|
Margaret Of Brieg
Margaret of Brieg (1342–1386) was a daughter of Ludwik I the Fair and his wife, Agnes of Sagan. She was Duchess consort of Bavaria by her marriage to Albert I, Duke of Bavaria. Family Margaret was the eldest of six siblings. Her brother was Henry VII of Brzeg and her sister, Hedwig was married to Jan II of Oświęcim. Margaret's maternal grandparents were Henry IV the Faithful and Matilde of Brandenburg. Her paternal grandparents were Bolesław III the Generous and his first wife Margaret of Bohemia. Margaret of Bohemia was the youngest surviving child of Wenceslaus II of Bohemia and Judith of Habsburg. Judith was the youngest daughter of Rudolf I of Germany and Gertrude of Hohenberg. Marriage In Passau after 19 July 1353, Margaret and Albert were married. Albert kept mistresses and lovers, but during his reign, troubles erupted between parties because of a woman, Aleid van Poelgeest. People did not like her because she gained political influence which was resented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchess Consort Of Bavaria
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranked below grand dukes and above or below princes, depending on the country or specific title. The title comes from French ''duc'', itself from the Latin '' dux'', 'leader', a term used in republican Rome to refer to a military commander without an official rank (particularly one of Germanic or Celtic origin), and later coming to mean the leading military commander of a province. In most countries, the word ''duchess'' is the female equivalent. Following the reforms of the emperor Diocletian (which separated the civilian and military administrations of the Roman provinces), a ''dux'' became the military commander in each province. The title ''dux'', Hellenised to ''doux'', survived in the Eastern Roman Empire where it continued i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judith Of Habsburg
Judith of Habsburg (; 13 March 1271 – 21 May 1297) was queen of Bohemia and Poland from 1285 until her death as the wife of the Přemyslid king Wenceslaus II. Early life Judith was the youngest daughter of King Rudolf I of Germany and Gertrude of Hohenberg. She was born in the Swabian town of Rheinfelden, where her father still resided as a count before he was elected king of Germany in 1273. When she was five, she became the object of her father's political plans: on 21 October 1276 King Rudolf accepted the homage of his bitter rival King Ottokar II of Bohemia in the Austrian capital Vienna, and to seal the peace, both decided that Judith should marry Ottokar's son Wenceslaus. The agreement, however, did not last and the conflict erupted again, ending with King Ottokar's final defeat and death in the 1278 Battle on the Marchfeld. After King Ottokar's death, the Brandenburg margrave Otto V had guardianship over minor King Wenceslaus II, acting as Bohemian regent. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John The Fearless
John I (; ; 28 May 1371 – 10 September 1419) was a scion of the French royal family who ruled the Burgundian State from 1404 until his assassination in 1419. He played a key role in French national affairs during the early 15th century, particularly in his struggle to remove the mentally ill King Charles VI and during the Hundred Years' War against the Kingdom of England. A rash, ruthless and unscrupulous politician, John murdered Charles's brother, the Duke of Orléans, in an attempt to gain control of the government, which led to the eruption of the Armagnac–Burgundian Civil War in France and in turn culminated in his own assassination in 1419. The involvement of Charles, the heir to the French throne, in his assassination prompted John's son and successor Philip to seek an alliance with the English, thereby bringing the Hundred Years' War to its final phase. John, like his father Philip before him, played an important role in the development of gunpowder artiller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; ; ), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river. A sub-prefecture of the department, Cambrai is a town which had 32,501 inhabitants in 2018. It is in the heart of the urban unit of Cambrai with 46,772 inhabitants. Its functional area, a more extensive range, included 94,576 inhabitants in 2018.Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Cambrai (108), Unité urbaine 2020 de Cambrai (59403), Commune de Cambrai (59122) INSEE With |
Dijon
Dijon (, ; ; in Burgundian language (Oïl), Burgundian: ''Digion'') is a city in and the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Côte-d'Or Departments of France, department and of the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté Regions of France, region in eastern France. the Communes of France, commune had a population of 156,920. The earliest archaeological finds within the city limits of Dijon date to the Neolithic Period (geology), period. Dijon later became a Roman Empire, Roman settlement named ''Divio'', located on the road between Lyon and Paris. The province was home to the Duke of Burgundy, Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th centuries, and Dijon became a place of tremendous wealth and power, one of the great European centres of art, learning, and science. The city has retained varied architectural styles from many of the main periods of the past millennium, including Capetian, Gothic architecture, Gothic, and Renaissance architecture, Renaissance. Many still-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wenceslaus, King Of The Romans
Wenceslaus IV (also ''Wenceslas''; ; , nicknamed "the Idle"; 26 February 136116 August 1419), also known as Wenceslaus of Luxembourg, was King of Bohemia from 1378 until his death and King of Germany from 1376 until he was deposed in 1400. As he belonged to the House of Luxembourg, he was also Duke of Luxembourg from 1383 to 1388. Biography Wenceslaus was born in the Imperial city of Nuremberg, the son of Emperor Charles IV by his third wife Anna Svídnická, a scion of the Silesian Piasts, and baptized at St. Sebaldus Church. He was raised by the Prague Archbishops Arnošt of Pardubice and Jan Očko of Vlašim. His father had the two-year-old crowned King of Bohemia in June 1363 and in 1373 also obtained for him the Electoral Margraviate of Brandenburg. When on 10 June 1376 Charles IV asserted Wenceslaus' election as King of the Romans by the prince-electors, two of seven votes, those of Brandenburg and Bohemia, were held by the emperor and his son themse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William I Of Gelders And Jülich
William is a masculine given name of Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will or Wil, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, Billie, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie). Female forms include Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germanic name is a compound of *''wiljô'' "will, wish, desire" and *''helmaz'' "helm, helmet".Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford Univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
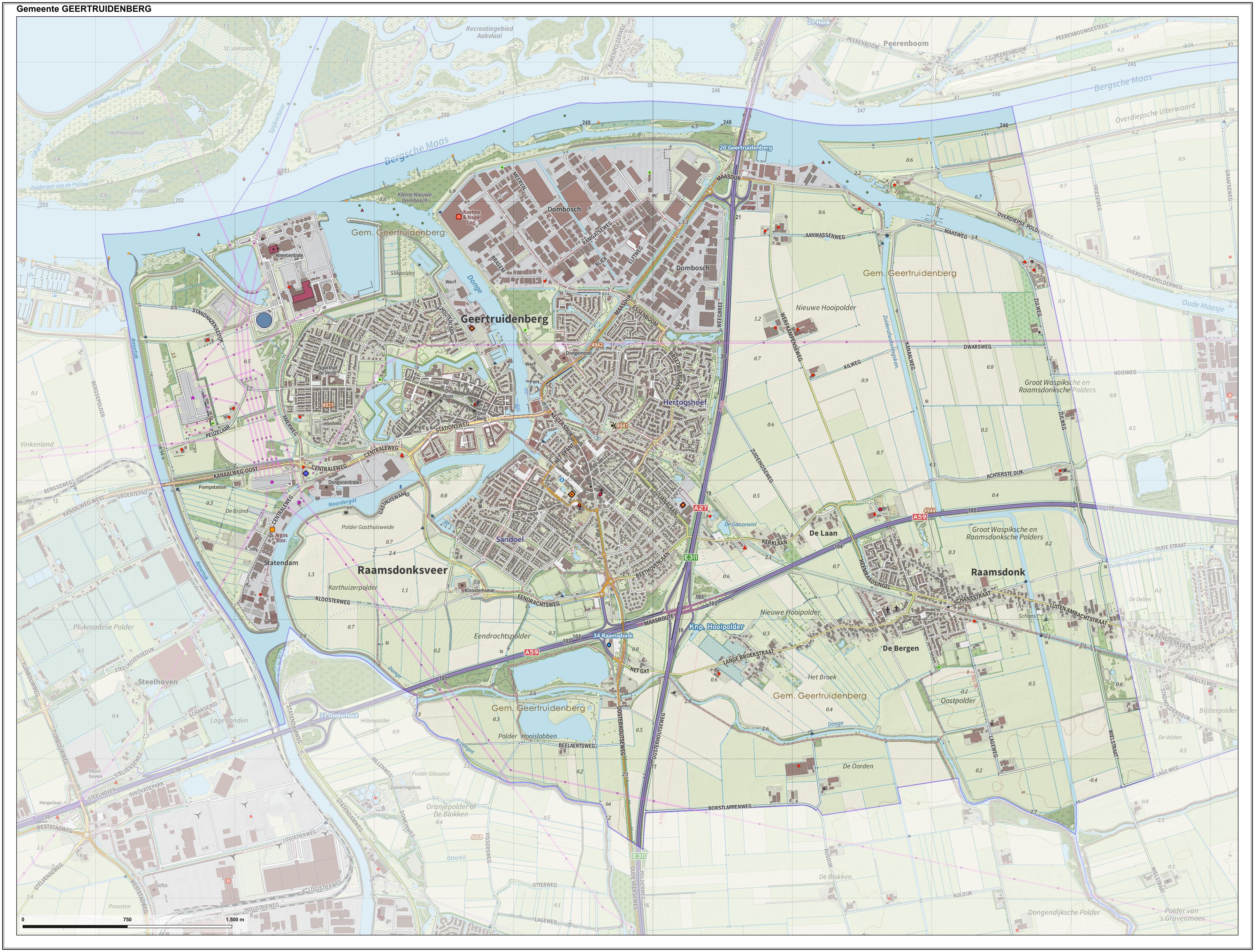
Geertruidenberg
Geertruidenberg () is a city and municipality in the province North Brabant in the south of the Netherlands. The city, named after Saint Gertrude of Nivelles, received city rights in 1213 from the count of Holland. The fortified city prospered until the 15th century. Today, the municipality of Geertruidenberg includes the population centres Raamsdonk and Raamsdonksveer. The municipality has a total area of and had a population of in . The city government consists of the mayor and three aldermen. History Geertruidenberg is named after Saint Gertrude of Nivelles. In 1213, Sint Geertruidenberg (English: "Saint Gertrude's Mountain") received city rights from Count William I of Holland. The fortified city became a trade center, where counts and other nobility gathered for negotiations. In 1323–1325, Geertruidenberg Castle was constructed very close to the city center. During the Hook and Cod wars, the city chose the Cod side in 1351, while the castle remained on the Hook ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
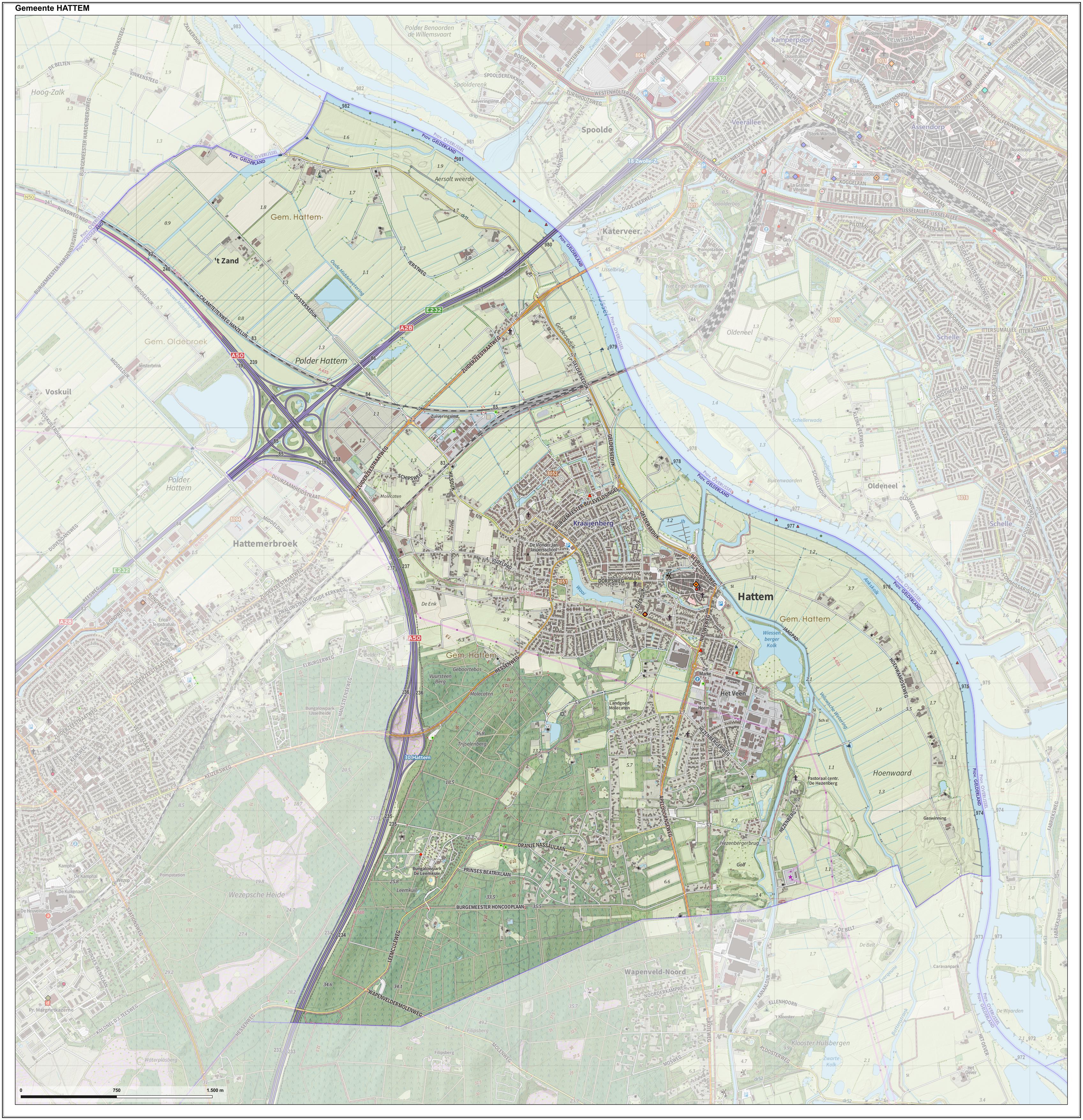
Hattem
Hattem () is a municipality and a city in the eastern Netherlands. The municipality had a population of in . The municipality includes the hamlet of 't Zand. Name origin The name “Hattem” is a typical farmyard name. The exact origin of “Hattem” is yet unclear. In general two explanation exist. Hattem would be the ‘heem’ (home) of a people who belong to the tribe of Chattuarii (or Hattuarii or Hatten). A second origin could refer to the leader of a people under the leader Hatto. This fits with the fact that a lot of farmyard names are deduced from persons names. History A document referring to Hattem is found is dated around 800. This document is the Codex Laureshamensis, in which the settlement Hattem is mentioned because two farmhouses in this place are donated to the Lorsch abbey. Established as parish Despite this early statement, no church or chapel was built in Hattem. In 1176 Hattem became a parish (‘kerspel’). The chapel, measuring 17,5 by 9,5 meter, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
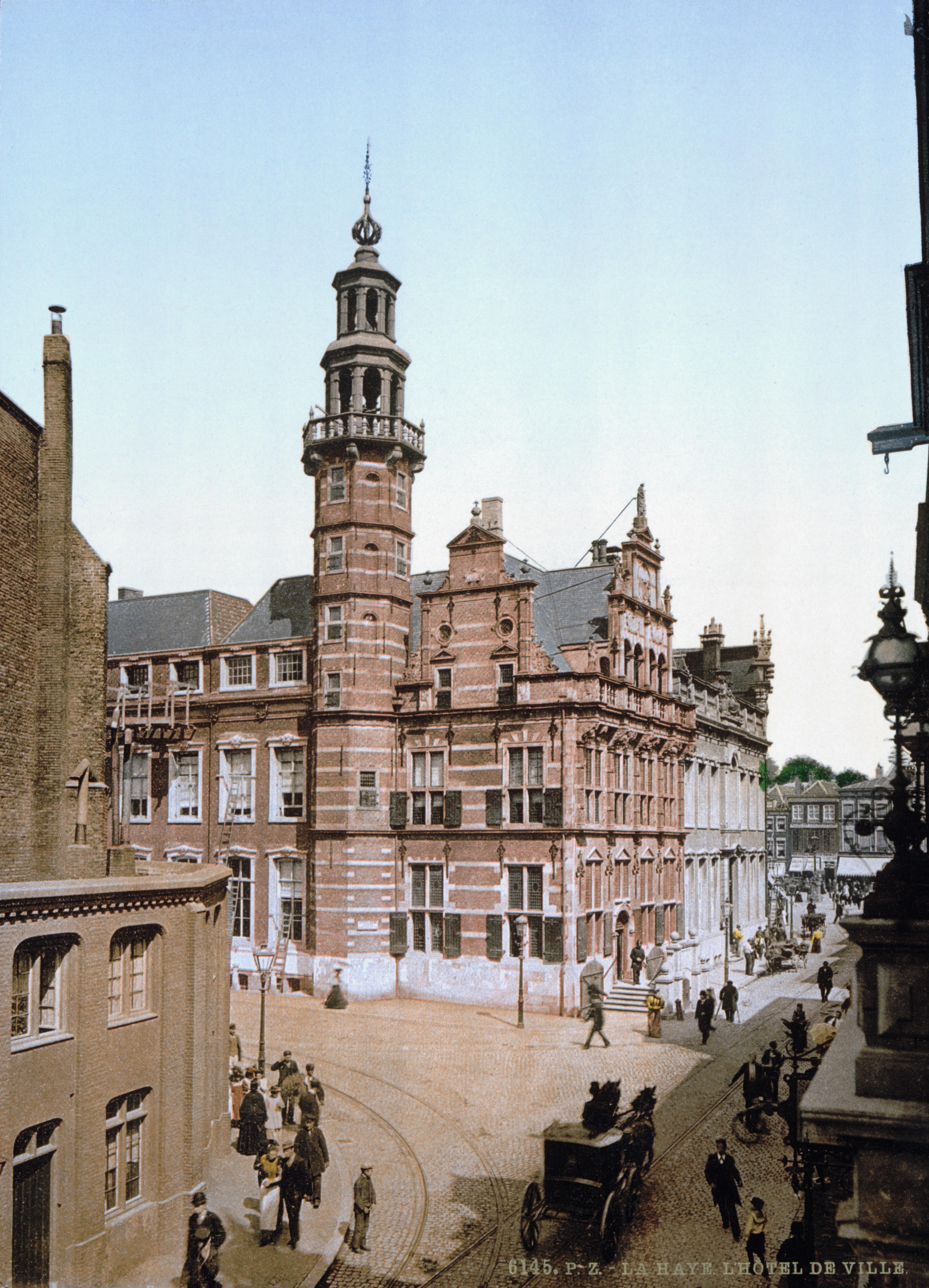
The Hague
The Hague ( ) is the capital city of the South Holland province of the Netherlands. With a population of over half a million, it is the third-largest city in the Netherlands. Situated on the west coast facing the North Sea, The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and has been described as the country's ''de facto'' capital since the time of the Dutch Republic, while Amsterdam is the official capital of the Netherlands. The Hague is the core municipality of the COROP, Greater The Hague urban area containing over 800,000 residents, and is also part of the Rotterdam–The Hague metropolitan area, which, with a population of approximately 2.6 million, is the largest metropolitan area of the Netherlands. The city is also part of the Randstad region, one of the largest conurbations in Europe. The Hague is the seat of the Cabinet of the Netherlands, Cabinet, the States General of the Netherlands, States General, the Supreme Court of the Neth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hook And Cod Wars
The Hook and Cod wars (; sometimes semi-anglicised as the wars of the Hoecks and the Cabbeljaws) comprise a series of wars and battles in the County of Holland between 1350 and 1490. Most of these wars were fought over who should hold the title of " Count of Holland". The Cod faction generally consisted of the more progressive cities of Holland. The Hook faction consisted for a large part of the conservative noblemen. The origin of the name "Cod" remains uncertain, but is most likely a case of reappropriation. Perhaps it derives from the Bavarian coat of arms, which resemble the scales of a fish. The ''Hook'' refers to the hooked stick that is used to catch cod. Another possible explanation of "Cod" points out that as a cod grows it tends to eat more, growing even bigger and eating even more, thus encapsulating how the noblemen perhaps saw the expanding middle classes of the time. Aftermath of William IV's reign (1345–1349) The reign of William IV of Holland and the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleid Van Poelgeest
Aleid of Poelgeest (Koudekerk aan den Rijn, c. 1370 - The Hague, September 22, 1392) was the mistress of the Count of Holland, Albert I of Bavaria.DVN, een project van Huygens ING en OGC (UU). Bronvermelding: Dimphéna Groffen, Poelgeest, Aleid van, in: Digitaal Vrouwenlexicon van Nederland. URL: http://resources.huygens.knaw.nl/vrouwenlexicon/lemmata/data/Poelgeest, Aleid van 3/01/2014/ref> Life Aleid van Poelgeest was the daughter of the court official Jan van Poelgeest and Aleid van Beest Gerbrandsdr. She is traditionally assumed to have served as a maid-of-honour to the spouse of Albert, Margaret of Brieg, prior to becoming his mistress. She never married. Van Poelgeest is noted to have been present at court at least since 1386. In June 1388, Albert gave her an allowance, her own house and maids and installed her as his official mistress. It was noted that she followed him around on his journeys in his domains. She was reputed to have had great influence over Albert, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |