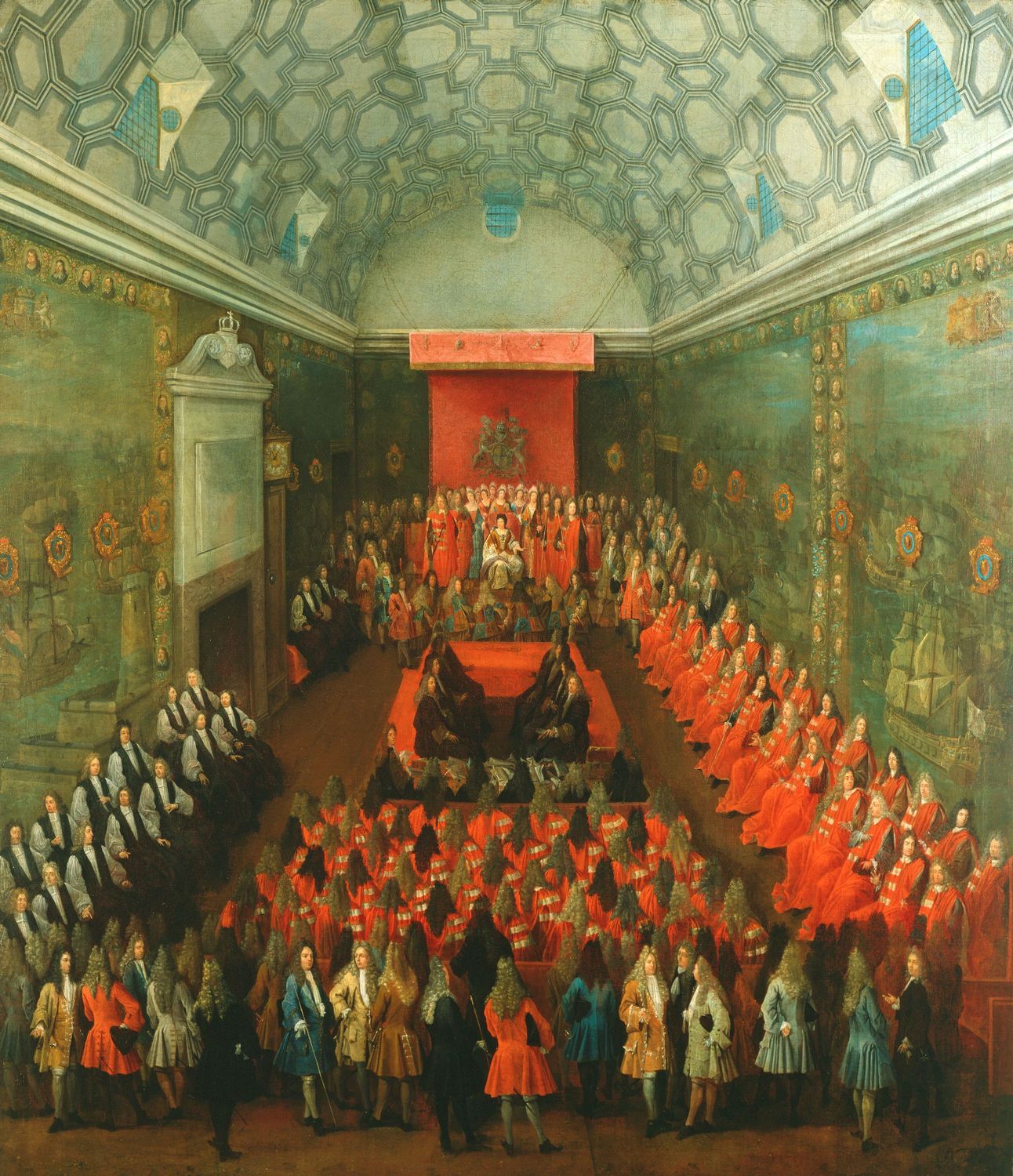
List Of Irish Representative Peers
This is a list of representative peers elected from the Peerage of Ireland to sit in the British House of Lords after the Kingdom of Ireland was brought into union with the Kingdom of Great Britain. No new members were added to the House after 1919, due to the creation of the Irish Free State, however, the already sitting members continued to remain part of the House, with the last member dying in 1961. Once elected, peers held their seats for life. Some of these peers were granted a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom which gave them a hereditary seat in the House of Lords. These peers also remained as representative peers and were not replaced until their deaths. List of Irish representative peers 1800–1850 1850–1900 1900–1919 Remaining representative peers after 1922 Representative peers with a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom See also *List of Scottish representative peers References *{{cite web , url=http://leighrayment.com/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British House Of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest extant institutions in the world, its origins lie in the early 11th century and the emergence of bicameralism in the 13th century. In contrast to the House of Commons, membership of the Lords is not generally acquired by election. Most members are appointed for life, on either a political or non-political basis. Hereditary membership was limited in 1999 to 92 excepted hereditary peers: 90 elected through internal by-elections, plus the Earl Marshal and Lord Great Chamberlain as members ''ex officio''. No members directly inherit their seats any longer. The House of Lords also includes up to 26 archbishops and bishops of the Church of England, known as Lords Spiritual. Since 2014, membership may be voluntarily relinquished or terminated upon expulsion. As the upper house of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelanda sovereign state covering five-sixths of the island) and Northern Ireland (part of the United Kingdomcovering the remaining sixth). It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest in the world. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islands by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); the remaining three are in the Republic of Ireland. It is the second-largest (after Munster) and second-most populous (after Leinster) of Ireland's four traditional provinces, with Belfast being its biggest city. Unlike the other provinces, Ulster has a high percentage of Protestantism in Ireland, Protestants, making up almost half of its population. English is the main language and Ulster English the main dialect. A minority also speak Irish, and there are (Irish-speaking regions) in County Donegal which is home to a quarter of the total Gaeltacht population of the Republic of Ireland. There are also large Irish-speaking networks in southern County Londonderry and in the Gaeltacht Quarter, Belfast. Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of Ireland
The counties of Ireland (Irish language, Irish: ) are historic administrative divisions of the island. They began as Normans in Ireland, Norman structures, and as the powers exercised by the Cambro-Norman barons and the Old English (Ireland), Old English nobility waned over time, new offices of political control came to be established at a county level. The number of counties varied depending on the time period, however thirty-two is the traditionally accepted and used number. Upon the partition of Ireland in 1921, six of the traditional counties became part of Northern Ireland. In Northern Ireland, Counties of Northern Ireland, counties ceased to be used for local government in 1973; Local government in Northern Ireland, districts are instead used. In the Republic of Ireland, some counties have been split resulting in the creation of new counties: there are currently 26 counties, 3 cities and 2 cities and counties that demarcate areas of local government in the Republic of Ire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county of the Republic of Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Ulster and is the northernmost county of Ireland. The county mostly borders Northern Ireland, sharing only a small border with the rest of the Republic. It is named after the town of Donegal (town), Donegal in the south of the county. It has also been known as County Tyrconnell or Tirconaill (), after Tyrconnell, the historical territory on which it was based. Donegal County Council is the local government in the Republic of Ireland, local council and Lifford is the county town. The population was 167,084 at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census. Name County Donegal is named after the town of Donegal (town), Donegal () in the south of the county. It has also been known by the alternative name County Tyrconnell or Tirconaill (, meaning 'Land of Conall Gulban, Conall'). The latter was its official name between 1922 and 1927. This is in reference to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |