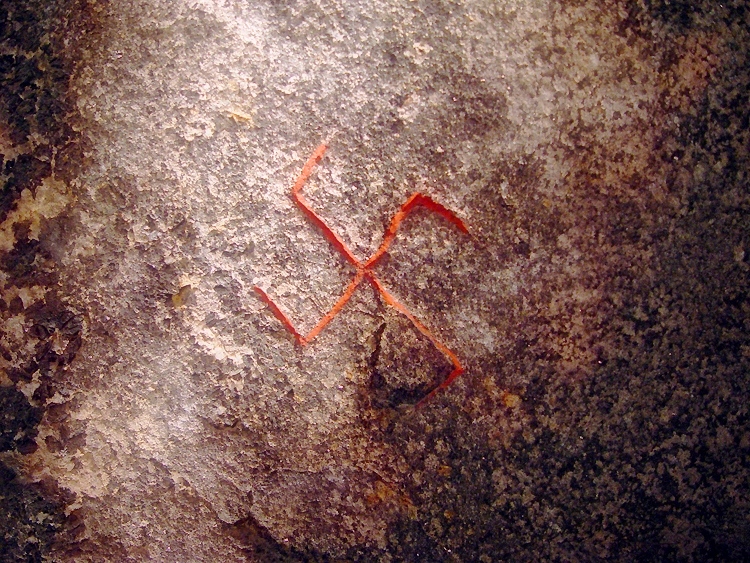|
Maricopa People
The Maricopa or PiipaashBarry Pritzker, ''A Native American Encyclopedia.'' Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998; p. 56 are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribe, who live in the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community and Gila River Indian Community (both in Arizona) along with the Pima people, Pima, a tribe with whom the Maricopa have long held a positive relationship. The Maricopa at the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community consist mostly of Xalychidom Piipaash members and are concentrated in Lehi, Arizona, Lehi. The Maricopa at the Gila River Indian Community are concentrated in Maricopa Colony, Arizona, Maricopa Colony. The Maricopa are a River Yuman group, formerly living along the banks of the Colorado River. Names The neighboring Akimel O'odham (Pima) and future allies, called these people the Kokmalik'op ('enemies in the big mountains'),. The Spanish transliterated this to ''Maricopa''. They call themselves Piipaa, Piipaash or Pee-Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maricopa Language
Maricopa or Piipaash is spoken by the Native American Maricopa people on two reservations in Arizona: the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community and the Gila River Indian Community. Most speakers live in Maricopa Colony. The language is considered severely endangered by UNESCO. Although the Maricopa now live among the Pima, their language is completely unrelated. It is a Yuman language, related to other languages such as Mohave, Cocopah, Havasupai, Yavapai and Kumeyaay, while the Pima speak a Uto-Aztecan language. According to the Ethnologue, language shift is occurring at Maricopa Colony: "The child-bearing generation can use the language among themselves, but it is not being transmitted to children." At Salt River, it is nearly extinct: "The only remaining users of the language are members of the grandparent generation or older who have little opportunity to use the language. There are about 100 speakers out of an ethnic population of 800. Salt River's cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechan
The Quechan ( Quechan: ''Kwatsáan'' 'those who descended'), or Yuma, are a Native American tribe who live on the Fort Yuma Indian Reservation on the lower Colorado River in Arizona and California just north of the Mexican border. Despite their name, they are not related to the Quechua people of the Andes. Members are enrolled in the Quechan Tribe of the Fort Yuma Indian Reservation. The federally recognized Quechan tribe's main office is located in Winterhaven, California. Its operations and the majority of its reservation land are located in California, United States. History The historic Yuman-speaking people in this region were skilled warriors and active traders, maintaining exchange networks with the Pima in southern Arizona, New Mexico, and with peoples of the Pacific coast. The first significant contact of the Quechan with Europeans was with the Spanish explorer Juan Bautista de Anza and his party in the winter of 1774. Relations were friendly. On Anza's retur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunkpapa
The Hunkpapa (Lakota: ) are a Native American group, one of the seven council fires of the Lakota tribe. The name ' is a Lakota word, meaning "Head of the Circle" (at one time, the tribe's name was represented in European-American records as ''Honkpapa''). By tradition, the set up their lodges at the entryway to the circle of the Great Council when the Sioux met in convocation."Hunkpapa Sioux Indian Tribe History" ''Handbook of American Indians'', 1906, carried in Access Genealogy, accessed 9 Dec 2009 They speak Lakȟóta, one of the three dialects of the Sioux language. Histor ...
|
Robert "Tree" Cody
Robert Tree Cody (April 20, 1951 – September 14, 2023) was an American musician, dancer, and educator. He graduated from John Marshall High School in 1969. Robert was an adopted son of Hollywood actor Iron Eyes Cody. Personal life Robert Tree Cody was the adopted son of the actor Iron Eyes Cody and Cody's wife Bertha Parker, an Assistant in Archaeology at Southwest Museum of the American Indian. Iron Eyes and Bertha adopted Robert and his brother Arthur, who served in the United States Marine Corps during the Vietnam War and died as a result of exposure to Agent Orange. The brothers were of Dakota and Maricopa heritage. Robert was an enrolled member of the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community. In the Maricopa language, his traditional name was ''Oou Kas Mah Quet'', meaning "Thunder Bear". Formerly of Big Bear, California, he resided in Santa Ana Pueblo, New Mexico with his wife, Rachel. His nickname, "Tree," came from his height: he was six feet nine and a half inche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
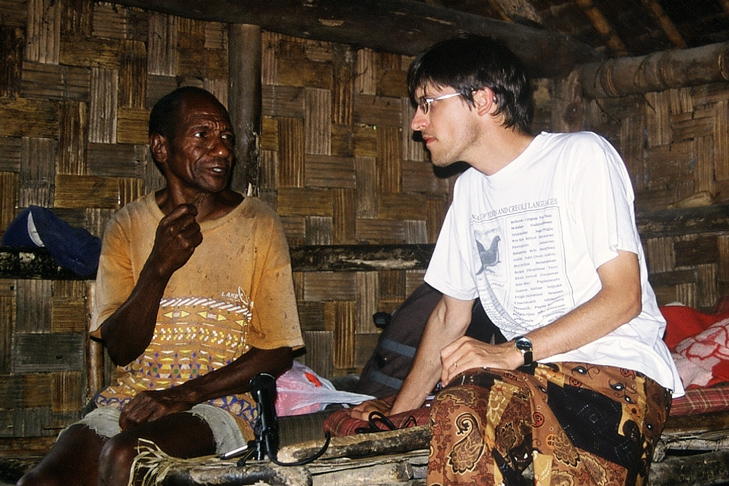
Informant (linguistics)
An informant or consultant in linguistics is a native speaker or member of a community who acts as a linguistic reference for a language or speech community being studied. The informant's role is that of a senior interpreter, who demonstrates native pronunciation, provides grammaticality judgments regarding linguistic well-formedness, and may also explain cultural references and other important contextual information to researchers from other cultures studying the language. Linguistic informants, especially those who frequently work with linguists, may play a greater than usual role in the researcher's work, and other titles such as consultant or coauthor may be used to acknowledge and accurately reflect that contribution. Ethics concerns In any research situation, there is "an unequal relationship between investigator and informants" – if that inequality already existed before the research, it tends to amplify it. (This power differential is generally true despite clear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
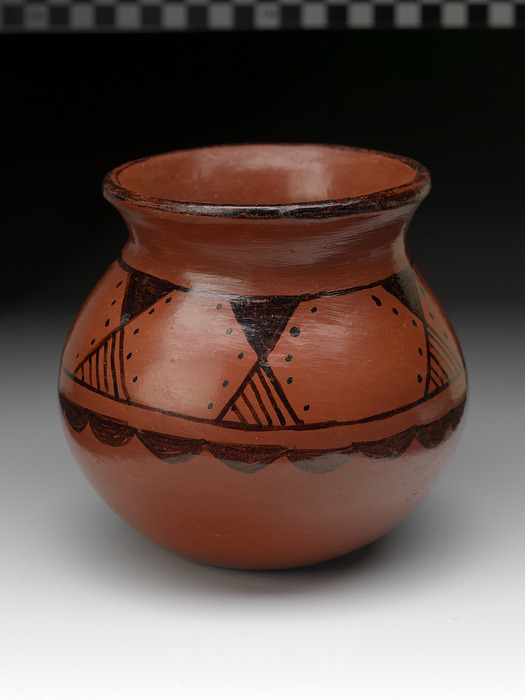
Ida Redbird
Ida Redbird ( Maricopa, 1892–1971) was a Native American potter from the Gila River Indian Community of the Gila River Indian Reservation in Arizona. She was the first president of the Maricopa Pottery Maker's Association and was widely credited with the revival of ancient Maricopa pottery techniques and forms. Her polished black-on-redware pottery was highly prized with collectors. Texas photographer Ted Sayles shot a series documenting Redbird sculpting her pottery. The series toured museums throughout the Western United States Early life Ida Redbird was born March 15, 1892, in Laveen on the Gila River Indian Reservation in Arizona to Hoot Somegustava. Hoot, Ida's mother, is sometimes described as Tohono O'odham and at other times as Maricopa/ Halchidhoma. Ida was the granddaughter of Kutox (also known as Kutŏ'x̣ or Uwȧ'nyȧ), who was Halchidhoma and wife of Charlie Redbird (also known as Matȧkwĭsnunyĕ'), who was Maricopa-Halchidhoma. Ida attended Phoenix Indian Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swastika
The swastika (卐 or 卍, ) is a symbol used in various Eurasian religions and cultures, as well as a few Indigenous peoples of Africa, African and Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American cultures. In the Western world, it is widely recognized as a symbol of the German Nazi Party who Cultural appropriation, appropriated it for their party insignia starting in the early 20th century. The appropriation continues with its use by Neo-Nazism, neo-Nazis around the world. The swastika was and continues to be used as a symbol of divinity and spirituality in Indian religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. It generally takes the form of a cross, the arms of which are of equal length and perpendicular to the adjacent arms, each bent midway at a right angle. The word ''swastika'' comes from , meaning 'conducive to well-being'. In Hinduism, the right-facing symbol (clockwise) () is called , symbolizing ('sun'), prosperity and good luck, while the left-facing symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piipaash Redware
The Maricopa or PiipaashBarry Pritzker, ''A Native American Encyclopedia.'' Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998; p. 56 are a Native American tribe, who live in the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community and Gila River Indian Community (both in Arizona) along with the Pima, a tribe with whom the Maricopa have long held a positive relationship. The Maricopa at the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community consist mostly of Xalychidom Piipaash members and are concentrated in Lehi. The Maricopa at the Gila River Indian Community are concentrated in Maricopa Colony. The Maricopa are a River Yuman group, formerly living along the banks of the Colorado River. Names The neighboring Akimel O'odham (Pima) and future allies, called these people the Kokmalik'op ('enemies in the big mountains'),. The Spanish transliterated this to ''Maricopa''. They call themselves Piipaa, Piipaash or Pee-Posh (″people″). The "Maricopa" of the American explorers of the 19th century at this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Reorganization Act
The Indian Reorganization Act (IRA) of June 18, 1934, or the Wheeler–Howard Act, was U.S. federal legislation that dealt with the status of American Indians in the United States. It was the centerpiece of what has been often called the "Indian New Deal". The Act also restored to Indians the management of their assets—land and mineral rights—and included provisions intended to create a sound economic foundation for the residents of Indian reservations. Total U.S. spending on Indians averaged $38 million a year in the late 1920s, dropping to an all-time low of $23 million in 1933, and reaching $38 million in 1940. The IRA was the most significant initiative of John Collier (sociologist), John Collier, who was President Franklin D. Roosevelt's Commissioner of the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) from 1933 to 1945. He had long studied Indian issues and worked for change since the 1920s, particularly with the American Indian Defense Association. He intended to reverse the assimi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Presbyterian'' is applied to churches that trace their roots to the Church of Scotland or to English Dissenter groups that were formed during the English Civil War, 1642 to 1651. Presbyterian theology typically emphasises the sovereignty of God, the authority of the Scriptures, and the necessity of grace through faith in Christ. Scotland ensured Presbyterian church government in the 1707 Acts of Union, which created the Kingdom of Great Britain. In fact, most Presbyterians in England have a Scottish connection. The Presbyterian denomination was also taken to North America, Australia, and New Zealand, mostly by Scots and Scots-Irish immigrants. Scotland's Presbyterian denominations hold to the Reformed theology of John Calvin and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau Of Indian Affairs
The Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA), also known as Indian Affairs (IA), is a United States List of United States federal agencies, federal agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior, Department of the Interior. It is responsible for implementing Federal law (United States), federal laws and policies related to Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans and Alaska Natives, and administering and managing over of Indian reservation, reservations Trust law, held in trust by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government for List of federally recognized tribes, indigenous tribes. It renders services to roughly 2 million indigenous Americans across 574 federally recognized tribes. The BIA is governed by a director and overseen by the assistant secretary for Indian affairs, who answers to the United States Secretary of the Interior, secretary of the interior. The BIA works with Tribal sovereignty in the United States, tribal governments to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pima Butte
The Battle of Pima Butte, or the Battle of Maricopa Wells, was fought on September 1, 1857 at Pima Butte, Arizona near Maricopa Wells in the Sierra Estrella. Yuma, Mohave, Apache and Yavapai warriors attacked a Maricopa village named Secate in one of the largest battles in Arizona's history. It was also the last major battle fought by the Yumas and the last major battle fought solely between Native Americans in North America. Battle For hundreds of years prior to 1857, the Yumas and the Maricopas were enemies. On many occasions the two tribes would gather their warriors together at the peak of Berdache Mountain. There the two sides would shout insults at each other before fighting a battle. Chief Francisco of the Yuma led the combined army which numbered at least 300 men and they arrived near Secate on August 31, 1857. Francisco began his attack the following morning and captured the Maricopa village and began burning the structures. The Yumas and their allies had just w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |